CREATE TABLE in SQL Server
Last Updated :
05 Apr, 2024
SQL Server provides a variety of data management tools such as querying, indexing, and transaction processing. It supports multiple programming languages and platforms, making it a versatile RDBMS for various applications. With its robust features and reliability, SQL Server is a popular choice for enterprise-level databases.
In this article, we will learn how to efficiently use CREATE TABLE statements to create a table in our database. We will cover all the basic concepts with clear and concise examples along with their respective.
CREATE TABLE Statement in SQL Server
In SQL Server, the CREATE TABLE statement is used to create a table in our database. We can say it is a fundamental step for defining a table with our database. This statement allows us to set the table name with attributes of its specified columns.
Syntax:
CREATE TABLE [Schema].[table_name ](
column_01 [datatype] (length){Add constraint optional},
column_02 [datatype] (length) {Add constraint optional}
…………..
…………
) ON [File group] ;
Example of CREATE TABLE Statement in a Specific Schema
In this, we are going to create a table named ‘geeksforgeeks’. It will consist of ‘id‘, ‘name‘, and ‘potd‘ as a column. We are also going to insert values in our table and display them. We are going to create our table in a specified schema i.e. ‘dbo‘.
Schema: It is a collection of database objects such as table, views etc.
Query:
CREATE TABLE [dbo].[geeksforgeeks]
(
[id] [int] IDENTITY(1,1) ,
[name] [varchar](20),
[potd] [int]
) ON [PRIMARY]
After executing this statement, we can see a table has been created in our database.
Output:
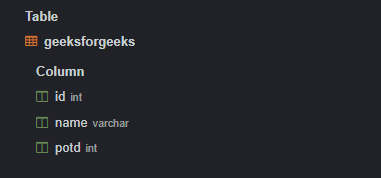
Creating table geeksforgeeks
Explanation: We can see our table has been created in our database. In our table, id, name, and potd columns have been created with integer, varchar, and integer data type respectively. IDENTITY(1,1) in the ‘id’ column means this column value will be automatically generated by SQL starting from 1 and then incrementing by 1 for each row.
Now we are done with creating our table, let’s add some data to our table and display them. We will use the “INSERT INTO” statement to insert data into our table.
Query:
-- Inserting values into our table 'geeksforgeeks'
INSERT INTO geeksforgeeks ([name],[potd])
VALUES ('Vishu', 200);
INSERT INTO geeksforgeeks ([name],[potd])
VALUES ('Neeraj', 150);
INSERT INTO geeksforgeeks ([name],[potd])
VALUES ('Aayush', 125);
INSERT INTO geeksforgeeks ([name],[potd])
VALUES ('Vivek', 100);
-- Displaying table's data
SELECT * FROM geeksforgeeks;
Output:

Table – geeksforgeeks
Explanation: We can observe that all our table’s entered data has been displayed. As specified earlier, we can see that we have not explicitly inserted value in our ‘id‘ column. We can see that the and ‘id’ column values start from 1 and then incremented by 1 for each next row.
Example of CREATE TABLE with Constraints
In this, we are going to create our table ‘courses‘ in our database. It will consist of the id, name, and the course as a column. Unlike previous example, we are going to specify UNIQUE and NOT NULL constraints in some of the columns of this table.
Query:
CREATE TABLE [courses]
(
[id] [int] UNIQUE,
[name] [varchar](20) NOT NULL,
[course] [varchar] (50)
) ON [PRIMARY]
Likewise in the previous example, our table will be created after the successful execution of the above query.
Output:

Table – courses
We can see that our table has been created. Now violating any of the above-mentioned constraints will result in an error.
Let’s try to break UNIQUE Key Constraint Condition
Query:
INSERT INTO courses ([id],[name],[course])
VALUES (1, 'Vishu', 'Python');
INSERT INTO courses ([id],[name],[course])
VALUES (1, 'Neeraj', 'Java');
Output:

Unique Key Error
Explanation: We can see that we have tried to duplicate the id which is prohibited in a column with a unique key constraint. We can see that an error has been thrown displaying the warning for inserting a duplicate value in a Unique key column.
Conclusion
Overall, SQL Server is a strong RDBMS built to efficiently manage large data sets. The CREATE TABLE command in SQL Server is used to establish and specify the structure of a table within a database. We have seen how to apply column constraints in conjunction with the CREATE TABLE statement in a particular schema. You now understand the CREATE TABLE statement. You can now create queries related to it and get the desired results.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...