Exchange first and last nodes in Circular Linked List
Last Updated :
22 Feb, 2023
Given Circular linked list exchange the first and the last node. The task should be done with only one extra node, you can not declare more than one extra node, and also you are not allowed to declare any other temporary variable.
Note: Extra node means the need of a node to traverse a list.
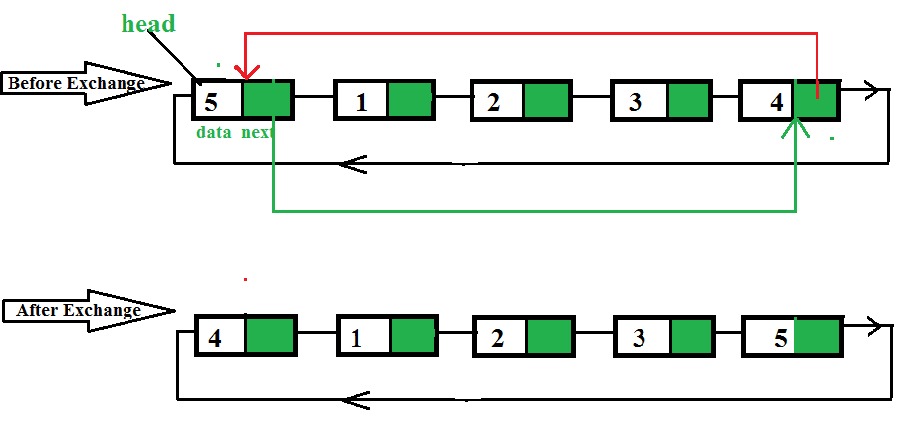
Examples:
Input : 5 4 3 2 1
Output : 1 4 3 2 5
Input : 6 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
Output : 9 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 6
Method 1: (By Changing Links of First and Last Nodes)
We first find a pointer to the previous to the last node. Let this node be p. Now we change the next links so that the last and first nodes are swapped.
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node* next;
};
struct Node* addToEmpty(struct Node* head, int data)
{
if (head != NULL)
return head;
struct Node* temp
= (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
temp->data = data;
head = temp;
head->next = head;
return head;
}
struct Node* addBegin(struct Node* head, int data)
{
if (head == NULL)
return addToEmpty(head, data);
struct Node* temp
= (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
temp->data = data;
temp->next = head->next;
head->next = temp;
return head;
}
void traverse(struct Node* head)
{
struct Node* p;
if (head == NULL) {
cout << "List is empty." << endl;
return;
}
p = head;
do {
cout << p->data << " ";
p = p->next;
} while (p != head);
}
struct Node* exchangeNodes(struct Node* head)
{
if (head->next->next == head) {
head = head->next;
return head;
}
struct Node* p = head;
while (p->next->next != head)
p = p->next;
p->next->next = head->next;
head->next = p->next;
p->next = head;
head = head->next;
return head;
}
int main()
{
int i;
struct Node* head = NULL;
head = addToEmpty(head, 6);
for (i = 5; i > 0; i--)
head = addBegin(head, i);
cout << "List Before: ";
traverse(head);
cout << endl;
cout << "List After: ";
head = exchangeNodes(head);
traverse(head);
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
public class GFG {
static class Node {
int data;
Node next;
};
static Node addToEmpty(Node head, int data)
{
if (head != null)
return head;
Node temp = new Node();
temp.data = data;
head = temp;
head.next = head;
return head;
}
static Node addBegin(Node head, int data)
{
if (head == null)
return addToEmpty(head, data);
Node temp = new Node();
temp.data = data;
temp.next = head.next;
head.next = temp;
return head;
}
static void traverse(Node head)
{
Node p;
if (head == null) {
System.out.print("List is empty.");
return;
}
p = head;
do {
System.out.print(p.data + " ");
p = p.next;
} while (p != head);
}
static Node exchangeNodes(Node head)
{
if (head.next.next == head) {
head = head.next;
return head;
}
Node p = head;
while (p.next.next != head)
p = p.next;
p.next.next = head.next;
head.next = p.next;
p.next = head;
head = head.next;
return head;
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
int i;
Node head = null;
head = addToEmpty(head, 6);
for (i = 5; i > 0; i--)
head = addBegin(head, i);
System.out.print("List Before: ");
traverse(head);
System.out.println();
System.out.print("List After: ");
head = exchangeNodes(head);
traverse(head);
}
}
|
Python3
import math
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.next = None
def addToEmpty(head, data):
if (head != None):
return head
temp = Node(data)
temp.data = data
head = temp
head.next = head
return head
def addBegin(head, data):
if (head == None):
return addToEmpty(head, data)
temp = Node(data)
temp.data = data
temp.next = head.next
head.next = temp
return head
def traverse(head):
if (head == None):
print("List is empty.")
return
p = head
print(p.data, end=" ")
p = p.next
while(p != head):
print(p.data, end=" ")
p = p.next
def exchangeNodes(head):
if head == None or head.next == head:
return head
elif head.next.next == head:
head = head.next
return head
else:
prev = None
curr = head
temp = head
while curr.next != head:
prev = curr
curr = curr.next
curr.next = temp.next
prev.next = temp
temp.next = curr
head = curr
return head
if __name__ == '__main__':
head = None
head = addToEmpty(head, 6)
for x in range(5, 0, -1):
head = addBegin(head, x)
print("List Before: ", end="")
traverse(head)
print()
print("List After: ", end="")
head = exchangeNodes(head)
traverse(head)
|
C#
using System;
public class GFG {
class Node {
public int data;
public Node next;
};
static Node addToEmpty(Node head, int data)
{
if (head != null)
return head;
Node temp = new Node();
temp.data = data;
head = temp;
head.next = head;
return head;
}
static Node addBegin(Node head, int data)
{
if (head == null)
return addToEmpty(head, data);
Node temp = new Node();
temp.data = data;
temp.next = head.next;
head.next = temp;
return head;
}
static void traverse(Node head)
{
Node p;
if (head == null) {
Console.Write("List is empty.");
return;
}
p = head;
do {
Console.Write(p.data + " ");
p = p.next;
} while (p != head);
}
static Node exchangeNodes(Node head)
{
if (head.next.next == head) {
head = head.next;
return head;
}
Node p = head;
while (p.next.next != head)
p = p.next;
p.next.next = head.next;
head.next = p.next;
p.next = head;
head = head.next;
return head;
}
public static void Main()
{
int i;
Node head = null;
head = addToEmpty(head, 6);
for (i = 5; i > 0; i--)
head = addBegin(head, i);
Console.Write("List Before: ");
traverse(head);
Console.WriteLine();
Console.Write("List After: ");
head = exchangeNodes(head);
traverse(head);
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
class Node {
constructor() {
this.data = 0;
this.next = null;
}
}
function addToEmpty(head , data) {
if (head != null)
return head;
var temp = new Node();
temp.data = data;
head = temp;
head.next = head;
return head;
}
function addBegin(head , data) {
if (head == null)
return addToEmpty(head, data);
var temp = new Node();
temp.data = data;
temp.next = head.next;
head.next = temp;
return head;
}
function traverse(head) {
var p;
if (head == null) {
document.write("List is empty.");
return;
}
p = head;
do {
document.write(p.data + " ");
p = p.next;
} while (p != head);
}
function exchangeNodes(head) {
if (head.next.next == head) {
head = head.next;
return head;
}
var p = head;
while (p.next.next != head)
p = p.next;
p.next.next = head.next;
head.next = p.next;
p.next = head;
head = head.next;
return head;
}
var i;
var head = null;
head = addToEmpty(head, 6);
for (i = 5; i > 0; i--)
head = addBegin(head, i);
document.write("List Before: ");
traverse(head);
document.write("<br/>");
document.write("List After: ");
head = exchangeNodes(head);
traverse(head);
</script>
|
Output
List Before: 6 1 2 3 4 5
List After: 5 1 2 3 4 6
Time Complexity: O(n), as we are using a loop to traverse n times. Where n is the number of nodes in the linked list.
Auxiliary Space: O(1), as we are not using any extra space.
Method 2: (By Swapping Values of First and Last nodes)
Algorithm:
- Traverse the list and find the last node(tail).
- Swap data of head and tail.
Below is the implementation of the algorithm:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node* next;
};
struct Node* addToEmpty(struct Node* head, int data)
{
if (head != NULL)
return head;
struct Node* temp
= (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
temp->data = data;
head = temp;
head->next = head;
return head;
}
struct Node* addBegin(struct Node* head, int data)
{
if (head == NULL)
return addToEmpty(head, data);
struct Node* temp
= (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
temp->data = data;
temp->next = head->next;
head->next = temp;
return head;
}
void traverse(struct Node* head)
{
struct Node* p;
if (head == NULL) {
cout << "List is empty." << endl;
return;
}
p = head;
do {
cout << p->data << " ";
p = p->next;
} while (p != head);
}
struct Node* exchangeNodes(struct Node* head)
{
if (head == NULL || head->next == NULL) {
return head;
}
Node* tail = head;
while (tail->next != head) {
tail = tail->next;
}
int temp = tail->data;
tail->data = head->data;
head->data = temp;
return head;
}
int main()
{
int i;
struct Node* head = NULL;
head = addToEmpty(head, 6);
for (i = 5; i > 0; i--)
head = addBegin(head, i);
cout << "List Before: ";
traverse(head);
cout << endl;
cout << "List After: ";
head = exchangeNodes(head);
traverse(head);
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
public class GFG{
static class Node {
int data;
Node next;
};
static Node addToEmpty(Node head, int data)
{
if (head != null)
return head;
Node temp
= new Node();
temp.data = data;
head = temp;
head.next = head;
return head;
}
static Node addBegin(Node head, int data)
{
if (head == null)
return addToEmpty(head, data);
Node temp
= new Node();
temp.data = data;
temp.next = head.next;
head.next = temp;
return head;
}
static void traverse(Node head)
{
Node p;
if (head == null) {
System.out.print("List is empty." +"\n");
return;
}
p = head;
do {
System.out.print(p.data+ " ");
p = p.next;
} while (p != head);
}
static Node exchangeNodes(Node head)
{
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return head;
}
Node tail = head;
while (tail.next != head) {
tail = tail.next;
}
int temp = tail.data;
tail.data = head.data;
head.data = temp;
return head;
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int i;
Node head = null;
head = addToEmpty(head, 6);
for (i = 5; i > 0; i--)
head = addBegin(head, i);
System.out.print("List Before: ");
traverse(head);
System.out.println();
System.out.print("List After: ");
head = exchangeNodes(head);
traverse(head);
}
}
|
Python3
class Node:
def __init__(self):
self.data = 0
self.next = None
def addToEmpty(head, data):
if (head != None):
return head
temp = Node()
temp.data = data
head = temp
head.next = head
return head
def addBegin(head, data):
if (head == None):
return addToEmpty(head, data)
temp = Node()
temp.data = data
temp.next = head.next
head.next = temp
return head
def traverse(head):
if (head == None):
print("List is empty.")
return
p = head
while (True):
print(p.data, end=" ")
p = p.next
if(p == head):
break
def exchangeNodes(head):
if (head == None or head.next == None):
return head
tail = head
while (tail.next != head):
tail = tail.next
temp = tail.data
tail.data = head.data
head.data = temp
return head
head = None
head = addToEmpty(head, 6)
for i in range(5, 0, -1):
head = addBegin(head, i)
print("List Before: ")
traverse(head)
print("")
print("List After: ")
head = exchangeNodes(head)
traverse(head)
|
C#
using System;
public class GFG {
public class Node {
public int data;
public Node next;
};
static Node addToEmpty(Node head, int data) {
if (head != null)
return head;
Node temp = new Node();
temp.data = data;
head = temp;
head.next = head;
return head;
}
static Node addBegin(Node head, int data) {
if (head == null)
return addToEmpty(head, data);
Node temp = new Node();
temp.data = data;
temp.next = head.next;
head.next = temp;
return head;
}
static void traverse(Node head) {
Node p;
if (head == null) {
Console.Write("List is empty." + "\n");
return;
}
p = head;
do {
Console.Write(p.data + " ");
p = p.next;
} while (p != head);
}
static Node exchangeNodes(Node head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return head;
}
Node tail = head;
while (tail.next != head) {
tail = tail.next;
}
int temp = tail.data;
tail.data = head.data;
head.data = temp;
return head;
}
public static void Main(String[] args) {
int i;
Node head = null;
head = addToEmpty(head, 6);
for (i = 5; i > 0; i--)
head = addBegin(head, i);
Console.Write("List Before: ");
traverse(head);
Console.WriteLine();
Console.Write("List After: ");
head = exchangeNodes(head);
traverse(head);
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
class Node {
constructor() {
this.data = 0;
this.next = null;
}
}
function addToEmpty(head , data) {
if (head != null)
return head;
var temp = new Node();
temp.data = data;
head = temp;
head.next = head;
return head;
}
function addBegin(head , data) {
if (head == null)
return addToEmpty(head, data);
var temp = new Node();
temp.data = data;
temp.next = head.next;
head.next = temp;
return head;
}
function traverse(head) {
var p;
if (head == null) {
document.write("List is empty." + "\n");
return;
}
p = head;
do {
document.write(p.data + " ");
p = p.next;
} while (p != head);
}
function exchangeNodes(head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return head;
}
var tail = head;
while (tail.next != head) {
tail = tail.next;
}
var temp = tail.data;
tail.data = head.data;
head.data = temp;
return head;
}
var i;
var head = null;
head = addToEmpty(head, 6);
for (i = 5; i > 0; i--)
head = addBegin(head, i);
document.write("List Before: <br/>");
traverse(head);
document.write("<br/>");
document.write("List After: <br/>");
head = exchangeNodes(head);
traverse(head);
</script>
|
Output
List Before: 6 1 2 3 4 5
List After: 5 1 2 3 4 6
Time Complexity: O(n), as we are using a loop to traverse n times. Where n is the number of nodes in the linked list.
Auxiliary Space: O(1), as we are not using any extra space.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...