What is Graph Data Structure?
Last Updated :
07 Jul, 2023
A Graph is a non-linear data structure consisting of vertices and edges. The vertices are sometimes also referred to as nodes and the edges are lines or arcs that connect any two nodes in the graph. More formally a Graph is composed of a set of vertices( V ) and a set of edges( E ). The graph is denoted by G(E, V).
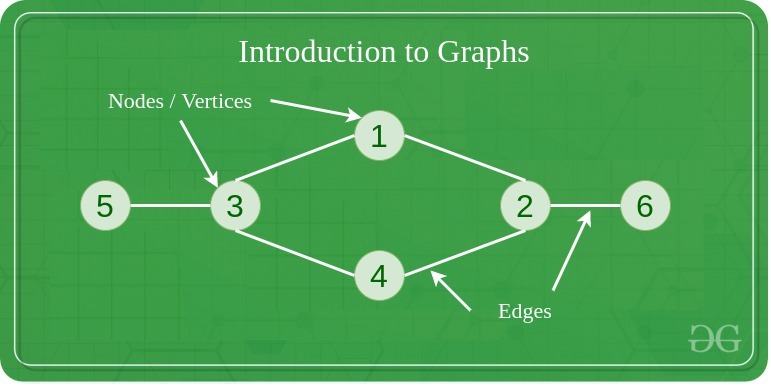
Components of a Graph
- Vertices: Vertices are the fundamental units of the graph. Sometimes, vertices are also known as vertices or nodes. Every node/vertex can be labeled or unlabelled.
- Edges: Edges are drawn or used to connect two nodes of the graph. It can be ordered pair of nodes in a directed graph. Edges can connect any two nodes in any possible way. There are no rules. Sometimes, edges are also known as arcs. Every edge can be labeled/unlabelled.
Types Of Graph
- Null Graph: A graph is known as a null graph if there are no edges in the graph.
- Trivial Graph: Graph having only a single vertex, it is also the smallest graph possible.
- Undirected Graph: A graph in which edges do not have any direction. That is the nodes are unordered pairs in the definition of every edge.
- Directed Graph: A graph in which edge has direction. That is the nodes are ordered pairs in the definition of every edge.
- Connected Graph: The graph in which from one node we can visit any other node in the graph is known as a connected graph.
- Disconnected Graph: The graph in which at least one node is not reachable from a node is known as a disconnected graph.
- Regular Graph: The graph in which the degree of every vertex is equal to K is called K regular graph.
- Complete Graph: The graph in which from each node there is an edge to each other node.
- Cycle Graph: The graph in which the graph is a cycle in itself, the degree of each vertex is 2.
- Cyclic Graph: A graph containing at least one cycle is known as a Cyclic graph.
- Directed Acyclic Graph: A Directed Graph that does not contain any cycle.
- Bipartite Graph: A graph in which vertex can be divided into two sets such that vertex in each set does not contain any edge between them.
- Weighted Graph: A graph in which the edges are already specified with suitable weight is known as a weighted graph. Weighted graphs can be further classified as:
- directed weighted graphs and
- undirected weighted graphs.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...