In an increasingly fast-changing web world, cloud services’ continuity, dependability, and security are among the elements that organizations should possess. AWS (Amazon Web Services), the major cloud service provider, based on its advanced bucket of tools and services helps to overcome these problems. Among them, the AWS Incident Manager positions itself as a key player in improving event management effectiveness. This post is going to walk you through what AWS Incident Manager is all about, including its importance, implementation strategies, and answering popular questions in the process.
What is AWS Incident Manager and how does it work?
AWS Incident Manager is a lambda-backed platform-as-a-service offering that lets organizations prepare for, respond to, and analyze incidents. It is a centralized facility that administers and effectively controls the events for your AWS resources and applications and resolves incidents. Incident Manager packs incident reporting, collaboration, and post-incident analysis tools that ensure a smooth process of incident response and reduce downtime thus safeguarding the business from the harmful impact of a failure.
Significant Aspects of Incident Manager
- Incident Detection: Incident Manager allows the organization to factor out and categorize the incidents with the help of prior defined criteria such as severity, effect, and systems or services that are involved. Through automated tracking mechanisms, alerts and case reports from the user go into the identification process.
- Incorporation of Triage and Security Control: When an issue is sensed, the incident manager serves as an assistant for the triage process, a part of which comprises the assessment, classification, and tackling of the issues in order of their urgency and the potential effect that they could have on business operations. Hence, through this step, there is a guarantee of fund allocation according to the intensity of the problems faced at the moment.
- Incident Response Coordination: The incident Manager is the single point responsible for organizing the incident response towers involving the support desk, tech support, security officers, and management team. It provides multiple functions including of real-time collaboration, task assignment, and tracking status to attain rapid resolution.
- Communication and Notification: Good communication becomes inevitable all the time in the process of incident response in which all the stakeholders ought to be equipped with an understanding of the incident status, update, and efforts towards resolution. Incident Manager offers communication bars, like email notifications, chat integrations and status messages, which are meant for swift and transparent information flow.
- Records compilation and studying the “post-incident” analysis of our platform: The incident manager directly documents important details of an incident like timescience as well as the steps taken and lessons learnt while resolving the incident. Referring to the documentation, we can come to the conclusion that it is an extremely important piece for the elapsed time analysis, the root cause determination and the process modifications.
Keys Functions of a Controller
- Incident Coordination: As the incident manager, you leave an immediate contact person for all incident activities. They enable the collective efforts of the many cross-functional teams including IT support, security and maintain operations too as management.
- Incident Assessment: Immediately upon receipt of the report, the incident manager assesses the level of threat, the magnitude of damages caused, and the degree of urgency of the given incident. They collect the needed information to gain a broader picture of the scenario and respond with high efficiency.
- Communication Management: Effective communication serves however is essential for incident resolution. The task of the incident manager is to rapidly react and promptly report to the relevant stakeholders such as internal teams, executives, customers, and other parties outside the company. They maintain contact with the affected community by offering frequent updates on the status of the incident, its advancement and measures planned for problem resolution.
- Resource Allocation: The PM, for this case, allocates resources such as personnel, tools, and equipment that would be relevant to the incident and take it effectively to end. This party examines whether there are guiding personnel and their capacities, and sets out the plan as and when the discord happens.
- Resolution Planning: By analyzing the incident from different perspectives, the incident manger will develop a response plan which will outline the steps needed to provide solutions to the incident. They involve technical teams in the process of error-trapping, risk mitigation, and safe recovery, as per the established procedures and practices.
- Post-Incident Review: Once the crisis is addressed, the incident manager hold a post-incident review or “post-mortem” to review the respond process, conduct a root cause analysis and offer preventive recommendations that can avoid these kinds of incident from happening next time.

key responsibilities of incident Manager
Tools and Technologies Used by Incident Managers
Incident Management Platforms: Analogues event managers can fully rely and trust incident management systems which will simplify how incidents communications and resolutions are handled. Such platforms usually consist of workflows, dashboards, and collaboration features to help the incident response team to be more efficient. Such platforms can be quite helpful for a better organization of the team.

Communication Tools: To achieve those goals, incident managers use email, chat programs, and collaboration solutions to facilitate coordination meetings, disseminate information in real-time and directly engage those stakeholders in the conversations.

Communication Tools
Monitoring and Alerting Function: Alerting and monitoring programs help create a real-time overview of the infrastructure’s health and the amount of achieved results by employees of the IT-sphere. These systems form the backbone of the work of Incident managers by alerting the operations team about potential anomalies and initiating incident response workflow.
Alerting Systems
Documentation and Knowledge Management: Incident managers curate diaries and journals containing all the response-on-incident procedure, runbooks, and good practices. With these resources businesses are able to work faster and smarter, making accident investigation efficient, convenience of responses, and constant improvement, a norm.
documentation and knowledge
Implementation of Incident Manager in AWS
Implementing an Incident Manager in AWS involves utilizing various AWS services and tools to streamline incident response workflows, coordinate communication, and ensure timely resolution of incidents.
Step 1: Setting Up AWS Services
Create an AWS Account: Start at the AWS Management Console by signing in or if you don’t have an AWS account, sign up for a new account.

aws login page
Navigate to AWS Systems Manager: On the AWS Management Console, enter “Systems Manager” into the services search bar and select it again from the dropdown list.

services search bar
Enable AWS Systems Manager Incident Manager: To begin, click on the “Incident Manager” from the navigation pane located on the main “System Manager” console.
Follow the suggestions to enable Incident Manager if your AWS account has the rights.

AWS navigation pane
Step 2: Creating an Incident Record
Navigate to Incident Manager Dashboard: Once Incident Manager is enabled, navigate to the Incident Manager dashboard from the Systems Manager console. Click on “Create incident” to initiate the incident creation process.
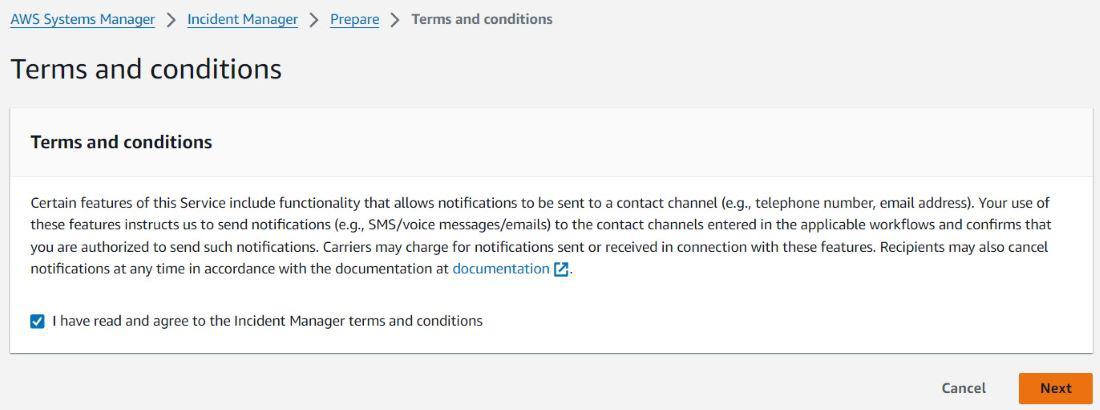
Provide Incident Details: Provide corresponding data for relevant events like name, description, gravity, urgency and the impacted resources or services. Click on “Create incident” to create the incident record.
STEP 3: Managing Incident Response
Assigning Tasks: In an incident record section, set up additional tasks according to the roles of the response team or teams that will facilitate incident resolution.

incident details
Start the incident: Go to incident Manager lists and select your incident created. Click on start incident, to start the incident.

start incident form
Tracking Incident Status: Monitor the progress of the situation, track response activities as they are being implemented, and manage teams responsible for operational activities. Have a look at the events chronogram in order to find out any (comments, updates, and actions) made by members.
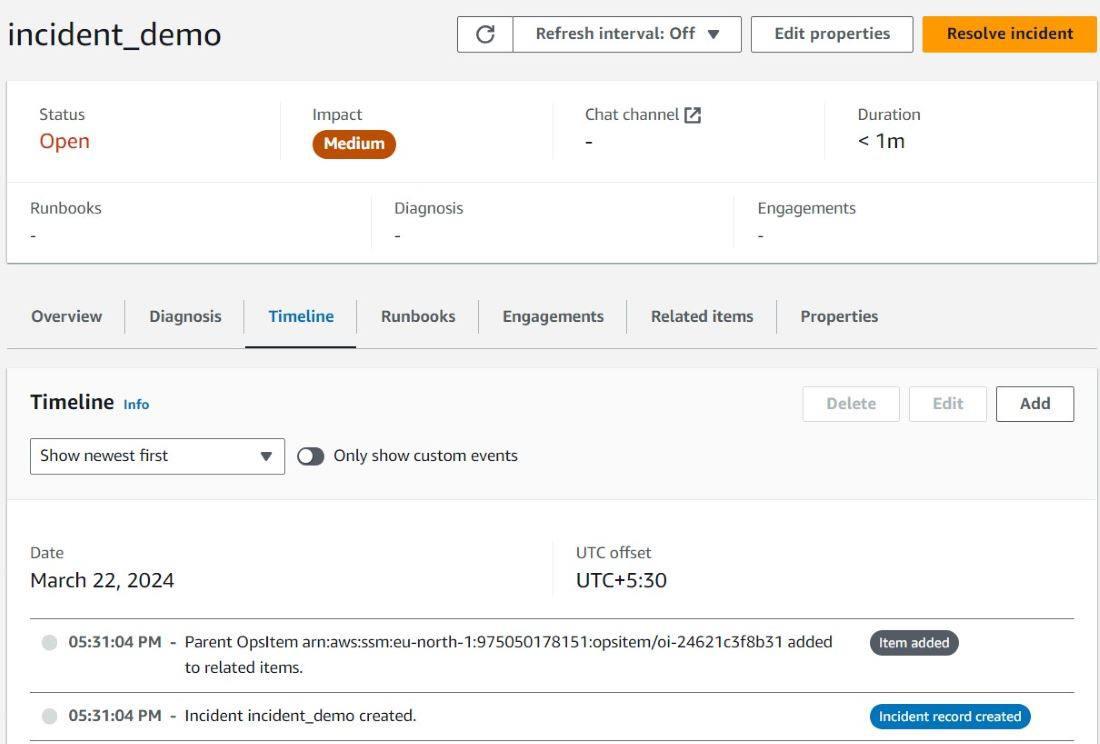
timeline to track incident
Importance of Incident Management
Planning and responding accurately during a crisis are super significant for maintaining business continuity plus yo catering to their customers. Here are some key reasons why it’s crucial:Here are some key reasons why it’s crucial:
- Reduced Downtime: Many issues arise during operation, prompt fixes inhibit further occurrences and allowing the business to operational breakdown as short as possible. The adage suggests that business owners should be prepared for everything that the changing environment might throw at them and that they should not halt their work.
- Enhanced Security: Incident management replaces seeing and acting at a really high speed in the cases involving security problems with data leakage or cyber-attacks. However, these challenges rapidly grew as the use of cloud computing escalated because we had to ensure safe and secure way to store the information in the cloud.
- Improved Customer Experience: The quick and straightforward response system demonstrates to the customers that we care about them. This creates a bond that inspires customers’ faith and brings joy to their commercial associations.
- Continuous Improvement: Knowing how things went in the worst case scenario and why they went so wrong, will help us act more wisely next time and do things better. The ability to recognize out of the ordinary incident, forecast the underlying issues and come up with new solutions are what really keep us going.
Incident Management Workflow
Incident Identification:
- Description: It goes without saying that the first step is lifting the edge when something’s not right. That could be through our monitoring systems, a user’s feedback as well as through automatic alarms.
- Responsibility: IT experts may respond, monitoring tools be used, users be tricked or the hacker become trapped in the technological labyrinth.
Logging:
- Description: When we realize that there is something wrong about it, we should then put into record all the data that are significant to the problem. The follow-up will also entail in detail what happened, when, and the possible outcomes on the system or service delivery.
- Responsibility: It might be IT personnel on duty or designated incident responders who ensure that all NIDs get recorded correctly in case of a possible data breach.
Categorization:
- Description: After that, we assign them to different groups according to what type the event is and how critical it is. This is also an important designer instrument that helps it decide what to focus on the most and how to manage it.
- Responsibility: The manager or employee subordinate assigned to incident handling classify incidents into their respective category or marker assigned by predefined criteria, hierarchical schemes, or templates.
Prioritization:
- Description: Newsrooms sort the incidents that are the most critical and demanding then. We always prioritize the issues that carry bigger situations in the company.
- Responsibility: The matter of incident (manager) or incident response team which comes up with priorities by initiating predefined criteria or service level agreements (SLAs) or business objectives.
Response:
- Description: Got it, now I will call the repair service or go to the near customer care. Our aim is to reduces the extent of the amount of damage done and restore the situation to as it was before. This can appear as changing our situation by using short fix, experts consultation or applying solutions we are already using to the problem site.
- Responsibility: The security staff members, incident response group, IT support parties or subject matter experts tend to spearhead remediation procedures and put the policies into action and accordingly.
Diagnosis:
- Description: Along the process of sorting it all out, we heavily rely on our past experiences and review what should have been done before. These self-exploring, problem-solving approaches might require delving into logs or checking off which production element has the issue, that is, the cause of the problem.
- Responsibility: The technical experts, system administrators or incident response teams read the event data carefully and every one of them tried to find out the reason for incident properly as a diagnose.
Escalations:
- Description: If we cannot fix something right away, or if we need somebody’s assistance, we report for a higher authority. In this case, we will probably engage senior or middle management, bring more support groups on board, or even hire outside experts if needed.
- Responsibility: The clear incident manager or delegate personnel resort to the escalation phase after they have reached the established escalation criteria and procedures.
Revolutions and Recovery:
- Description: If we know the reason that a disease is occurring and what we can do to prevent it, we will work at it until it is fixed forever. Gladly, we go back to the way like before fast and examine everything to ensure it won’t repeat.
- Responsibility: Technical team and/or system administrators can work together with or through the vendors t0 execute resolution actions appropriate to the situation, and ensures that all services are up and running.
Closure:
- Description: After the incident is settled, it officially ends on the incident management system disclosing it. The closing of the incident necessitates a revision of the incident-record tag with a resolution status, documenting lessons learned, and obtaining users’ confirmation or feedback.
- Responsibility: The incident manager or whoever is responsible can verify the problem is solved, and then the incident record can be closed and, information regarding the issue has ended, can be provided to stakeholders.

Incident Management workflow
Conclusion
AWS Incident Manager holds an integral position towards helping companies address incidents with timely resolution, minimum impact, as well as continuous business operations in the digital space. Keeping the incident management duties concentrated, supporting cross-functional teams and allowing for automation through Incident Manager helps businesses respond to incidents fast and with proper efficiency. Instead of Incident Manager being just a tool to enhance operational resilience, it can be a platform from which, post incident analysis and learning, an organization can learn to improve. With the rise of the businesses in the cloud services rapidly, AWS Incident Manager plays an important role in ensuring their applications and infrastructure is running as it should be.
Incident Manager – FAQs
Which types of incidents will be treated by the AWS Incident Manager?
The AWS Incident Manager can resolve many diverse incidents like infrastructure failures, application errors, security violation, and normal operational surprises.
How do I come up with a bespoke service response plan in AWS Incident Manager?
Yes, you will be able to develop response plans that you feel comfortable with and what your organization needs/demands the most. You can, for example, define actions of various types of response, escalation policies, and communication channels that will be tailored to the nature of the emergency.
I wonder how AWS Incident Manager helps individuals to work together in a team.
AWS Incident Manager offers centralized communication(collaboration) channels and incident timelines that help the cross-functional teams (multi-disciplinary teams) to work efficiently together to address an incident. It gives the ability to index teams of work, give them updates, and monitor progress.
What integration options with other tools AWS Incident Manager wheeloff?
Indeed, AWS Incident Manager provides integration of multiple types of third-party monitoring, alerting, and ticketing with Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) or the AWS Partner Network (APN) integrations. Thus you empower the sharing of data and divide and conquer’s roots in your current incident management framework.
Is AWS Incident Manager sufficient for a business with less than 50 employees?
Certainly, AWS Incident Manager can be used by companies of any sizes of their incident management requirements for different companies of varying sizes. Incident Manager will have you covered, regardless of your organization’s size or complexity. Small and large enterprises will all experience good incident management performance thanks to the scalable and customizable capabilities.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...