How to Create a simple TCP Client-Server Connection in Java?
Last Updated :
04 Apr, 2024
TCP can be defined as Transmission Control Protocol. This is the standard protocol for transmitting data over a network. It provides reliable, structured, and error-checked data delivery between applications running on hosts connected via an IP (Internet Protocol) network. In Java, we can create TCP client-server connections using the Socket and ServerSocket classes from the java.net package.
In this article, we will learn how to create a simple TCP client-server connection in Java.
TCP client-server connection
- TCP client-server communication consists of two important components. These two consist of a server and more than one client.
- The servers receive incoming connections from clients on a specific port number using a ServerSocket.
- The client then connects to the port using a Socket with the server’s IP address.
- Once the connection is created, the data can be exchanged between the server and the client using input and output streams.
Key Terminologies
- TCP: Transmission Control Protocol used to transmit data over a network and can provide network communications, point-to-point communication channels and can ensure data integrity and sequencing.
- Socket: It is the terminal connection between two devices on the network and the Socket class can represent the client-side socket and can provide a connection to the server
Step-by-Step implementation of Server-Side to Create Connection
- Create the Java class named Server in that class write the main method.
- Create the instance of the ServerSocket and assign the port as 9090.
- Accept the client connections using accept() method of the ServerSocket to the wait for incoming client connections.
- Now, we can setup the input and output streams of the client socket and read and process the client data.
- Send the response to the client and close the sockets.
Implementation:
Java
import java.io.*;
import java.net.*;
public class Server {
public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException
{
// create a server socket on port number 9090
ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(9090);
System.out.println("Server is running and waiting for client connection...");
// Accept incoming client connection
Socket clientSocket = serverSocket.accept();
System.out.println("Client connected!");
// Setup input and output streams for communication with the client
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(clientSocket.getInputStream()));
PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(clientSocket.getOutputStream(), true);
// Read message from client
String message = in.readLine();
System.out.println("Client says: " + message);
// Send response to the client
out.println("Message received by the server.");
// Close the client socket
clientSocket.close();
// Close the server socket
serverSocket.close();
}
}
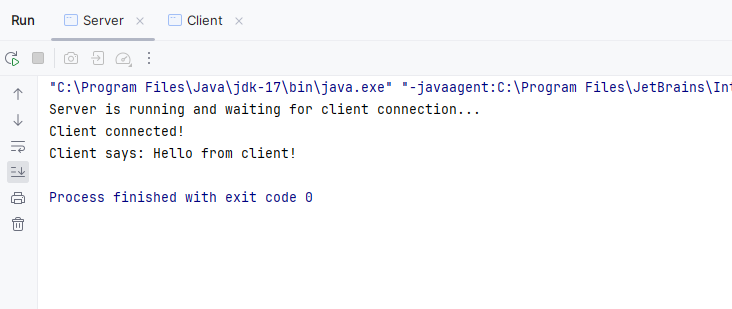
Output:
Before client connected to the server:
Server is running and waiting for client connection...
After client connected:
Step-by-Step implementation of Client-Side to Create Connection
- Create the Java class named as Client in that class write the main method of the program.
- Create the instance of the Socket and assign the port as 9090.
- Setup the input and output streams and send the data to the server.
- Setup the receive the response from the server.
- Close the socket.
Implementation:
Java
import java.io.*;
import java.net.*;
public class Client {
public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException
{
// create a socket to connect to the server running on localhost at port number 9090
Socket socket = new Socket("localhost", 9090);
// Setup output stream to send data to the server
PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(socket.getOutputStream(), true);
// Setup input stream to receive data from the server
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(socket.getInputStream()));
// Send message to the server
out.println("Hello from client!");
// Receive response from the server
String response = in.readLine();
System.out.println("Server says: " + response);
// Close the socket
socket.close();
}
}
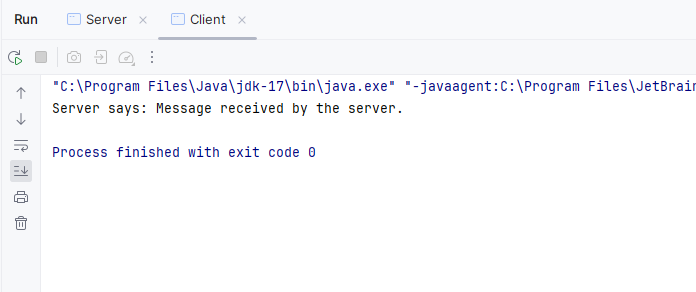
Output:
Below we can see the output received by the client in console.
In the above example, we have created a TCP connection between client and server by sending and receiving data between client and server on port 9090.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...