Partition problem | DP-18
Last Updated :
22 Feb, 2023
The partition problem is to determine whether a given set can be partitioned into two subsets such that the sum of elements in both subsets is the same.
Examples:
Input: arr[] = {1, 5, 11, 5}
Output: true
The array can be partitioned as {1, 5, 5} and {11}
Input: arr[] = {1, 5, 3}
Output: false
The array cannot be partitioned into equal sum sets.
The following are the two main steps to solve this problem:
- Calculate the sum of the array. If the sum is odd, there can not be two subsets with an equal sum, so return false.
- If the sum of the array elements is even, calculate sum/2 and find a subset of the array with a sum equal to sum/2.
The first step is simple. The second step is crucial, it can be solved either using recursion or Dynamic Programming.
Partition problem using recursion:
To solve the problem follow the below idea:
Let isSubsetSum(arr, n, sum/2) be the function that returns true if there is a subset of arr[0..n-1] with sum equal to sum/2
The isSubsetSum problem can be divided into two subproblems
- isSubsetSum() without considering last element (reducing n to n-1)
- isSubsetSum considering the last element (reducing sum/2 by arr[n-1] and n to n-1)
If any of the above subproblems return true, then return true.
isSubsetSum (arr, n, sum/2) = isSubsetSum (arr, n-1, sum/2) || isSubsetSum (arr, n-1, sum/2 – arr[n-1])
Follow the below steps to solve the problem:
- First, check if the sum of the elements is even or not
- After checking, call the recursive function isSubsetSum with parameters as input array, array size, and sum/2
- If the sum is equal to zero then return true (Base case)
- If n is equal to 0 and sum is not equal to zero then return false (Base case)
- Check if the value of the last element is greater than the remaining sum then call this function again by removing the last element
- else call this function again for both the cases stated above and return true, if anyone of them returns true
- Print the answer
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
bool isSubsetSum(int arr[], int n, int sum)
{
if (sum == 0)
return true;
if (n == 0 && sum != 0)
return false;
if (arr[n - 1] > sum)
return isSubsetSum(arr, n - 1, sum);
return isSubsetSum(arr, n - 1, sum)
|| isSubsetSum(arr, n - 1, sum - arr[n - 1]);
}
bool findPartiion(int arr[], int n)
{
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
sum += arr[i];
if (sum % 2 != 0)
return false;
return isSubsetSum(arr, n, sum / 2);
}
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 3, 1, 5, 9, 12 };
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
if (findPartiion(arr, n) == true)
cout << "Can be divided into two subsets "
"of equal sum";
else
cout << "Can not be divided into two subsets"
" of equal sum";
return 0;
}
|
C
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <stdio.h>
bool isSubsetSum(int arr[], int n, int sum)
{
if (sum == 0)
return true;
if (n == 0 && sum != 0)
return false;
if (arr[n - 1] > sum)
return isSubsetSum(arr, n - 1, sum);
return isSubsetSum(arr, n - 1, sum)
|| isSubsetSum(arr, n - 1, sum - arr[n - 1]);
}
bool findPartiion(int arr[], int n)
{
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
sum += arr[i];
if (sum % 2 != 0)
return false;
return isSubsetSum(arr, n, sum / 2);
}
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 3, 1, 5, 9, 12 };
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
if (findPartiion(arr, n) == true)
printf("Can be divided into two subsets "
"of equal sum");
else
printf("Can not be divided into two subsets"
" of equal sum");
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.io.*;
class Partition {
static boolean isSubsetSum(int arr[], int n, int sum)
{
if (sum == 0)
return true;
if (n == 0 && sum != 0)
return false;
if (arr[n - 1] > sum)
return isSubsetSum(arr, n - 1, sum);
return isSubsetSum(arr, n - 1, sum)
|| isSubsetSum(arr, n - 1, sum - arr[n - 1]);
}
static boolean findPartition(int arr[], int n)
{
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
sum += arr[i];
if (sum % 2 != 0)
return false;
return isSubsetSum(arr, n, sum / 2);
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int arr[] = { 3, 1, 5, 9, 12 };
int n = arr.length;
if (findPartition(arr, n) == true)
System.out.println("Can be divided into two "
+ "subsets of equal sum");
else
System.out.println(
"Can not be divided into "
+ "two subsets of equal sum");
}
}
|
Python3
def isSubsetSum(arr, n, sum):
if sum == 0:
return True
if n == 0 and sum != 0:
return False
if arr[n-1] > sum:
return isSubsetSum(arr, n-1, sum)
return isSubsetSum(arr, n-1, sum) or isSubsetSum(arr, n-1, sum-arr[n-1])
def findPartion(arr, n):
sum = 0
for i in range(0, n):
sum += arr[i]
if sum % 2 != 0:
return false
return isSubsetSum(arr, n, sum // 2)
if __name__ == '__main__':
arr = [3, 1, 5, 9, 12]
n = len(arr)
if findPartion(arr, n) == True:
print("Can be divided into two subsets of equal sum")
else:
print("Can not be divided into two subsets of equal sum")
|
C#
using System;
class GFG {
static bool isSubsetSum(int[] arr, int n, int sum)
{
if (sum == 0)
return true;
if (n == 0 && sum != 0)
return false;
if (arr[n - 1] > sum)
return isSubsetSum(arr, n - 1, sum);
return isSubsetSum(arr, n - 1, sum)
|| isSubsetSum(arr, n - 1, sum - arr[n - 1]);
}
static bool findPartition(int[] arr, int n)
{
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
sum += arr[i];
if (sum % 2 != 0)
return false;
return isSubsetSum(arr, n, sum / 2);
}
public static void Main()
{
int[] arr = { 3, 1, 5, 9, 12 };
int n = arr.Length;
if (findPartition(arr, n) == true)
Console.Write("Can be divided into two "
+ "subsets of equal sum");
else
Console.Write("Can not be divided into "
+ "two subsets of equal sum");
}
}
|
PHP
<?php
function isSubsetSum ($arr, $n, $sum)
{
if ($sum == 0)
return true;
if ($n == 0 && $sum != 0)
return false;
if ($arr[$n - 1] > $sum)
return isSubsetSum ($arr, $n - 1, $sum);
return isSubsetSum ($arr, $n - 1, $sum) ||
isSubsetSum ($arr, $n - 1,
$sum - $arr[$n - 1]);
}
function findPartiion ($arr, $n)
{
$sum = 0;
for ($i = 0; $i < $n; $i++)
$sum += $arr[$i];
if ($sum % 2 != 0)
return false;
return isSubsetSum ($arr, $n, $sum / 2);
}
$arr = array(3, 1, 5, 9, 12);
$n = count($arr);
if (findPartiion($arr, $n) == true)
echo "Can be divided into two subsets of equal sum";
else
echo "Can not be divided into two subsets of equal sum";
?>
|
Javascript
<script>
function isSubsetSum(arr,n,sum)
{
if (sum == 0)
return true;
if (n == 0 && sum != 0)
return false;
if (arr[n - 1] > sum)
return isSubsetSum(arr, n - 1, sum);
return isSubsetSum(arr, n - 1, sum)
|| isSubsetSum(arr, n - 1, sum - arr[n - 1]);
}
function findPartition(arr,n)
{
let sum = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++)
sum += arr[i];
if (sum % 2 != 0)
return false;
return isSubsetSum(arr, n, Math.floor(sum / 2));
}
let arr=[3, 1, 5, 9, 12 ];
let n = arr.length;
if (findPartition(arr, n) == true)
document.write("Can be divided into two "
+ "subsets of equal sum");
else
document.write(
"Can not be divided into "
+ "two subsets of equal sum");
</script>
|
Output
Can be divided into two subsets of equal sum
Time Complexity: O(2N) In the worst case, this solution tries two possibilities (whether to include or exclude) for every element.
Auxiliary Space: O(N). Recursion stack space
Partition problem using memoization:
To solve the problem follow the below idea:
As the above recursive solution has overlapping subproblems so we can declare a 2-D array to save the values for different states of the recursive function instead of solving them more than once
Follow the below steps to solve the problem:
- Declare a 2-D array of size N+1 X sum+1
- Call the recursive function with parameters as input array, size, sum, and dp array
- In this recursive function
- If the sum is equal to zero then return true (Base case)
- If n is equal to 0 and sum is not equal to zero then return false (Base case)
- If the value of this subproblem is already calculated then return the answer from dp array
- Else calculate the answer for this subproblem using the recursive formula in the above approach and save the answer in the dp array
- Return the answer as true or false
- Print the answer
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
bool isSubsetSum(int arr[], int n, int sum,
vector<vector<int> >& dp)
{
if (sum == 0)
return true;
if (n == 0 && sum != 0)
return false;
if (dp[n][sum] != -1) {
return dp[n][sum];
}
if (arr[n - 1] > sum)
return isSubsetSum(arr, n - 1, sum, dp);
return dp[n][sum]
= isSubsetSum(arr, n - 1, sum, dp)
|| isSubsetSum(arr, n - 1, sum - arr[n - 1],
dp);
}
bool findPartiion(int arr[], int n)
{
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
sum += arr[i];
if (sum % 2 != 0)
return false;
vector<vector<int> > dp(n + 1,
vector<int>(sum + 1, -1));
return isSubsetSum(arr, n, sum / 2, dp);
}
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 3, 1, 5, 9, 12 };
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
if (findPartiion(arr, n) == true)
cout << "Can be divided into two subsets "
"of equal sum";
else
cout << "Can not be divided into two subsets"
" of equal sum";
int arr2[] = { 3, 1, 5, 9, 14 };
int n2 = sizeof(arr2) / sizeof(arr2[0]);
if (findPartiion(arr2, n2) == true)
cout << endl
<< "Can be divided into two subsets "
"of equal sum";
else
cout << endl
<< "Can not be divided into two subsets"
" of equal sum";
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
static int isSubsetSum(int arr[], int n, int sum,
int[][] dp)
{
if (sum == 0)
return 1;
if (n == 0 && sum != 0)
return 0;
if (dp[n][sum] != -1) {
return dp[n][sum];
}
if (arr[n - 1] > sum)
return isSubsetSum(arr, n - 1, sum, dp);
if (isSubsetSum(arr, n - 1, sum, dp) != 0
|| isSubsetSum(arr, n - 1, sum - arr[n - 1], dp)
!= 0)
return dp[n][sum] = 1;
return dp[n][sum] = 0;
}
static int findPartiion(int arr[], int n)
{
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
sum += arr[i];
if (sum % 2 != 0)
return 0;
int dp[][] = new int[n + 1][sum + 1];
for (int row[] : dp)
Arrays.fill(row, -1);
return isSubsetSum(arr, n, sum / 2, dp);
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int arr[] = { 3, 1, 5, 9, 12 };
int n = arr.length;
if (findPartiion(arr, n) == 1)
System.out.println(
"Can be divided into two subsets of equal sum");
else
System.out.println(
"Can not be divided into two subsets of equal sum");
int arr2[] = { 3, 1, 5, 9, 14 };
int n2 = arr2.length;
if (findPartiion(arr2, n2) == 1)
System.out.println(
"Can be divided into two subsets of equal sum");
else
System.out.println(
"Can not be divided into two subsets of equal sum");
}
}
|
Python3
def isSubsetSum(arr, n, sum, dp):
if (sum == 0):
return True
if (n == 0 and sum != 0):
return False
if (dp[n][sum] != -1):
return dp[n][sum]
if (arr[n - 1] > sum):
return isSubsetSum(arr, n - 1, sum, dp)
dp[n][sum] = isSubsetSum(
arr, n - 1, sum, dp) or isSubsetSum(arr, n - 1, sum - arr[n - 1], dp)
return dp[n][sum]
def findPartiion(arr, n):
sum = 0
for i in range(n):
sum += arr[i]
if (sum % 2 != 0):
return False
dp = [[-1]*(sum+1) for i in range(n+1)]
return isSubsetSum(arr, n, sum // 2, dp)
arr = [3, 1, 5, 9, 12]
n = len(arr)
if (findPartiion(arr, n) == True):
print("Can be divided into two subsets of equal sum")
else:
print("Can not be divided into two subsets of equal sum")
arr2 = [3, 1, 5, 9, 14]
n2 = len(arr2)
if (findPartiion(arr2, n2) == True):
print("Can be divided into two subsets of equal sum")
else:
print("Can not be divided into two subsets of equal sum")
|
C#
using System;
public class GFG {
static int isSubsetSum(int[] arr, int n, int sum,
int[, ] dp)
{
if (sum == 0)
return 1;
if (n == 0 && sum != 0)
return 0;
if (dp[n, sum] != -1) {
return dp[n, sum];
}
if (arr[n - 1] > sum)
return isSubsetSum(arr, n - 1, sum, dp);
if (isSubsetSum(arr, n - 1, sum, dp) != 0
|| isSubsetSum(arr, n - 1, sum - arr[n - 1], dp)
!= 0)
return dp[n, sum] = 1;
return dp[n, sum] = 0;
}
static int findPartiion(int[] arr, int n)
{
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
sum += arr[i];
if (sum % 2 != 0)
return 0;
int[, ] dp = new int[n + 1, sum + 1];
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j <= sum; ++j) {
dp[i, j] = -1;
}
}
return isSubsetSum(arr, n, sum / 2, dp);
}
static public void Main()
{
int[] arr = { 3, 1, 5, 9, 12 };
int n = arr.Length;
if (findPartiion(arr, n) == 1)
Console.WriteLine(
"Can be divided into two subsets of equal sum");
else
Console.WriteLine(
"Can not be divided into two subsets of equal sum");
int[] arr2 = { 3, 1, 5, 9, 14 };
int n2 = arr2.Length;
if (findPartiion(arr2, n2) == 1)
Console.WriteLine(
"Can be divided into two subsets of equal sum");
else
Console.WriteLine(
"Can not be divided into two subsets of equal sum");
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
function isSubsetSum(arr,n,sum,dp)
{
if (sum == 0)
return true;
if (n == 0 && sum != 0)
return false;
if (dp[n][sum] != -1) {
return dp[n][sum];
}
if (arr[n - 1] > sum)
return isSubsetSum(arr, n - 1, sum, dp);
return dp[n][sum]
= isSubsetSum(arr, n - 1, sum, dp)
|| isSubsetSum(arr, n - 1, sum - arr[n - 1],
dp);
}
function findPartiion(arr, n)
{
let sum = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++)
sum += arr[i];
if (sum % 2 != 0)
return false;
let dp = new Array(n + 1).fill(new Array(sum+1).fill(-1));
return isSubsetSum(arr, n, sum / 2, dp);
}
let arr = [ 3, 1, 5, 9, 12 ];
let n = arr.length;
if (findPartiion(arr, n) == true)
document.write("Can be divided into two subsets of equal sum");
else document.write("Can not be divided into two subsets of equal sum");
let arr2 = [ 3, 1, 5, 9, 14 ];
let n2 = arr2.length;
if (findPartiion(arr2, n2) == true)
document.write("</br>","Can be divided into two subsets of equal sum");
else document.write("</br>","Can not be divided into two subsets of equal sum");
</script>
|
Output
Can be divided into two subsets of equal sum
Can not be divided into two subsets of equal sum
Time Complexity: O(sum * N)
Auxiliary Space: O(sum * N)
To solve the problem follow the below idea:
The problem can be solved using dynamic programming when the sum of the elements is not too big. As the recomputations of the same subproblems can be avoided by constructing a temporary array part[][] in a bottom-up manner using the above recursive formula and it should satisfy the following formula:
part[i][j] = true if a subset of {arr[0], arr[1], ..arr[j-1]} has sum equal to i, otherwise false
Follow the below steps to solve the problem:
- First, check if the sum of the elements is even or not
- Declare a 2-D array part[][] of size (sum/2)+1 * (N + 1)
- Run a for loop for 0 <= i <= n and set part[0][i] equal to true as zero-sum is always possible
- Run a for loop for 1 <= i <= sum/2 and set part[i][0] equal to zero as any sum with zero elements is never possible
- Run a nested for loop for 1 <= i <= sum/2 and 1 <= j <= N
- Set part[i][j] equal to part[i][j-1]
- If i is greater than or equal to arr[j-1], if part[i – arr[j-1]][j-1] is true then set part[i][j] as true
- Print the answer
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
bool findPartiion(int arr[], int n)
{
int sum = 0;
int i, j;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
sum += arr[i];
if (sum % 2 != 0)
return false;
bool part[sum / 2 + 1][n + 1];
for (i = 0; i <= n; i++)
part[0][i] = true;
for (i = 1; i <= sum / 2; i++)
part[i][0] = false;
for (i = 1; i <= sum / 2; i++) {
for (j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
part[i][j] = part[i][j - 1];
if (i >= arr[j - 1])
part[i][j] = part[i][j]
|| part[i - arr[j - 1]][j - 1];
}
}
return part[sum / 2][n];
}
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 3, 1, 1, 2, 2, 1 };
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
if (findPartiion(arr, n) == true)
cout << "Can be divided into two subsets of equal "
"sum";
else
cout << "Can not be divided into"
<< " two subsets of equal sum";
return 0;
}
|
C
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
bool findPartiion(int arr[], int n)
{
int sum = 0;
int i, j;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
sum += arr[i];
if (sum % 2 != 0)
return false;
bool part[sum / 2 + 1][n + 1];
for (i = 0; i <= n; i++)
part[0][i] = true;
for (i = 1; i <= sum / 2; i++)
part[i][0] = false;
for (i = 1; i <= sum / 2; i++) {
for (j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
part[i][j] = part[i][j - 1];
if (i >= arr[j - 1])
part[i][j] = part[i][j]
|| part[i - arr[j - 1]][j - 1];
}
}
return part[sum / 2][n];
}
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 3, 1, 1, 2, 2, 1 };
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
if (findPartiion(arr, n) == true)
printf(
"Can be divided into two subsets of equal sum");
else
printf("Can not be divided into two subsets of "
"equal sum");
getchar();
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.io.*;
class Partition {
static boolean findPartition(int arr[], int n)
{
int sum = 0;
int i, j;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
sum += arr[i];
if (sum % 2 != 0)
return false;
boolean part[][] = new boolean[sum / 2 + 1][n + 1];
for (i = 0; i <= n; i++)
part[0][i] = true;
for (i = 1; i <= sum / 2; i++)
part[i][0] = false;
for (i = 1; i <= sum / 2; i++) {
for (j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
part[i][j] = part[i][j - 1];
if (i >= arr[j - 1])
part[i][j]
= part[i][j]
|| part[i - arr[j - 1]][j - 1];
}
}
return part[sum / 2][n];
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int arr[] = { 3, 1, 1, 2, 2, 1 };
int n = arr.length;
if (findPartition(arr, n) == true)
System.out.println(
"Can be divided into two subsets of equal sum");
else
System.out.println(
"Can not be divided into two subsets of equal sum");
}
}
|
Python3
def findPartition(arr, n):
sum = 0
i, j = 0, 0
for i in range(n):
sum += arr[i]
if sum % 2 != 0:
return false
part = [[True for i in range(n + 1)]
for j in range(sum // 2 + 1)]
for i in range(0, n + 1):
part[0][i] = True
for i in range(1, sum // 2 + 1):
part[i][0] = False
for i in range(1, sum // 2 + 1):
for j in range(1, n + 1):
part[i][j] = part[i][j - 1]
if i >= arr[j - 1]:
part[i][j] = (part[i][j] or
part[i - arr[j - 1]][j - 1])
return part[sum // 2][n]
arr = [3, 1, 1, 2, 2, 1]
n = len(arr)
if findPartition(arr, n) == True:
print("Can be divided into two",
"subsets of equal sum")
else:
print("Can not be divided into ",
"two subsets of equal sum")
|
C#
using System;
class GFG {
static bool findPartition(int[] arr, int n)
{
int sum = 0;
int i, j;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
sum += arr[i];
if (sum % 2 != 0)
return false;
bool[, ] part = new bool[sum / 2 + 1, n + 1];
for (i = 0; i <= n; i++)
part[0, i] = true;
for (i = 1; i <= sum / 2; i++)
part[i, 0] = false;
for (i = 1; i <= sum / 2; i++) {
for (j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
part[i, j] = part[i, j - 1];
if (i >= arr[j - 1])
part[i, j]
= part[i, j - 1]
|| part[i - arr[j - 1], j - 1];
}
}
return part[sum / 2, n];
}
public static void Main()
{
int[] arr = { 3, 1, 1, 2, 2, 1 };
int n = arr.Length;
if (findPartition(arr, n) == true)
Console.Write("Can be divided"
+ " into two subsets of"
+ " equal sum");
else
Console.Write("Can not be "
+ "divided into two subsets"
+ " of equal sum");
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
function findPartition(arr , n)
{
var sum = 0;
var i, j;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
sum += arr[i];
if (sum % 2 != 0)
return false;
var part = Array(parseInt(sum / 2) + 1).
fill().map(()=>Array(n + 1).fill(0));
for (i = 0; i <= n; i++)
part[0][i] = true;
for (i = 1; i <= parseInt(sum / 2); i++)
part[i][0] = false;
for (i = 1; i <= parseInt(sum / 2); i++) {
for (j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
part[i][j] = part[i][j - 1];
if (i >= arr[j - 1])
part[i][j] = part[i][j] ||
part[i - arr[j - 1]][j - 1];
}
}
return part[parseInt(sum / 2)][n];
}
var arr = [ 3, 1, 1, 2, 2, 1 ];
var n = arr.length;
if (findPartition(arr, n) == true)
document.write(
"Can be divided into two subsets of equal sum"
);
else
document.write(
"Can not be divided into two subsets of equal sum"
);
</script>
|
Output
Can be divided into two subsets of equal sum
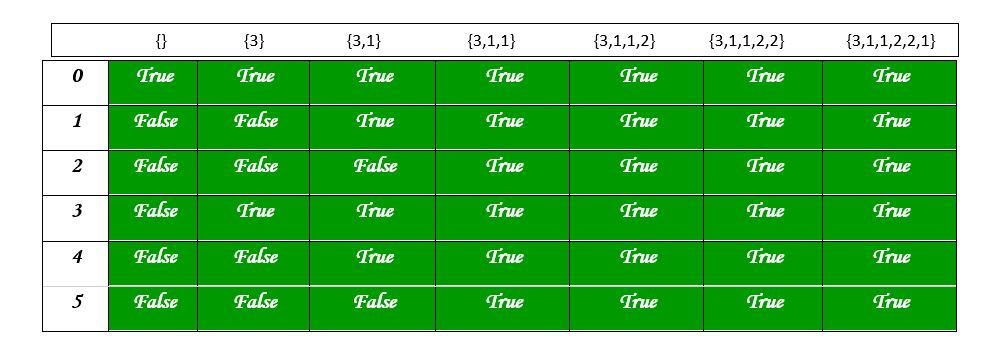
The following diagram shows the values in the partition table:
Time Complexity: O(sum * N)
Auxiliary Space: O(sum * N)
Note: this solution will not be feasible for arrays with a big sum
Space-optimized approach for the above solution:
To solve the problem follow the below idea:
We can space optimize the above dp approach as for calculating the values of the current row we require only previous row
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
bool findPartiion(int arr[], int n)
{
int sum = 0;
int i, j;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
sum += arr[i];
if (sum % 2 != 0)
return false;
bool part[sum / 2 + 1];
for (i = 0; i <= sum / 2; i++) {
part[i] = 0;
}
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (j = sum / 2; j >= arr[i];
j--) {
if (part[j - arr[i]] == 1 || j == arr[i])
part[j] = 1;
}
}
return part[sum / 2];
}
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 1, 3, 3, 2, 3, 2 };
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
if (findPartiion(arr, n) == true)
cout << "Can be divided into two subsets of equal "
"sum";
else
cout << "Can not be divided into"
<< " two subsets of equal sum";
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.io.*;
class GFG {
public static boolean findPartiion(int arr[], int n)
{
int sum = 0;
int i, j;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
sum += arr[i];
if (sum % 2 != 0)
return false;
boolean[] part = new boolean[sum / 2 + 1];
for (i = 0; i <= sum / 2; i++) {
part[i] = false;
}
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (j = sum / 2; j >= arr[i]; j--) {
if (part[j - arr[i]] == true || j == arr[i])
part[j] = true;
}
}
return part[sum / 2];
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int arr[] = { 1, 3, 3, 2, 3, 2 };
int n = 6;
if (findPartiion(arr, n) == true)
System.out.println("Can be divided into two "
+ "subsets of equal sum");
else
System.out.println(
"Can not be divided into "
+ "two subsets of equal sum");
}
}
|
Python3
def findPartiion(arr, n):
Sum = 0
for i in range(n):
Sum += arr[i]
if (Sum % 2 != 0):
return 0
part = [0] * ((Sum // 2) + 1)
for i in range((Sum // 2) + 1):
part[i] = 0
for i in range(n):
for j in range(Sum // 2, arr[i] - 1, -1):
if (part[j - arr[i]] == 1 or j == arr[i]):
part[j] = 1
return part[Sum // 2]
arr = [1, 3, 3, 2, 3, 2]
n = len(arr)
if (findPartiion(arr, n) == 1):
print("Can be divided into two subsets of equal sum")
else:
print("Can not be divided into two subsets of equal sum")
|
C#
using System;
class GFG {
static bool findPartiion(int[] arr, int n)
{
int sum = 0;
int i, j;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
sum += arr[i];
if (sum % 2 != 0)
return false;
bool[] part = new bool[sum / 2 + 1];
for (i = 0; i <= sum / 2; i++) {
part[i] = false;
}
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (j = sum / 2; j >= arr[i]; j--) {
if (part[j - arr[i]] == true || j == arr[i])
part[j] = true;
}
}
return part[sum / 2];
}
static void Main()
{
int[] arr = { 1, 3, 3, 2, 3, 2 };
int n = 6;
if (findPartiion(arr, n) == true)
Console.WriteLine("Can be divided into two "
+ "subsets of equal sum");
else
Console.WriteLine("Can not be divided into "
+ "two subsets of equal sum");
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
function findPartiion(arr, n)
{
let sum = 0;
let i, j;
for(i = 0; i < n; i++)
sum += arr[i];
if (sum % 2 != 0)
return false;
let part = new Array(parseInt(sum / 2 + 1, 10));
for(i = 0; i <= parseInt(sum / 2, 10); i++)
{
part[i] = false;
}
for(i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for(j = parseInt(sum / 2, 10);
j >= arr[i];
j--)
{
if (part[j - arr[i]] == true ||
j == arr[i])
part[j] = true;
}
}
return part[parseInt(sum / 2, 10)];
}
let arr = [ 1, 3, 3, 2, 3, 2 ];
let n = arr.length;
if (findPartiion(arr, n) == true)
document.write("Can be divided into two " +
"subsets of equal sum");
else
document.write("Can not be divided into " +
"two subsets of equal sum");
</script>
|
Output
Can be divided into two subsets of equal sum
Time Complexity: O(sum * N)
Auxiliary Space: O(sum)
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...