C# | Methods
Last Updated :
16 Aug, 2021
Methods are generally the block of codes or statements in a program that gives the user the ability to reuse the same code which ultimately saves the excessive use of memory, acts as a time saver and more importantly, it provides a better readability of code. So basically, a method is a collection of statements that perform some specific task and return the result to the caller. A method can also perform some specific task without returning anything.
Example :
// Method Name --> GetCircleArea()
// Return Type ---> double
static double GetCircleArea(double radius)
{
const float pi = 3.14F;
double area = pi * radius * radius;
return area;
}
Method Declaration
Method declaration means the way to construct method including its naming.
Syntax :
<Access_Modifier> <return_type> <method_name>([<param_list>])
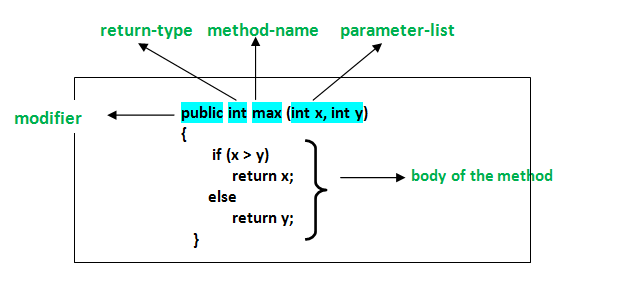
In C# a method declaration consists of the following components as follows :
- Modifier : It defines access type of the method i.e. from where it can be accessed in your application. In C# there are Public, Protected, Private access modifiers.
- Name of the Method : It describes the name of the user defined method by which the user calls it or refer it. Eg. GetName()
- Return type: It defines the data type returned by the method. It depends upon user as it may also return void value i.e return nothing
- Body of the Method : It refers to the line of code of tasks to be performed by the method during its execution. It is enclosed between braces.
- Parameter list : Comma separated list of the input parameters are defined, preceded with their data type, within the enclosed parenthesis. If there are no parameters, then empty parentheses () have to use out.
Method Signature : Method Signature is defined by mainly two parameters(number of parameters, type of the parameters and order of the parameters), One of them is Method Name and second one is its Parameter list.
Method Naming : Name of a method or a function in any programming language whether in C++ or Java or C# holds great importance and is mainly used in order to call that method for its execution. For example, findSum, computeMax, setX and getX etc. There are certain pre-defined rules for naming methods which a user should follow :
- The method name must be some kind of Noun or a verb.
- It’s naming should be done in such a way that it must describe the purpose of that method.
- The first letter of the method name can be either a small letter or a Capital letter, however, it is recommended to use the capital one.
These rules are not mandatory, but recommendable. Generally, a method has a unique name within the class in which it is defined but sometime a method might have the same name as other method names within the same class as method overloading is allowed in C#.
The Method Body : As discussed above the body of the method consists of statements of code which a user wants to perform. After the method has been declared, it is dependent on the user whether to define its implementation or not. Not writing any implementation, makes the method not to perform any task. However, when the user wants to perform certain tasks using method then it must write the statements for execution in the body of the method. The below syntax describes the basic structure of the method body :
Syntax :
<return_type> <method_name>(<parameter_list>)
{
// Implementation of the method code goes here.....
}
Method Calling
Method Invocation or Method Calling is done when the user wants to execute the method. The method needs to be called for using its functionality. A method returns to the code that invoked it when:
- It completes all the statements in the method
- It reaches a return statement
- Throws an exception
Example : In the code below, a method named Sum() is called.
CSHARP
using System;
namespace ConsoleApplication1 {
class Geeks {
static int Sum(int x, int y)
{
int a = x;
int b = y;
int result = a + b;
return result;
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int a = 12;
int b = 23;
int c = Sum(a, b);
Console.WriteLine("The Value of the sum is " + c);
}
}
}
|
Output :
The Value of the sum is 35
Method Parameters
There might be certain situations the user want to execute a method but sometimes that method requires some value inputs in order to execute and complete its tasks. These input values are known as Parameters in a computer language terms. Now, these parameters can be either int, long or float or double or char. However, it depends upon the user requirements. The methods in C# can be classified into different categories based on return type as well as input parameters.
- Example Program Without Parameters & Without Return Type
CSHARP
using System;
namespace ConsoleApplication2 {
class Geeks {
static void PrintSentence()
{
Console.WriteLine("No parameters and return type void");
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
PrintSentence();
}
}
}
|
No parameters and return type void
- Example Program Without Parameters & With Return Value Type
CSHARP
using System;
namespace ConsoleApplication3 {
class Geeks {
static int sum()
{
int a = 78, b = 70, add;
add = a + b;
return add;
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int getresult = sum();
Console.WriteLine(getresult);
}
}
}
|
148
- Example Program With Parameters & Without Return Value Type
CSHARP
using System;
namespace ConsoleApplication3 {
class Geeks {
static void perimeter(int p)
{
Console.WriteLine("Perimeter of the Square is " + 4 * p);
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int p = 5;
perimeter(p);
}
}
}
|
Perimeter of the Square is 20
- Example Program With Parameters & With Return Value Type
CSHARP
using System;
namespace ConsoleApplication4 {
class Geeks {
static int factorial(int n)
{
int f = 1;
for (int i = 1; i<= n; i++)
{
f = f * i;
}
return f;
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int p = 4;
Console.WriteLine("Factorial is : " + factorial(p));
}
}
}
|
Factorial is : 24
Advantages of using the Methods :
There are many advantages of using methods. Some of them are listed below:
- It makes the program well structured.
- Methods enhance the readability of the code.
- It provides an effective way for the user to reuse the existing code.
- It optimizes the execution time and memory space.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...