Combining Matrices in R
Last Updated :
07 Sep, 2021
Combining matrices involves the concatenation of two or more smaller matrices, either row or column wise to form a larger matrix. It is basically a data manipulation operation where the involved matrices must be of compatible sizes to execute the operation. Matrices can be combined either horizontally or vertically.

There are two ways of combining matrices in R:
- Column-wise combination
- Row-wise Combination
Column-Wise Combination
Column bind, cbind() function in R, is used to merge two data frames or matrices 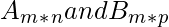 (n may or may not be equal to p) together by their columns. The matrices involved should have the same number of rows.
(n may or may not be equal to p) together by their columns. The matrices involved should have the same number of rows.

Example:
Python3
B = matrix(c(1, 2), nrow = 1, ncol = 2)
C = matrix(c(3, 4, 5), nrow = 1, ncol = 3)
print(B)
print(C)
print (cbind(B, C))
|
Output:
[,1] [,2]
[1,] 1 2
[,1] [,2] [,3]
[1,] 3 4 5
[,1] [,2] [,3] [,4] [,5]
[1,] 1 2 3 4 5
In the above code, the columns [3 4 5] of matrix C are added in order to the columns [1 2] of the matrix B. These changes are not made to any of the existing matrices.
Properties:
- The number of columns of the resultant matrix is the sum of the columns of the two matrices.
- Non-Commutative: The columns are merged in the order in which the parameters are specified in the function. Therefore, cbind(a, b) != cbind(b, a)
- Associative: cbind(cbind(a, b), c) = cbind(a, cbind(b, c))
Row-Wise Combination
Row bind, rbind() function in R, is used to merge two data frames or matrices 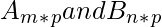 (m may or may not be equal to n), together by their rows. The matrices involved should have the same number of columns.
(m may or may not be equal to n), together by their rows. The matrices involved should have the same number of columns.

Example:
Python3
B = matrix(c(1, 2, 3), nrow = 1, ncol = 3)
C = matrix(c(4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9), nrow = 2, ncol = 3)
print(B)
print(C)
print (rbind(B, C))
|
Output:
[,1] [,2] [,3]
[1,] 1 2 3
[,1] [,2] [,3]
[1,] 4 6 8
[2,] 5 7 9
[,1] [,2] [,3]
[1,] 1 2 3
[2,] 4 6 8
[3,] 5 7 9
The rows [4 6 8] and [5 7 9] are appended to a row of matrix B[1 2 3] in order. No changes are made to the original matrices.
Properties:
- The number of rows of the resultant matrix is the sum of the rows of the two matrices.
- Non-Commutative: The rows are merged in the order in which the parameters are specified in the function. Therefore, rbind(a, b) != rbind(b, a)
- Associative: rbind(rbind(a, b), c) = rbind(a, rbind(b, c))
Time Complexity: O(m+n)
Space Complexity: O(m+n), where m is the total number of elements of first matrix and n of the second matrix.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...