Check if a number is an Unusual Number or not
Last Updated :
10 Aug, 2021
Given a positive integer N. The task is to check if N is an unusual number or not. Print ‘YES’ if M is an unusual number else print ‘NO’.
Unusual number : In Mathematics, an unusual number is a natural number whose greatest prime factor is strictly greater than square root of n.
The first few unusual numbers are –
2, 3, 5, 6, 7, 10, 11, 13, 14, 15, 17, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 26, 28, 29, 31, 33, 34, 35, 37, 38, 39, 41, 42, 43, 44, 46, 47, 51
Examples:
Input : N = 14
Output : YES
Explanation : 7 is largest prime factor of 14
and 7 is strictly greater than square root of 14
Input : N = 16
Output : NO
Explanation : 2 is largest prime factor of 16
and 2 is less than square root of 16 ( i.e 4 ).
Approach :
- Find the largest prime factor of the given number N. To find the largest prime factor of N refer this .
- Check if the largest prime factor of N is strictly greater than square root of N.
- If ‘YES’ then N is an Unusual number otherwise Not.
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int largestPrimeFactor(int n)
{
int max = -1;
while (n % 2 == 0) {
max = 2;
n >>= 1;
}
for (int i = 3; i <= sqrt(n); i += 2) {
while (n % i == 0) {
max = i;
n = n / i;
}
}
if (n > 2)
max = n;
return max;
}
bool checkUnusual(int n)
{
int factor = largestPrimeFactor(n);
if (factor > sqrt(n)) {
return true;
}
else {
return false;
}
}
int main()
{
int n = 14;
if (checkUnusual(n)) {
cout << "YES"
<< "\n";
}
else {
cout << "NO"
<< "\n";
}
return 0;
}
|
Java
class GFG {
static int largestPrimeFactor(int n)
{
int max = -1;
while (n % 2 == 0) {
max = 2;
n >>= 1;
}
for (int i = 3; i <= Math.sqrt(n); i += 2) {
while (n % i == 0) {
max = i;
n = n / i;
}
}
if (n > 2)
max = n;
return max;
}
static boolean checkUnusual(int n)
{
int factor = largestPrimeFactor(n);
if (factor > Math.sqrt(n)) {
return true;
}
else {
return false;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int n = 14;
if (checkUnusual(n)) {
System.out.println("YES");
}
else {
System.out.println("NO");
}
}
}
|
Python3
from math import sqrt
def largestPrimeFactor(n):
max = -1
while n % 2 == 0:
max = 2;
n >>= 1;
for i in range(3,int(sqrt(n))+1,2):
while n % i == 0:
max = i;
n = n / i;
if n > 2:
max = n
return max
def checkUnusual(n):
factor = largestPrimeFactor(n)
if factor > sqrt(n):
return True
else :
return False
if __name__ == '__main__':
n = 14
if checkUnusual(n):
print("YES")
else:
print("NO")
|
C#
using System;
class GFG {
static int largestPrimeFactor(int n)
{
int max = -1;
while (n % 2 == 0) {
max = 2;
n >>= 1;
}
for (int i = 3; i <= Math.Sqrt(n); i += 2) {
while (n % i == 0) {
max = i;
n = n / i;
}
}
if (n > 2)
max = n;
return max;
}
static bool checkUnusual(int n)
{
int factor = largestPrimeFactor(n);
if (factor > Math.Sqrt(n)) {
return true;
}
else {
return false;
}
}
public static void Main()
{
int n = 14;
if (checkUnusual(n)) {
Console.WriteLine("YES");
}
else {
Console.WriteLine("NO");
}
}
}
|
PHP
<?php
function largestPrimeFactor($n)
{
$max = -1;
while ($n % 2 == 0) {
$max = 2;
$n >>= 1;
}
for ($i = 3; $i <= sqrt($n); $i += 2) {
while ($n % $i == 0) {
$max = $i;
$n = $n / $i;
}
}
if ($n > 2)
$max = $n;
return $max;
}
function checkUnusual($n)
{
$factor = largestPrimeFactor($n);
if ($factor > sqrt($n)) {
return true;
}
else {
return false;
}
}
$n = 14;
if (checkUnusual($n)) {
echo "YES"."\n";
}
else {
echo "NO"."\n";
}
?>
|
Javascript
<script>
function largestPrimeFactor( n)
{
var max = -1;
while (n % 2 == 0) {
max = 2;
n >>= 1;
}
for (var i = 3; i <= Math.sqrt(n); i += 2) {
while (n % i == 0) {
max = i;
n = n / i;
}
}
if (n > 2)
max = n;
return max;
}
function checkUnusual(n)
{
var factor = largestPrimeFactor(n);
if (factor > Math.sqrt(n)) {
return true;
}
else {
return false;
}
}
var n = 14;
if (checkUnusual(n)) {
document.write("YES");
}
else {
document.write("NO");
}
</script>
|
Output: YES
Time complexity:

Auxiliary space:
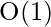
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...