AUB is defined by the elements that belong to either set A or set B. The union operation i.e., A∪B is one of the important operations in sets. This article explores the A∪B formula, the number of elements in A∪B formula, A∪B formula in probability, and the complement of the A union B formula.

AUB Formula
We will also solve some examples and answer some FAQs related to the A∪B formula. Let’s start our learning on the topic “A∪B formula”.
What is A Union B?
A union B represented as A∪B is the set with elements that belong to either of the sets. The union is represented by the symbol ∪. If A and B are two sets the union of A and B is denoted as A∪B. Union is a set operation that unites the elements of two or more sets.
Union of two sets is performed by combining the elements of the two sets and taking common sets only once.
A∪B formula is defined as the elements that either belong to set A or set B. The combination of the elements of A or B gives the A∪B formula. The set builder form representation of the A∪B formula is:
A ∪ B = {x : x ∈ A or x ∈ B}
Venn Diagram for AUB Formula
The Venn diagram for AUB formula is given below. In the below diagram, the pink region shows the union of two sets A and B.

Number of elements in the A∪B is defined as the sum of the number of elements in A and B minus number of elements in A∩B. The formula for the number of elements in A∪B formula is given by:
n(A∪B) = n(A) + n(B) – n(A∩B)
where,
- n(A∪B) is number of elements in A∪B
- n(A) is number of elements in A
- n(B) is number of elements in B
- n(A∩B) is number of elements in A∩B
A∪B formula in Probability is used to find the probability of A∪B with the help of the probability of the events A, B and A∩B respectively. There are two A∪B formula in probability one for the mutually exclusive events and other for non-mutually exclusive events.
A∪B Formula for Non-Mutually Exclusive Events
The A∪B formula for non-mutually exclusive events uses the probabilities of A, B and A∩B.
P(AUB) = P(A) + P(B) – P(A∩B)
where,
- P(A∪B) is probability of A∪B
- P(A) is probability of A
- P(B) is probability of B
- P(A∩B) is probability of A∩B
A∪B Formula for Mutually Exclusive Events
The A∪B formula for mutually exclusive events uses the probabilities of A and B as for mutually exclusive events A∩B =0.
P(A∪B) = P(A) + P(B)
where,
- P(A∪B) is probability of A∪B
- P(A) is probability of A
- P(B) is probability of B
The complement of A∪B formula is defined as the intersection of complement of A and complement of B. This is called De Morgan’s law.
(A ∪ B)’ = A’ ∩ B’
(A ∪ B)’ = {x: x ∉ (A∪B)’}
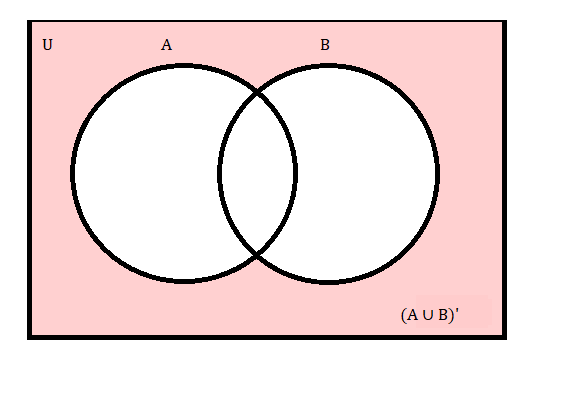
Venn Diagram for Complement of A∪B Formula
Complement of A union B is the region except the region of A union B. The Venn diagram for complement of A∪B is given below. The pink region shows the region of compliment of A union B.
What is A Union B Union C?
The A union B union C is defined as the set of elements that belongs to set A or set B or set C. It is represented as A ∪ B ∪ C. The set builder form of A ∪ B ∪ C is:
A ∪ B ∪ C = {x: x∈ A or x ∈ B or x ∈ C}
A Union B Union C Formula
The formula for finding number of elements in A U B U C set is given by:
n(A ∪ B ∪ C) = n(A) + n(B) + n(C) – n(A∩B) – n(B∩C) – n(A∩C) + n(A∩B∩C)
where,
- n(A∪B∪C) is number of elements in A∪B∪C
- n(A) is number of elements in A
- n(B) is number of elements in B
- n(A∩B) is number of elements in A∩B
- n(B∩C) is number of elements in B∩C
- n(A∩C) is number of elements in A∩C
- n(A∩B∩C) is number of elements in A∩B∩C
A Union B Union C Venn Diagram
The Venn diagram for A Union B Union C is given below. All the three circles consisting of white region shows A union B union C.

What is A union B intersection C?
The A union B intersection C is defined as the set of elements that belongs to either A or B∩C. The set builder form of A union B intersection C is:
A ∪ (B ∩ C) = {x: x ∈ A or x ∈ (B ∩C)}
A union B intersection C Formula
The formula for the A union B intersection C is given by:
A ∪ (B ∩ C) = (A ∪ B) ∩ (A ∪ C)
A union B intersection C Venn Diagram
The Venn diagram for A union B intersection C is given below. The region colored by blue colour shows A union B intersection C.

Also Check
Example 1. Find A∪B using A∪B formula where, A = {9, 22} and B = {10, 16}.
Solution:
Given
A = {9, 22} and B = {10, 16}
A∪B = {9, 10, 16, 22}
Example 2. Find the cardinality of X∪Y where, X = {x, y} and Y = {x, z}.
Solution:
Given
X = {x, y} and Y = {x, z}
X ∩ Y = {x}
n(X) = 2 and n(Y) = 2
n(X ∩ Y) = 1
By number of elements in AUB formula
n(X∪Y) = n(X) + n(Y) – n(X ∩ Y)
n(X∪Y) = 2 + 2 – 1
n(X∪Y) = 3
Example 3. If the number of elements in P, Q and P∩Q is 10, 12 and 5 respectively, then find the number of elements in P∪Q.
Solution:
Given
n(P) = 10 and n(Q) = 12
n(P ∩ Q) = 5
By number of elements in AUB formula
n(P∪Q) = n(P) + n(Q) – n(P ∩ Q)
n(P∪Q) = 10 + 12 – 5
n(P∪Q) = 17
Example 4. If the probability of event A is 0.7, probability of event B is 0.9 and the probability of event A∩B is 0.8 then find probability of A∪B.
Solution:
Given
Probability of event A = 0.7
Probability of event B = 0.9
Probability of event A∩B = 0.8
P(A∪B) = P(A) + P(B) – P(A∩B)
P(A∪B) = 0.7 + 0.9 – 0.8
P(A∪B) = 0.8
Q1. Find A∪B using A∪B formula where, A = {1, 2} and B = {5, 6}.
Q2. Find the cardinality of P∪Q where, P = {a, b, c} and Q = {e, f}
Q3. If the number of elements in A, B and A∩B is 3, 4 and 1 respectively, then find the number of elements in A∪B.
Q4. If the probability of event A is 0.5, probability of event B is 0.7 and the probability of event A∩B is 0.2 then find probability of A∪B.
What is A∪B Formula in Mathematics?
The A∪B formula in Mathematics is given by A∪B = {x : x ∈ A or x ∈ B}
Is AUB Commutative?
Yes, AUB is commutative.
What is the cardinality formula for A∪B?
The cardinality formula for A∪B is:
n(A∪B) = n(A) + n(B) – n(A ∩ B)
where,
- n(A∪B) is number of elements in A∪B
- n(A) is number of elements in A
- n(B) is number of elements in B
- n(A∩B) is number of elements in A∩B
Define A∪B in Mathematics
The union of two sets A∪B is defined as the set containing elements of set A or Set B or Math. A union B is given as A∪B = {x: x ∈ A or x ∈ B}
What is the formula for (A∪B)’?
The formula for (A∪B)’ is given by: (A∪B)’ = A’ ∩ B’
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...