Difference between Simultaneous and Hierarchical Access Memory Organisations
Last Updated :
19 Dec, 2018
In the Computer System Design, Memory organisation is primarily divided into two main types on the basis of the manner in which CPU tries to access different levels of Memory.
These two types include
Simultaneous Access Memory Organisation and
Hierarchical Access Memory Organisation. Let us understand the difference between the two from the following table:
 Figure – Simultaneous Access Memory Organisation
Figure – Simultaneous Access Memory Organisation
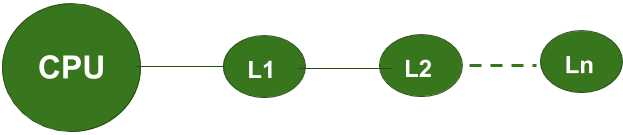 Figure – Hierarchical Access Memory Organisation
Difference between Simultaneous and Hierarchical Access Memory Organisations:
Figure – Hierarchical Access Memory Organisation
Difference between Simultaneous and Hierarchical Access Memory Organisations:
| Simultaneous Access Memory Organisation |
Hierarchical Access Memory Organisation |
In this organisation, CPU is directly connected to all the levels of Memory. |
In this organisation, CPU is always directly connected to L1
i.e. Level-1 Memory only. |
| CPU accesses the data from all levels of Memory simultaneously. |
CPU always accesses the data from Level-1 Memory. |
| For any “miss” encountered in L1 memory, CPU can directly access data from higher memory levels
(i.e. L2, L3, …..Ln). |
For any “miss” encountered in L1 memory, CPU cannot directly access data from higher memory levels(i.e. L2, L3, …..Ln). First the desired data will be transferred from higher memory levels to L1 memory.
Only then it can be accessed by the CPU. |
If H1 and H2 are the Hit Ratios and T1 and T2 are the access time of L1 and L2 memory levels respectively then the
Average Memory Access Time can be calculated as:
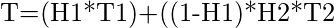 |
If H1 and H2 are the Hit Ratios and T1 and T2 are the access time of L1 and L2 memory levels respectively then the
Average Memory Access Time can be calculated as:
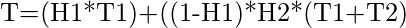 |
NOTE:
- By default the memory structure of Computer Systems is designed with Hierarchical Access Memory Organisation.It is so because in this type of memory organisation the average access time is reduced due to locality of references.
- Simultaneous access Memory organisation is used for the implementation of Write Through Cache.
- In both types of memory organisation, the Hit Ratio of last memory level is always 1.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...