8085 program for bubble sort
Last Updated :
25 Apr, 2023
Prerequisite – Bubble Sort
Problem – Write an assembly language program in 8085 microprocessor to sort a given list of n numbers using Bubble Sort.
Example –
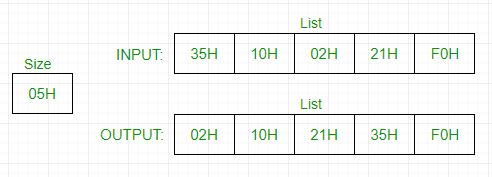
Assumption – Size of list is stored at 2040H and list of numbers from 2041H onwards.
Algorithm –
- Load size of list in C register and set D register to be 0
- Decrement C as for n elements n-1 comparisons occur
- Load the starting element of the list in Accumulator
- Compare Accumulator and next element
- If accumulator is less than or equal to the next element jump to step 8
- Swap the two elements
- Set D register to 1
- Decrement C
- If C>0 take next element in Accumulator and go to point 4
- If D=0, this means in the iteration, no exchange takes place consequently we know that it won’t take place in further iterations so the loop in exited and program is stopped
- Jump to step 1 for further iterations
Program –
| Address |
Label |
Instruction |
Comment |
| 2000H |
START |
LXI H, 2040H |
Load size of array |
| 2003H |
|
MVI D, 00H |
Clear D register to set up a flag |
| 2005H |
|
MOV C, M |
Set C register with number of elements in list |
| 2006H |
|
DCR C |
Decrement C |
| 2007H |
|
INX H |
Increment memory to access list |
| 2008H |
CHECK |
MOV A, M |
Retrieve list element in Accumulator |
| 2009H |
|
INX H |
Increment memory to access next element |
| 200AH |
|
CMP M |
Compare Accumulator with next element |
| 200BH |
|
JC NEXTBYTE |
If accumulator is less then jump to NEXTBYTE |
| 200EH |
|
JZ NEXTBYTE |
If accumulator is equal then jump to NEXTBYTE |
| 2011H |
|
MOV B, M |
Swap the two elements |
| 2012H |
|
MOV M, A |
|
| 2013H |
|
DCX H |
|
| 2014H |
|
MOV M, B |
|
| 2015H |
|
INX H |
|
| 2016H |
|
MVI D, 01H |
If exchange occurs save 01 in D register |
| 2018H |
NEXTBYTE |
DCR C |
Decrement C for next iteration |
| 2019H |
|
JNZ CHECK |
Jump to CHECK if C>0 |
| 201CH |
|
MOV A, D |
Transfer contents of D to Accumulator |
| 201DH |
|
CPI 01H |
Compare accumulator contents with 01H |
| 201FH |
|
JZ START |
Jump to START if D=01H |
| 2022H |
|
HLT |
HALT |
Explanation-
Bubble sort is a simple sorting algorithm that repeatedly steps through the list to be sorted, compares each adjacent pair of elements, and swaps them if they are in the wrong order. The algorithm gets its name from the way smaller elements “bubble” to the top of the list. Here’s an 8085 assembly language program for bubble sort
Advantages of bubble sort:
- Bubble sort is easy to understand and implement, even in assembly language.
- Bubble sort is efficient for small lists and nearly sorted lists.
- Bubble sort has a simple logic that is easy to debug and modify.
Disadvantages of bubble sort:
- bubble sort has a worst-case and average-case time complexity of O(n^2), which makes it inefficient for large lists.
- Bubble sort takes more time to execute compared to other sorting algorithms like Quick sort and Merge sort.
- Bubble sort does not work efficiently for lists with random or unsorted elements.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...