Deletion in Linked List
Last Updated :
22 Jun, 2023
We have discussed Linked List Introduction and Linked List Insertion in previous posts on a singly linked list.
Let us formulate the problem statement to understand the deletion process.
Delete from a Linked List:-
You can delete an element in a list from:
1) Delete from Beginning:
Point head to the next node i.e. second node
temp = head
head = head->next
Make sure to free unused memory
free(temp); or delete temp;
2) Delete from End:
Point head to the previous element i.e. last second element
Change next pointer to null
struct node *end = head;
struct node *prev = NULL;
while(end->next)
{
prev = end;
end = end->next;
}
prev->next = NULL;
Make sure to free unused memory
free(end); or delete end;
3) Delete from Middle:
Keeps track of pointer before node to delete and pointer to node to delete
temp = head;
prev = head;
for(int i = 0; i < position; i++)
{
if(i == 0 && position == 1)
head = head->next;
free(temp)
else
{
if (i == position - 1 && temp)
{
prev->next = temp->next;
free(temp);
}
else
{
prev = temp;
if(prev == NULL) // position was greater than number of nodes in the list
break;
temp = temp->next;
}
}
}
Iterative Method to delete an element from the linked list:
To delete a node from the linked list, we need to do the following steps:
- Find the previous node of the node to be deleted.
- Change the next of the previous node.
- Free memory for the node to be deleted.
Below is the implementation to delete a node from the list at some position:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct Node {
int number;
Node* next;
};
void Push(Node** head, int A)
{
Node* n = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
n->number = A;
n->next = *head;
*head = n;
}
void deleteN(Node** head, int position)
{
Node* temp;
Node* prev;
temp = *head;
prev = *head;
for (int i = 0; i < position; i++) {
if (i == 0 && position == 1) {
*head = (*head)->next;
free(temp);
}
else {
if (i == position - 1 && temp) {
prev->next = temp->next;
free(temp);
}
else {
prev = temp;
if (prev == NULL)
break;
temp = temp->next;
}
}
}
}
void printList(Node* head)
{
while (head) {
if (head->next == NULL)
cout << "[" << head->number << "] "
<< "[" << head << "]->"
<< "(nil)" << endl;
else
cout << "[" << head->number << "] "
<< "[" << head << "]->" << head->next
<< endl;
head = head->next;
}
cout << endl << endl;
}
int main()
{
Node* list = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
list->next = NULL;
Push(&list, 1);
Push(&list, 2);
Push(&list, 3);
printList(list);
deleteN(&list, 1);
printList(list);
return 0;
}
|
C
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef struct Node {
int number;
struct Node* next;
} Node;
void Push(Node** head, int A)
{
Node* n = malloc(sizeof(Node));
n->number = A;
n->next = *head;
*head = n;
}
void deleteN(Node** head, int position)
{
Node* temp;
Node* prev;
temp = *head;
prev = *head;
for (int i = 0; i < position; i++) {
if (i == 0 && position == 1) {
*head = (*head)->next;
free(temp);
}
else {
if (i == position - 1 && temp) {
prev->next = temp->next;
free(temp);
}
else {
prev = temp;
if (prev == NULL)
break;
temp = temp->next;
}
}
}
}
void printList(Node* head)
{
while (head) {
printf("[%i] [%p]->%p\n", head->number, head,
head->next);
head = head->next;
}
printf("\n\n");
}
int main()
{
Node* list = malloc(sizeof(Node));
list->next = NULL;
Push(&list, 1);
Push(&list, 2);
Push(&list, 3);
printList(list);
deleteN(&list, 1);
printList(list);
return 0;
}
|
Java
class Node {
int number;
Node next;
}
class Main {
public static Node push(Node head, int A) {
Node n = new Node();
n.number = A;
n.next = head;
head = n;
return head;
}
public static Node deleteN(Node head, int position) {
Node temp = head;
Node prev = head;
for (int i = 0; i < position; i++) {
if (i == 0 && position == 1) {
head = head.next;
} else {
if (i == position - 1 && temp != null) {
prev.next = temp.next;
} else {
prev = temp;
if (prev == null)
break;
temp = temp.next;
}
}
}
return head;
}
public static void printList(Node head) {
while (head != null) {
if (head.next == null) {
System.out.println("[" + head.number + "] [" + head + "]->" + "(null)");
} else {
System.out.println("[" + head.number + "] [" + head + "]->" + head.next);
}
head = head.next;
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Node list = new Node();
list.next = null;
list = push(list, 1);
list = push(list, 2);
list = push(list, 3);
printList(list);
list = deleteN(list, 1);
printList(list);
}
}
|
Python3
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.number = data
self.next = None
def push(head, A):
n = Node(A)
n.number = A
n.next = head
head = n
return head
def deleteN(head, position):
temp = head
prev = head
for i in range(0, position):
if i == 0 and position == 1:
head = head.next
else:
if i == position-1 and temp is not None:
prev.next = temp.next
else:
prev = temp
if prev is None:
break
temp = temp.next
return head
def printList(head):
while(head):
if head.next == None:
print("[", head.number, "] ", "[", hex(id(head)), "]->", "nil")
else:
print("[", head.number, "] ", "[", hex(
id(head)), "]->", hex(id(head.next)))
head = head.next
print("")
print("")
head = Node(0)
head = push(head, 1)
head = push(head, 2)
head = push(head, 3)
printList(head)
head = deleteN(head, 1)
printList(head)
|
Javascript
class Node {
constructor(number) {
this.number = number;
this.next = null;
}
}
function push(head, number) {
const node = new Node(number);
node.next = head;
head = node;
return head;
}
function deleteN(head, position) {
let temp = head;
let prev = head;
for (let i = 0; i < position; i++) {
if (i === 0 && position === 1) {
head = head.next;
temp = null;
} else {
if (i === position - 1 && temp) {
prev.next = temp.next;
temp = null;
} else {
prev = temp;
if (prev === null) break;
temp = temp.next;
}
}
}
return head;
}
function printList(head) {
while (head) {
if (head.next === null)
console.log(`[${head.number}] [${head}]->(nil)`);
else console.log(`[${head.number}] [${head}]->${head.next}`);
head = head.next;
}
console.log('\n');
}
let list = new Node(0);
list.next = null;
list = push(list, 1);
list = push(list, 2);
list = push(list, 3);
printList(list);
list = deleteN(list, 1);
printList(list);
|
C#
using System;
public class Node {
public int number;
public Node next;
}
public class Program {
public static void Push(ref Node head, int A)
{
Node n = new Node();
n.number = A;
n.next = head;
head = n;
}
public static void deleteN(ref Node head, int position)
{
Node temp = head;
Node prev = head;
for (int i = 0; i < position; i++) {
if (i == 0 && position == 1) {
head = head.next;
temp = null;
}
else {
if (i == position - 1 && temp != null) {
prev.next = temp.next;
temp = null;
}
else {
prev = temp;
if (prev == null) {
break;
}
temp = temp.next;
}
}
}
}
public static void printList(Node head)
{
while (head != null) {
if (head.next == null) {
Console.WriteLine("[" + head.number + "] "
+ "[" + head + "]->"
+ "(nil)");
}
else {
Console.WriteLine("[" + head.number + "] "
+ "[" + head + "]->"
+ head.next);
}
head = head.next;
}
Console.WriteLine("\n");
}
public static void Main()
{
Node list = new Node();
list.next = null;
Push(ref list, 1);
Push(ref list, 2);
Push(ref list, 3);
printList(list);
deleteN(ref list, 1);
printList(list);
}
}
|
Output
[3] [0x1b212c0]->0x1b212a0
[2] [0x1b212a0]->0x1b21280
[1] [0x1b21280]->0x1b21260
[0] [0x1b21260]->(nil)
[2] [0x1b212a0]->0x1b21280
[1] [0x1b21280]->0x1b21260
[0] [0x1b21260]->(nil)
Time Complexity: O(n)
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
Recursive Method to delete a node from linked list:
To delete a node of a linked list recursively we need to do the following steps:
- We pass node* (node pointer) as a reference to the function (as in node* &head)
- Now since the current node pointer is derived from the previous node’s next (which is passed by reference) so now if the value of the current node pointer is changed, the previous next node’s value also gets changed which is the required operation while deleting a node (i.e points previous node’s next to current node’s (containing key) next).
- Find the node containing the given value.
- Store this node to deallocate it later using the free() function.
- Change this node pointer so that it points to its next and by performing this previous node’s next also gets properly linked.
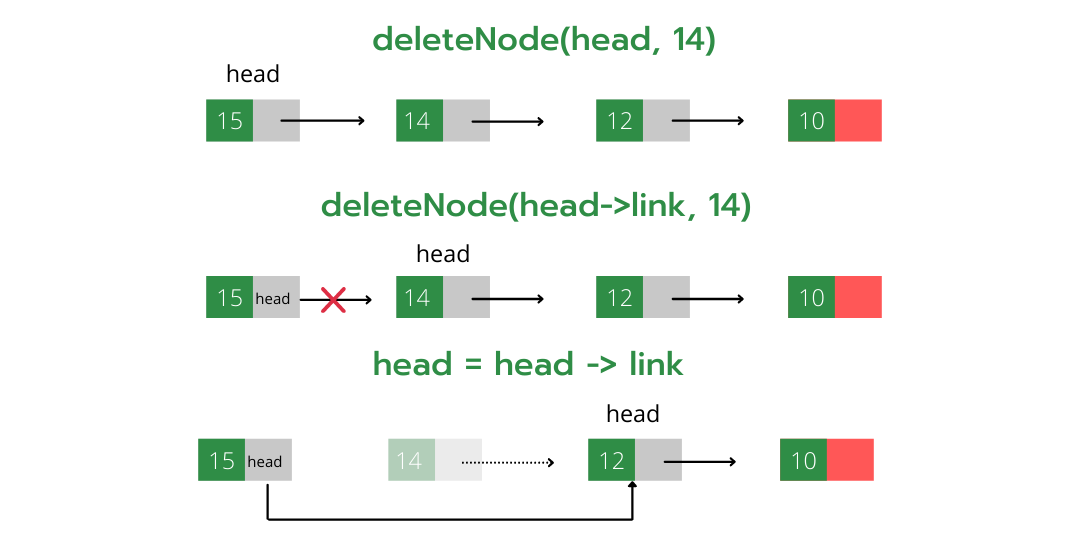
Below is the implementation of the above approach.
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct node {
int info;
node* link = NULL;
node() {}
node(int a)
: info(a)
{
}
};
void deleteNode(node*& head, int val)
{
if (head == NULL) {
cout << "Element not present in the list\n";
return;
}
if (head->info == val) {
node* t = head;
head = head->link;
delete (t);
return;
}
deleteNode(head->link, val);
}
void push(node*& head, int data)
{
node* newNode = new node(data);
newNode->link = head;
head = newNode;
}
void print(node* head)
{
if (head == NULL and cout << endl)
return;
cout << head->info << ' ';
print(head->link);
}
int main()
{
node* head = NULL;
push(head, 10);
push(head, 12);
push(head, 14);
push(head, 15);
print(head);
deleteNode(head, 20);
print(head);
deleteNode(head, 10);
print(head);
deleteNode(head, 14);
print(head);
return 0;
}
|
Python3
class Node:
def __init__(self,data):
self.data = data
self.next = None
def deleteNode(head, val):
if (head == None):
print("Element not present in the list")
return -1
if (head.data == val):
if head.next:
head.data = head.next.data
head.next = head.next.next
return 1
else: return 0
if deleteNode(head.next, val) == 0:
head.next = None
return 1
def push(head, data):
newNode = Node(data)
newNode.next = head
head = newNode
return head
def printLL(head):
if (head == None):
return
temp = head
while temp:
print(temp.data,end=' ')
temp = temp.next
print()
head = None
head = push(head, 10)
head = push(head, 12)
head = push(head, 14)
head = push(head, 15)
printLL(head)
deleteNode(head, 20)
printLL(head)
deleteNode(head, 10)
printLL(head)
deleteNode(head, 14)
printLL(head)
|
C#
using System;
class LinkedList
{
public class Node
{
public int info;
public Node link;
public Node(int a)
{
info = a;
link = null;
}
}
public static void deleteNode(ref Node head, int val)
{
if (head == null)
{
Console.WriteLine("Element not present in the list");
return;
}
if (head.info == val)
{
Node t = head;
head = head.link;
t = null;
return;
}
deleteNode(ref head.link, val);
}
public static void push(ref Node head, int data)
{
Node newNode = new Node(data);
newNode.link = head;
head = newNode;
}
public static void print(Node head)
{
if (head == null)
{
Console.WriteLine();
return;
}
Console.Write(head.info + " ");
print(head.link);
}
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
Node head = null;
push(ref head, 10);
push(ref head, 12);
push(ref head, 14);
push(ref head, 15);
print(head);
deleteNode(ref head, 20);
print(head);
deleteNode(ref head, 10);
print(head);
deleteNode(ref head, 14);
print(head);
}
}
|
Javascript
class Node {
constructor(data) {
this.data = data;
this.next = null;
}
}
function deleteNode(head, val)
{
if (!head) {
console.log("Element not present in the list");
return -1;
}
if (head.data == val) {
if (head.next) {
head.data = head.next.data;
head.next = head.next.next;
return 1;
} else return 0;
}
if (deleteNode(head.next, val) == 0) {
head.next = null;
return 1;
}
}
function push(head, data) {
let newNode = new Node(data);
newNode.next = head;
head = newNode;
return head;
}
function printLL(head) {
if (!head) return;
let temp = head;
while (temp) {
console.log(temp.data, " ");
temp = temp.next;
}
console.log();
}
let head = null;
head = push(head, 10);
head = push(head, 12);
head = push(head, 14);
head = push(head, 15);
printLL(head);
deleteNode(head, 20);
printLL(head);
deleteNode(head, 10);
printLL(head);
deleteNode(head, 14);
printLL(head);
|
Java
class Node {
int data;
Node next;
public Node(int data) {
this.data = data;
this.next = null;
}
}
public class Main {
public static int deleteNode(Node head, int val) {
if (head == null) {
System.out.println("Element not present in the list");
return -1;
}
if (head.data == val) {
if (head.next != null) {
head.data = head.next.data;
head.next = head.next.next;
return 1;
} else
return 0;
}
if (deleteNode(head.next, val) == 0) {
head.next = null;
return 1;
}
return -1;
}
public static Node push(Node head, int data) {
Node newNode = new Node(data);
newNode.next = head;
head = newNode;
return head;
}
public static void printLL(Node head) {
if (head == null)
return;
Node temp = head;
while (temp != null) {
System.out.print(temp.data + " ");
temp = temp.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Node head = null;
head = push(head, 10);
head = push(head, 12);
head = push(head, 14);
head = push(head, 15);
printLL(head);
deleteNode(head, 20);
printLL(head);
deleteNode(head, 10);
printLL(head);
deleteNode(head, 14);
printLL(head);
}
}
|
Output
15 14 12 10
Element not present in the list
15 14 12 10
15 14 12
15 12
Time Complexity: O(n)
Auxiliary Space: O(n) (due to recursion call stack)
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...