Exchange Of Gases Notes CBSE Class 11
Last Updated :
04 Sep, 2023
The exchange of gases refers to the process that happens between carbon dioxide and oxygen. Gas exchange takes place between the capillaries and alveoli. The rate of diffusion depends on the solubility and thickness of the membrane which are involved in the exchange of gases. Oxygen is transferred from the lungs to the bloodstream whereas carbon dioxide is eliminated from the bloodstream to the lungs.
Exchange of Gases
The primary site of exchange of gases is the alveoli and therefore exchange of CO2 and O2 occurs between blood and tissues. In these type of sites, gas exchange occurs by simple diffusion which are based on the pressure or concentration gradient. The rate of diffusion depends on the solubility and thickness of the membrane which are involved in the exchange of gases.
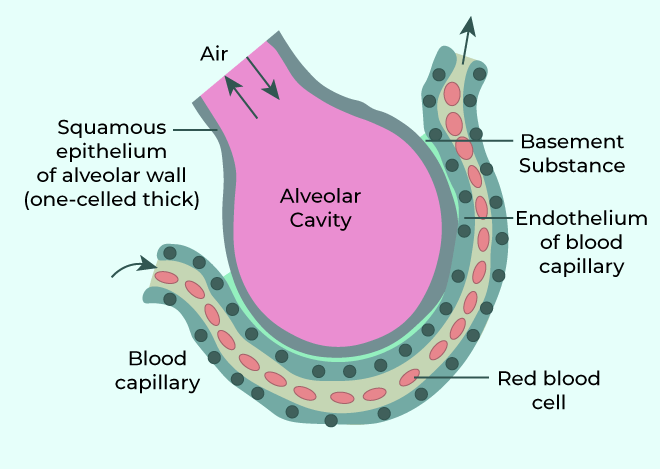
Diffusion Membrane
The thickness of the diffusion membrane is less than a millimetre. There are three types of layers of diffusion membrane:
- Alveoli is the thin squamous epithelium.
- The endothelium consists of the alveolar capillaries.
- In between the epithelium and endothelium, there lies a basement substance.
Transport of Gases
The transport of carbon dioxide and oxygen occurs through the blood. In carbon dioxide the red blood cells carry 20% to 25%, plasma consists of 7% of carbon dioxide which is in a dissolved state whereas the remaining 70% is carried by the bicarbonate. The red blood cells in the blood consist of 97% of oxygen whereas the plasma consists of the remaining 3% of oxygen which is generally in a dissolved state.
Transport of Carbon dioxide
Carbamino-haemoglobin is the haemoglobin which also carries 20% to 25% of Carbon dioxide apart from oxygen. The binding in this is generally related to the partial pressure of the carbon dioxide. The main factor which affects the binding is pO2. When pCO2 is high and pO2 is low, more binding of CO2 takes place whereas when pCO2 is low and pO2 is high from the alveoli, CO2 gets dissociated from the carbamino-haemoglobin which is released in the alveoli and formed in the tissues. Carbonic anhydrase is an enzyme which is present in high concentrations in red blood cells.
Transport of Oxygen
Haemoglobin is a red color pigment in the red blood cells which consists of iron. Oxyhaemoglobin is given generally when O2 binds reversibly to the haemoglobin in the blood. In a molecule of haemoglobin at max, only 4 molecules can be bound. The factor which affects the binding is the partial pressure of O2. In alveoli pO2 is high and pCO2 is low which forms the oxyhaemoglobin whereas when pO2 is low and pCO2 is high it dissociates O2 from oxyhaemoglobin.

FAQs on Exchange of Gases
1. What do you mean by the exchange of gases?
Answer:
The exchange of gases is defined as the process in the alveoli where the exchange of CO2 and O2 occurs between blood and tissues.
2. Name the types of layers in the diffusion membrane?
Answer:
There are three types of layers of diffusion membrane are:
- Alveoli.
- Endothelium consists of the alveolar capillaries.
- In between the epithelium and endothelium there lies a basement substance.
3. In which factors the rate of diffusion occurs?
Answer:
The rate of diffusion depends on the solubility and thickness of the biological membrane.
4. How transport of gases occurs?
Answer:
Transport of gases occurs in carbon dioxide the red blood cells carry 20% to 25%, plasma consists of 7% of carbon dioxide which is in a dissolved state whereas the remaining 70% is carried by the bicarbonate and in the red blood cells in the blood consists of 97% of oxygen whereas the plasma consists of the remaining 3% of oxygen which is generally in a dissolved state.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...