Deleting a Column in SQL Server
Last Updated :
25 Jan, 2024
Structure Query Language (SQL) is a standard language to manipulate and manage the database. SQL is a very powerful language for managing the database. SQL Server Delete command is one of the SQL commands that is used to remove the data that is not useful or due to which inconsistency occurred in the database. In this article, we will see a detailed explanation of the Delete command, the syntax of the Delete command, and an explanation of examples of the delete command step by step.
In the world of relational databases, the structure of tables plays a pivotal role in data organization. There are instances where it becomes necessary to modify the structure of a table, and one common operation is deleting columns. This article will guide you through the process of efficiently deleting columns from a table in SQL.
Prerequisites
- Know how to use MS SQL Server
- Basic knowledge of SQL Syntax
- Understanding of the primary key in the database to check whether data needs to be deleted.
Create Table Command
The create table command is used to create a table in the database. This is a command very important command in SQL Server.
Syntax:
CREATE TABLE table_name(column_name1 datatype1,
column_name2 datatype2,
column_name3 datatype3,
.
.
columns);
Here,
- table_name: Name of table.
- column_name: Name of column.
- datatype: Datatype of column name
Remove Duplicate Rows in SQL Server
Duplicate data can be a persistent challenge in relational databases, impacting both performance and data integrity. In SQL Server, crafting a script to eliminate duplicate rows is a powerful strategy.
Syntax:
WITH DuplicateCTE AS (
SELECT
YourColumns,
ROW_NUMBER() OVER (PARTITION BY Column1, Column2 ORDER BY (SELECT NULL)) AS RowNum
FROM YourTable
)
DELETE FROM DuplicateCTE WHERE RowNum > 1;
Here,
- Replace
YourColumns with the actual column names you want to consider.
- Modify
Column1, Column2 to the columns that determine duplicates.
- The
ROW_NUMBER() function assigns a unique number to each row based on the specified columns.
- The
PARTITION BY clause ensures that the numbering restarts for each unique combination of columns.
- The
DELETE statement removes rows with a row number greater than 1, keeping only the first occurrence.
Examples of Removing Duplicate Rows in SQL Server
Step 1: Create a Sample Table
Consider a table named Employee with the following structure:
Step 2: Create Script to Remove Duplicate Rows
Now, let’s use a script to remove duplicate rows based on the FirstName and LastName columns:
Examples of SQL Server DELETE Single Row
Example 1: Deleting single Record
Let’s take a table named ‘Employee’ and we want to delete the record of employee_id is 10..
SQL Query:
DELETE from Employee
WHERE employee_id=10;
Before Deletion:

Before Deletion
Explanation: Here in the above image, we see the records of the table before deleting any record from the table. You can fetch these records from the table using the SELECT Statement.
Running Delete query:
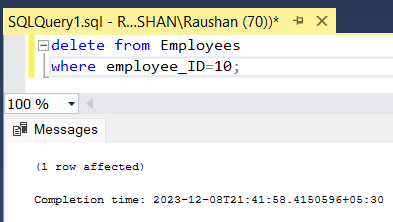
Query for Deleting Single row
Explanation: In the above image you see that running delete query to remove the record from the table. In this example we remove single data of employees whose employee_ID is 10 for this we use the condition using the WHERE keyword
After Deletion:
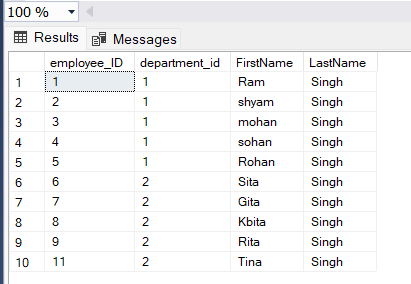
Output
Explanation: In this image, you can see that after deletion of the record of an employee whose employee_ID is 10 is removed from the employee table.
Example 2: Deleting Multiple Records
In this example we delete multiple records from the table, we delete the record of all whose department ID is 2
SQL Query:
DELETE from Employee
WHERE department_id= 2;
Before Deletion:
.png)
Single row deleted table
Explanation: Here in the above image, we see the records of the table before deleting any record from the table. You can fetch these records from the table using the SELECT Statement
Running Delete Query:
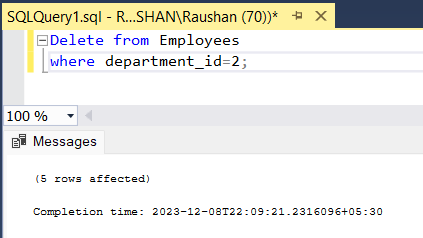
Query for delete multiple rows
Explanation: In the above image you see that running delete query to remove the record from the table. In this example, all the records whose department_id is 2 will be removed because we use the condition to remove all employee data whose department_id is 2.
After Deletion:
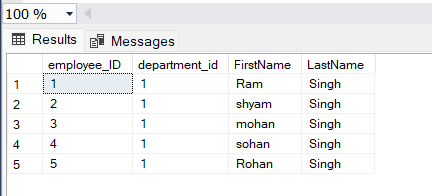
Output after deletion of multiple rows
Explanation: In this image, you can see that after deletion of the records of employees whose department_id is 2 is removed from the employee table.
Example 3: Deleting All Records
In this example, we delete all the records from a table. It can be done by running a delete query without using a condition.
SQL Query:
DELETE From Employee;
Before Deletion:
.png)
after multiple delete
Explanation: Here in the above image, we see the records of the table before deleting any record from the table. You can fetch these records from the table using the SELECT Statement.
Running SQL Query:
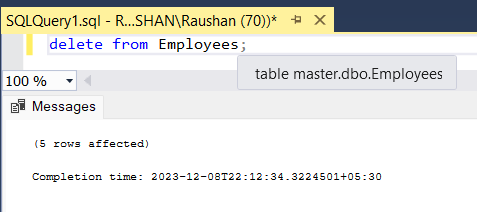
all delete statement
Explanation: In the above image you see that running delete query to remove the record from the table. In this example, all the records will be removed from the table because there is no condition so it will delete all the records from the table.
After Deletion:

Output
Explanation: In this image, you can see that after deletion of all records of employees from the employee table.
Conclusion
SQL Server DELETE is a very important tool that is used to remove unwanted data from the tables. Understanding the syntax and its usage is important and is effective in managing and maintaining the database. You can easily understand the concept of DELETE command from the given examples.The DELETE statement contributes to maintaining a well-organized and optimized database by allowing the removal of unwanted or outdated information.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...