Creating an Server-Client Application using the DatagramPacket and DatagramSocket classes
Last Updated :
20 Nov, 2021
To create an application that uses UDP to establish the connection between a client and server, we need to perform the following steps:
- Create a server program
- Create a client program
- Execute the client and server program
Let’s perform the steps in the following subsections:
Creating the Server Program
Let’s create the server class, named UDPServerEx which takes messages from a user and sends the messages (datagrams) to the clients. Listing 1 shows the code of the UDPServerEx.java file:
Filename: UDPServerEx.java
Java
import java.net.*;
class UDPServerEx {
public static DatagramSocket mySocket;
public static byte myBuffer[] = new byte[2000];
public static void serverMethod() throws Exception
{
int position = 0;
while (true) {
int charData = System.in.read();
switch (charData) {
case -1:
System.out.println(
"The execution of "
+ "the server has been terminated");
return;
case '\r':
break;
case '\n':
mySocket.send(
new DatagramPacket(
myBuffer,
position,
InetAddress.getLocalHost(),
777));
position = 0;
break;
default:
myBuffer[position++]
= (byte)charData;
}
}
}
public static void main(String args[]) throws Exception
{
System.out.println("Please enter some text here");
mySocket = new DatagramSocket(888);
serverMethod();
}
}
|
To compile the UDPServerEx.java file:
D:\UDPExample>javac UDPServerEx.java
Note: The path may vary according to where you save file.
Creating the ClientProgram
Let’s create a client class, named UDPClient, which accepts the messages sent from the server, UDPServerEx class. The client then displays the messages received in the Command Prompt. Listing 2 shows the code of the UDPClient.java file:
Filename: UDPClient.java
Java
import java.net.*;
class UDPClient {
public static DatagramSocket mySocket;
public static byte myBuffer[] = new byte[2000];
public static void clientMethod() throws Exception
{
while (true) {
DatagramPacket dataPacket
= new DatagramPacket(myBuffer,
myBuffer.length);
mySocket.receive(dataPacket);
System.out.println("Message Received :");
System.out.println(
new String(
dataPacket.getData(),
0,
dataPacket.getLength()));
}
}
public static void main(String args[]) throws Exception
{
System.out.println(
"You need to press CTRL+C"
+ " in order to quit.");
mySocket = new DatagramSocket(777);
clientMethod();
}
}
|
Use the following command to compile the UDPClient.java file:
D:\UDPExample>javac UDPClient.java
Output
Note: To execute the UDPServerEx and UDPClient classes, run the UDPServerEx.java and UDPClient.java in two separate Command Prompt windows. Remember, the UDPServerEx class is executed before the UDPClient class. Figure 1 shows the output of the UDP Server java and UDPClient.java files:
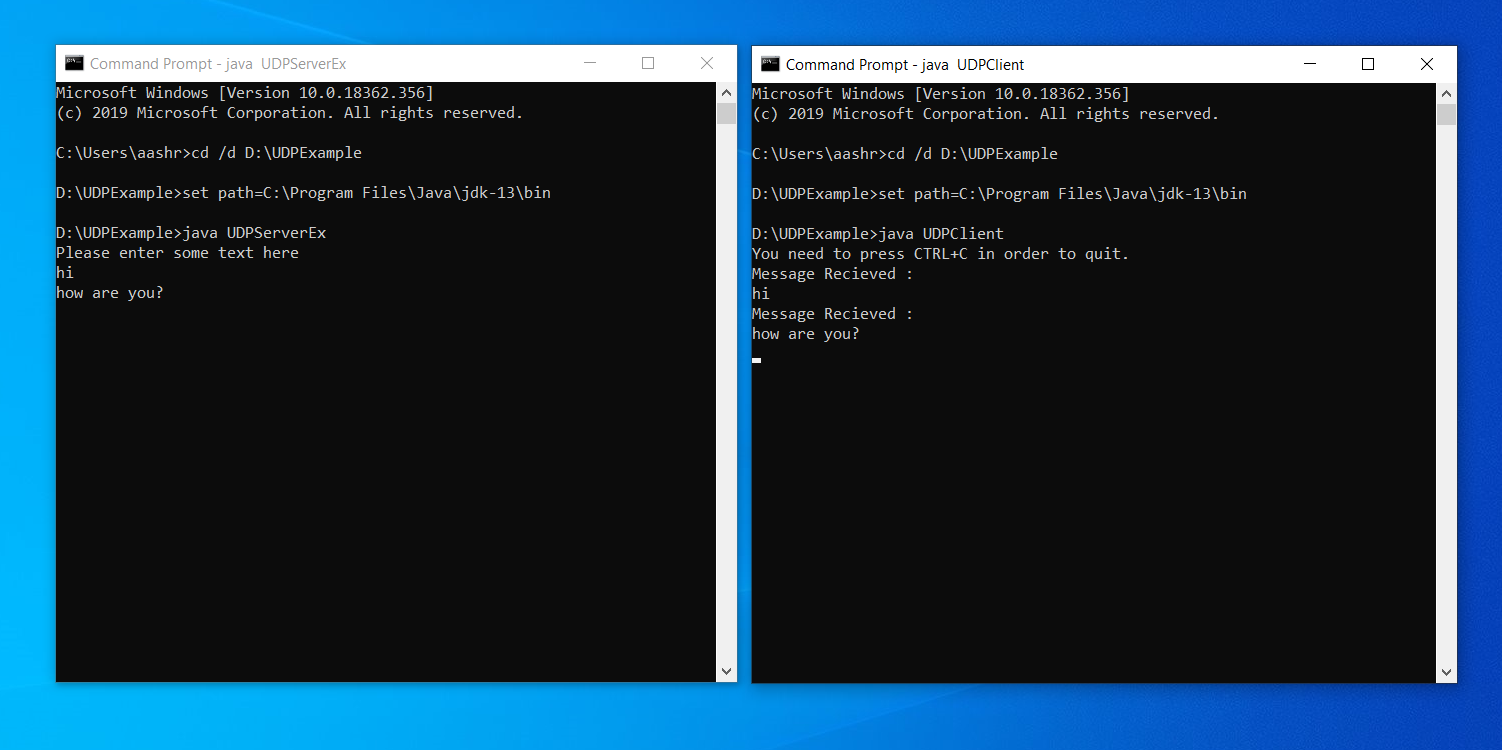
Showing the Output of the UDPServerEx and UDPClient Classes
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...