Check if it is possible to move from X to Z using point Y
Last Updated :
24 Apr, 2023
Given three points X, Y, and Z of a 2D plane, the task is to check if it is possible to move from X to Z using point Y with at most one turn of 90 degrees. If possible return “YES” else return “NO”.
Note: Diagonal moves are not allowed, only vertical or horizontal moves are allowed.
Examples:
Input: X = {1, 3}, Y{4, 3}, Z = {4, 5}
Output: YES
Explanation:
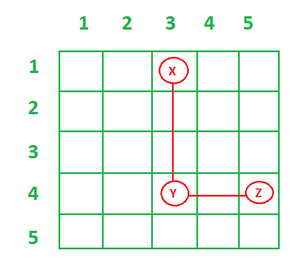
Explanation of first test case
Input: X = {1, 1}, Y = {2, 2}, Z = {3, 3}
Output: NO
Explanation: It can be verified that we can’t reach point Z from X using point Y.
Brute Force Approach :
We can check all possible paths from X to Z that involve at most one turn of 90 degrees at Y. We can start by moving from X to Y in a straight line, and then from Y to Z in a straight line, and check if this path is valid. If not, we can check all paths that involve one turn of 90 degrees at Y by considering all possible directions of the turn (left, right, up, or down), and checking if each path is valid. If we find a valid path, we can return “YES”, otherwise we return “NO”.
Below is the Implementation of the above approach :
C++
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
struct Point {
int x, y;
};
bool isOnLine(Point p1, Point p2) {
return (p1.x == p2.x || p1.y == p2.y);
}
string isPossible(Point X, Point Y, Point Z) {
if (isOnLine(X, Z)) {
return "YES";
}
for (int dx = -1; dx <= 1; dx++) {
for (int dy = -1; dy <= 1; dy++) {
if (dx == 0 || dy == 0 || dx == dy || dx == -dy) {
Point p = {Y.x + dx, Y.y + dy};
if (isOnLine(X, p) && isOnLine(p, Z)) {
return "YES";
}
}
}
}
return "NO";
}
int main() {
Point X = {1, 3};
Point Y = {4, 3};
Point Z = {4, 5};
cout << isPossible(X, Y, Z) << endl;
return 0;
}
|
Java
public class Main {
static class Point {
int x, y;
public Point(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
}
static boolean isOnLine(Point p1, Point p2) {
return (p1.x == p2.x || p1.y == p2.y);
}
static String isPossible(Point X, Point Y, Point Z) {
if (isOnLine(X, Z)) {
return "YES";
}
for (int dx = -1; dx <= 1; dx++) {
for (int dy = -1; dy <= 1; dy++) {
if (dx == 0 || dy == 0 || dx == dy || dx == -dy) {
Point p = new Point(Y.x + dx, Y.y + dy);
if (isOnLine(X, p) && isOnLine(p, Z)) {
return "YES";
}
}
}
}
return "NO";
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Point X = new Point(1, 3);
Point Y = new Point(4, 3);
Point Z = new Point(4, 5);
System.out.println(isPossible(X, Y, Z));
}
}
|
Python3
class Point:
def __init__(self, x, y):
self.x = x
self.y = y
def isOnLine(p1, p2):
return (p1.x == p2.x or p1.y == p2.y)
def isPossible(X, Y, Z):
if isOnLine(X, Z):
return "YES"
for dx in range(-1, 2):
for dy in range(-1, 2):
if dx == 0 or dy == 0 or dx == dy or dx == -dy:
p = Point(Y.x + dx, Y.y + dy)
if isOnLine(X, p) and isOnLine(p, Z):
return "YES"
return "NO"
X = Point(1, 3)
Y = Point(4, 3)
Z = Point(4, 5)
print(isPossible(X, Y, Z))
|
C#
using System;
public class Program {
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Point X = new Point(1, 3);
Point Y = new Point(4, 3);
Point Z = new Point(4, 5);
Console.WriteLine(
isPossible(X, Y, Z));
}
class Point {
public int x, y;
public Point(int x, int y)
{
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
}
static bool isOnLine(Point p1, Point p2)
{
return (p1.x == p2.x || p1.y == p2.y);
}
static string isPossible(Point X, Point Y, Point Z)
{
if (isOnLine(X, Z)) {
return "YES";
}
for (int dx = -1; dx <= 1; dx++) {
for (int dy = -1; dy <= 1; dy++) {
if (dx == 0 || dy == 0 || dx == dy
|| dx == -dy) {
Point p = new Point(Y.x + dx, Y.y + dy);
if (isOnLine(X, p) && isOnLine(p, Z)) {
return "YES";
}
}
}
}
return "NO";
}
}
|
Javascript
function Point(x, y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
function isOnLine(p1, p2) {
return (p1.x == p2.x || p1.y == p2.y);
}
function isPossible(X, Y, Z) {
if (isOnLine(X, Z)) {
return "YES";
}
for (let dx = -1; dx <= 1; dx++) {
for (let dy = -1; dy <= 1; dy++) {
if (dx == 0 || dy == 0 || dx == dy || dx == -dy) {
let p = new Point(Y.x + dx, Y.y + dy);
if (isOnLine(X, p) && isOnLine(p, Z)) {
return "YES";
}
}
}
}
return "NO";
}
let X = new Point(1, 3);
let Y = new Point(4, 3);
let Z = new Point(4, 5);
console.log(isPossible(X, Y, Z));
|
Output :
YES
Complexity Analysis :
The time complexity of this solution is O(1) for the initial check if X and Z are on the same line, and O(9) for the nested loops that consider all possible paths with one turn at Y. Therefore, the overall time complexity is O(1) + O(9) = O(1).
The auxiliary space of this solution is O(1) as it only uses a constant amount of additional space to store the three points and the intermediate point after the turn.
Approach: Implement the idea below to solve the problem:
The problem is observation based and can be solved via implementing those observations. For more clarification see the Concept of approach section below.
Concept of approach:
It should be noted that Reaching from X to Z is only possible when Y is an intermediate point between X and Z. We can move in the horizontal or vertical direction, So that either the Y should be in between x coordinate of X and Z or y coordinate of X and Z also. So the conditions at which reaching is possible are:
- x2 ? min(x1, x3) && x2 ? max(x1, x3) && (y2 == y1 || y2 == y3)
- y2 ? min(y1, y3) && y2 ? max(y1, y3) && (x2 == x1 || x2 == x3)
Where X = {x1, y1}, Y = {x2, y2}, Z = {x3, y3}. All other cases will have no path with at most one turn.
Follow the below steps to solve the problem:
- Check for the conditions:
- if (x2 ? min(x1, x3) && x2 ? max(x1, x3) && (y2 == y1 ||y2 == y3))
- else if (y2 ? min(y1, y3) && y2 ? max(y1, y3) && (x2 == x1 || x2 == x3)), Only at these conditions a path will exist.
- Otherwise, no path is possible.
Below is the Implementation of the above approach:
C++
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
long x1 = 1, x2 = 2, x3 = 2, y1 = 4, y2 = 4, y3 = 5;
long smallx = min(x1, x3);
long bigx = max(x1, x3);
long bigy = max(y1, y3);
long smally = min(y1, y3);
if (x2 >= smallx && x2 <= bigx
&& (y2 == y1 || y2 == y3)) {
cout << "YES" << endl;
}
else if (y2 >= smally && y2 <= bigy
&& (x2 == x1 || x2 == x3)) {
cout << "YES" << endl;
}
else {
cout << "NO" << endl;
}
return 0;
}
|
Java
public class GFG {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
long x1 = 1, x2 = 2, x3 = 2, y1 = 4, y2 = 4, y3 = 5;
long smallx = Math.min(x1, x3);
long bigx = Math.max(x1, x3);
long bigy = Math.max(y1, y3);
long smally = Math.min(y1, y3);
if (x2 >= smallx && x2 <= bigx
&& (y2 == y1 || y2 == y3)) {
System.out.println("YES");
}
else if (y2 >= smally && y2 <= bigy
&& (x2 == x1 || x2 == x3)) {
System.out.println("YES");
}
else
System.out.println("NO");
}
}
|
Python3
import sys
x1, x2, x3, y1, y2, y3 = 1, 2, 2, 4, 4, 5
smallx = min(x1, x3)
bigx = max(x1, x3)
bigy = max(y1, y3)
smally = min(y1, y3)
if x2 >= smallx and x2 <= bigx and (y2 == y1 or y2 == y3):
print("YES")
elif y2 >= smally and y2 <= bigy and (x2 == x1 or x2 == x3):
print("YES")
else:
print("NO")
|
C#
using System;
public class GFG {
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
long x1 = 1, x2 = 2, x3 = 2, y1 = 4, y2 = 4, y3 = 5;
long smallx = Math.Min(x1, x3);
long bigx = Math.Max(x1, x3);
long bigy = Math.Max(y1, y3);
long smally = Math.Min(y1, y3);
if (x2 >= smallx && x2 <= bigx
&& (y2 == y1 || y2 == y3)) {
Console.WriteLine("YES");
}
else if (y2 >= smally && y2 <= bigy
&& (x2 == x1 || x2 == x3)) {
Console.WriteLine("YES");
}
else {
Console.WriteLine("NO");
}
}
}
|
Javascript
let x1 = 1, x2 = 2, x3 = 2, y1 = 4, y2 = 4, y3 = 5;
let smallx = Math.min(x1, x3);
let bigx = Math.max(x1, x3);
let bigy = Math.max(y1, y3);
let smally = Math.min(y1, y3);
if (x2 >= smallx && x2 <= bigx
&& (y2 == y1 || y2 == y3)) {
console.log("YES");
}
else if (y2 >= smally && y2 <= bigy
&& (x2 == x1 || x2 == x3)) {
console.log("YES");
}
else {
console.log("NO");
}
|
Time Complexity: O(1)
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...