Modulation is a process in which a low-frequency message signal is combined or imposed with a high-frequency carrier signal. It can also be defined as the process through which a message or baseband signal is transmitted with the help of a carrier signal to the receiver end. It enhances the signal strength and helps to transmit signal for a large distance range. It also helps to reduce the size of the antenna. Modulation can be Digital modulation or Analog modulation. There are various types of modulation that change the properties of carrier waves. Modulation can be Amplitude Modulation or Angle Modulation.
In Amplitude Modulation, the amplitude of the carrier signal is changed or modulated with the message signal While the angle that has phase and frequency are constant. In Angle Modulation angle that is, the phase and frequency of the carrier signal are changed or modulated with respect to the message signal, and the amplitude is kept constant.
In this article, we will get to know about Angle Modulation, Types of Angle Modulation, the Relation between FM and PM, Advantages and Disadvantages of Phase and Frequency Modulation, and its application.
Angle Modulation
Angle Modulation is a modulation process in which the angle of the carrier wave or signal is changed with respect to the message signal or baseband signal. The angle of the signal is a combination of phase and frequency therefore Angle Modulation is a process in which the frequency or phase of the carrier wave is changed with respect to the message signal while keeping the amplitude constant. Angle modulation occurs due to the Time-varying phase or Time-varying Frequency.
Mathematical Representation of Angle Modulation
Unmodulated carrier signal c(t) is expressed as

 c t +
c t + 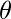 0 ….(ii)
0 ….(ii)
differentiating both side with respect to t
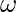 c =
c =  ….(iii)
….(iii)
Here A = Amplitude of carrier , 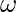 c = Carrier Frequency ,
c = Carrier Frequency , 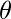 0 = phase angle ,
0 = phase angle , 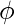 = total angle
= total angle
From eq – (iii) dϕ/dt is constant for unmodulated carrier , but it may change with time . Therefore angular velocity will also change with respect with time and this time-dependent angular velocity is called Instantaneous Angular velocity denoted by 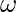 i and equation (iii) become
i and equation (iii) become
 i ….(iv)
i ….(iv)
 i dt ….(v)
i dt ….(v)
equation (v) represent Angle Modulation of 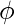 is changed according to instantaneous angular frequency of message signal.
is changed according to instantaneous angular frequency of message signal.
Types of Angle Modulation
Angle consist of Phase and Frequency so Angle Modulation is divided into
- Frequency Modulation
- Phase Modulation
Frequency Modulation
Frequency Modulation is process in which frequency of carrier signal is varied with respect to amplitude of message signal. In this amplitude and phase of carrier signal do not change they remain constant . It is process in which instantaneous frequency change with respect to message signal . As the amplitude of baseband or message signal increase frequency of modulated signal also increases and as amplitude of baseband signal or message signal decreases frequency of modulated signal also decreases.

Frequency Modulation
Mathematical Representation of Frequency Modulation
Frequency modulated signal is expressed as
s(t)=A cos ϕi(t) …(vi)
here s(t) = standard frequency modulated signal ; ϕi = instantaneous phase angle of modulated signal
The instantaneous angular velocity or frequency is represented as
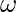 i =
i = 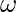 c + kf m(t) ….(vii)
c + kf m(t) ….(vii)
here kf = frequency sensitivity ; m(t) = message signal ; 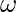 c = carrier frequency or velocity
c = carrier frequency or velocity
based on equation (v) we can write
ϕi = ∫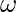 i dt …(viii)
i dt …(viii)
substituting value of 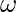 i from equation (vii) in equation (viii)
i from equation (vii) in equation (viii)
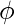 i =∫[
i =∫[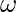 c + kf m(t) ] dt =
c + kf m(t) ] dt = 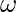 c t + kf ∫ m(t) dt …(ix)
c t + kf ∫ m(t) dt …(ix)
substituting value of 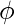 i from equation (ix) to s(t) in equation (vi)
i from equation (ix) to s(t) in equation (vi)
s(t) =A cos [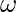 ct + kf ∫ m(t) dt] ….(x)
ct + kf ∫ m(t) dt] ….(x)
Equation (x) is expression of Frequency Modulated wave or signal.
Types of Frequency Modulation
Frequency Modulation is classified as following two types
- Narrow Band Frequency Modulation
- Wide Band Frequency Modulation
Narrow Band Frequency Modulation
Frequency Modulation having modulation index (β) less than one is called Narrowband FM. It have small bandwidth and occupies only small part of frequency modulation . Spectrum of Narrowband FM consist of carrier , upper sideband and lower sideband. It is mostly used in mobile communication .
Wide Band Frequency Modulation
Frequency Modulation in which value of modulation index (β) grater than one is called Wideband FM . It have infinite bandwidth . It use wide band of frequencies and occupies large part in frequency modulation . Spectrum of this FM consist of carrier and infinite number of sideband .It is mostly used in broadcasting of signal .
Phase Modulation
Phase Modulation can be defined as the process in which phase of carrier signal is changed with respect to amplitude of baseband signal or message signal .In this modulation frequency and amplitude of carrier signal do not change they remain constant .The phase angle of carrier signal change according to amplitude of message signal when amplitude is positive phase angle is in one direction and phase angle is in opposite direction when amplitude is negative.

Phase Modulation
Mathematical Representation of Phase Modulation
We have unmodulated carrier signal represented by c(t) as in equation (i)
Ignoring θ0 in equation (ii) we get
 ct …(xi)
ct …(xi)
Now as in phase modulation phase (ϕ) of carrier signal is changed according to message signal m(t)
now let ϕi be instantaneous phase angle which can be given as
ϕi = 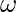 ct + kp m(t) …(xii)
ct + kp m(t) …(xii)
here kp is phase sensitivity and m(t) is message signal
Phase modulated signal is expressed as
s(t)=A cos ϕi(t) …(xiii)
putting value of ϕi from equation (xii) to equation (xiii)
s(t) = A ct + kp m(t)] …(xiv)
ct + kp m(t)] …(xiv)
Equation (xiv) is expression of Phase Modulated Signal.
Relationship Between Frequency Modulation (FM) and Phase Modulation (PM)
Angle of carrier signal is combination of phase and frequency . A change in phase results in a change in the phase of the signal, and a change in phase results in a frequency change of the modulated signal. There is a nonlinear relationship between the phase and frequency of the signal.
Phase Modulation of m(t) = Frequency Modulation of d/dt m(t)
Frequency Modulation of m(t) = Phase Modulation of ∫ m(t)dt

Relation Between FM and PM
In frequency Modulation of signal , modulating signal m(t) is passed through integrator and then phase modulation is done in signal .
In phase Modulation of signal , Modulating signal m(t) is passed through differentiator and then frequency modulation of signal is done.
Advantages of Frequency Modulation
Following are some of the advantages of Frequency Modulation
- Signal Quality is enhanced .
- Signal to Noise Ratio is large .
- For transmission of signal it does not required any extra component like amplifier , repeater .
- Less noise susceptible .
- Good transmission rate of signal .
Advantages of Phase Modulation
Following are some of the advantages of Phase Modulation
- Less energy consumption .
- Fastest Modulation Technique .
- It is also appropriate for digital Modulation .
- Less signal Fading .
- Easy to convert into Frequency Modulation .
Disadvantages of Frequency Modulation
Following are some of the disadvantages of Frequency Modulation
- Transmitter and Receiver should be in same channel .
- Not suitable for large distance coverage .
- Require wide range of frequency .
- It is costly .
Disadvantages of Phase Modulation
Following are some of the disadvantages of Phase Modulation
- Low noise immunity .
- Require extra equipment for transmission .
- Low signal to noise Ratio .
Applications of Frequency Modulation
Following are some of the applications of Frequency Modulation
- Used in Radio .
- used in Magnetic Tape storage .
- Used in broadcasting of signal in TV .
- Used in Satellite .
- Used in video cassette recorder .
Applications of Phase Modulation
Following are some of the applications of Phase Modulation
- Used in Radar system .
- Used in GPS system .
- Used in sound synthesis.
- Used in Optical Communication .
Conclusion
Modulation plays a important role in communication engineering . Modulation can be either Amplitude Modulation or Angle Modulation . In Angle Modulation angle of carrier signal is changed .Signal angle is composition of phase and frequency so Phase Modulation and Frequency Modulation leads to Angle Modulation . Angle Modulation plays a important role in communication system its main advantage is that it provide large signal to noise ration and is less susceptible to noise . From above article we got to know about what is Angle Modulation , Frequency Modulation and Phase Modulation along with its mathematical representation , advantages , disadvantages and their applications .
Angle Modulation – FAQs
What do you mean by Demodulation of Signal ?
Demodulation is reverse or opposite process of Modulation . It means to extract or take original information from modulated signal .It can be defined as separating Message Signal from Carrier signal.
What do you mean by carrier signal ?
A carrier signal is signal which do not have any information but have some phase , frequency and amplitude which is modulated with baseband or message signal.
What is PCM ?
PCM stands for Pulse Code Modulation . Used to convert analog signal to digital signal using sampling .
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...