What is Data Structure?
Last Updated :
07 Jul, 2023
A data structure is a way of organizing and storing data in a computer so that it can be accessed and used efficiently. It refers to the logical or mathematical representation of data, as well as the implementation in a computer program.
Classification:
Data structures can be classified into two broad categories:
- Linear Data Structure: A data structure in which data elements are arranged sequentially or linearly, where each element is attached to its previous and next adjacent elements, is called a linear data structure. Examples are array, stack, queue, etc.
- Non-linear Data Structure: Data structures where data elements are not placed sequentially or linearly are called non-linear data structures. Examples are trees and graphs.
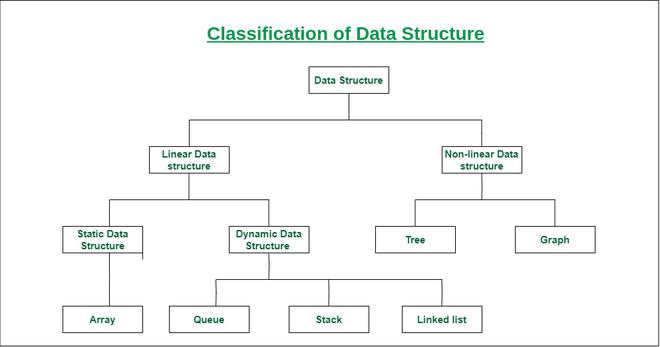
Classification of Data Structure
To learn more about different data structures, refer to this article.
Applications of Data Structures:
Data structures are used in a wide range of computer programs and applications, including:
- Databases: Data structures are used to organize and store data in a database, allowing for efficient retrieval and manipulation.
- Operating systems: Data structures are used in the design and implementation of operating systems to manage system resources, such as memory and files.
- Computer graphics: Data structures are used to represent geometric shapes and other graphical elements in computer graphics applications.
- Artificial intelligence: Data structures are used to represent knowledge and information in artificial intelligence systems.
Advantages of Data Structures:
The use of data structures provides several advantages, including:
- Efficiency: Data structures allow for efficient storage and retrieval of data, which is important in applications where performance is critical.
- Flexibility: Data structures provide a flexible way to organize and store data, allowing for easy modification and manipulation.
- Reusability: Data structures can be used in multiple programs and applications, reducing the need for redundant code.
- Maintainability: Well-designed data structures can make programs easier to understand, modify, and maintain over time.
What else can you read?
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...