The Pallavas (275CE-897CE): History, Time Period, Architecture
Last Updated :
24 Jan, 2024
The Pallavas were an ancient South Indian dynasty (275 CE to 897 CE) known for ruling over the Deccan, particularly Tondaimandalam. They significantly influenced the history and heritage of southern India, leaving a lasting impact on art, architecture, and culture.
In this article, We have covered Pllava’s Complete History along with the period and founder, meaning, Art and architecture of the Pallavas, Rise and Decline, and many more.
Let’s dive right in.

The Pallavas- 275 CE to 897 CE
Who were the Pallavas?
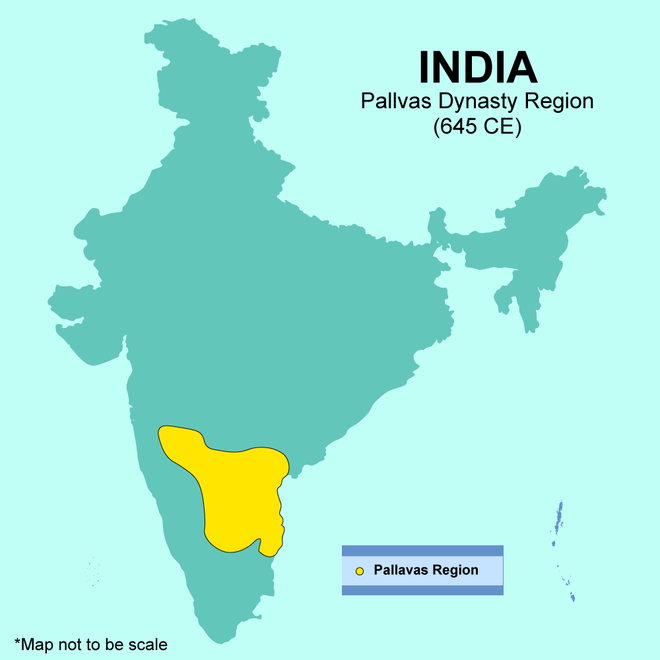
The Pallavas were as similar to the Pulindas. It was mentioned in Ashoka’s Inscriptions. Simha Vishnu was the founder of this dynasty and was an efficient ruler. Pallavas ruled from Kanchipuram and it was their capital.
The Pallavas
The Pallavas were a South Indian dynasty that ruled from the 3rd to the 9th century CE. They were known for their contributions to art and architecture, especially the creation of rock-cut temples and monolithic structures.
The dynasty had a significant impact on the cultural and religious development of the region, transitioning from Jainism to Hinduism. The Pallavas played a crucial role in trade and cultural exchanges with Southeast Asia. The Chola dynasty eventually invaded and marked the decline of the Pallava power in the 9th century.
The Pallavas Overview
The following is a brief overview of the Pallavas:
| Dynasty Name |
Pallava Dynasty |
| Founder |
Simhavishnu |
| Capital |
Kanchipuram (also known as Kanchi or Conjeevaram) |
| Period of Existence |
3rd century CE to 9th century CE |
| Territory |
Initially in Northern Tamil Nadu, later expanded to Andhra Pradesh and parts of Karnataka |
| Notable Rulers |
1. Simhavishnu |
|
2. Mahendravarman I |
|
3. Narasimhavarman I (Mamalla) |
|
4. Rajasimha (Narasimhavarman II) |
| Contributions |
1. Architectural marvels, especially in the form of rock-cut temples and monolithic rathas (chariots) at Mamallapuram (Mahabalipuram). |
|
2. Promotion of literature and learning, with notable contributions to Sanskrit and Tamil literature. |
|
3. Maritime activities, contributing to trade and cultural exchanges with Southeast Asian countries. |
| Religion |
Initially followers of Jainism, later adopted Hinduism. |
| Decline |
Invaded by the Chola dynasty in the 9th century, leading to the decline of the Pallava power. |
| Legacy |
1. Significant influence on the art and architecture of South India. |
|
2. Cultural and religious contributions continue to be celebrated and studied. |
History of Pallavas
The following is the History of Pallavas:
- Origins and Early Period (3rd – 6th Century CE):
- The Pallava dynasty is believed to have originated in the Tondaimandalam region, in present-day Northern Tamil Nadu.
- The earliest known ruler was Simhavishnu, who established the dynasty in the 3rd century CE.
- Initially, the Pallavas were followers of Jainism.
- Transition to Hinduism (6th Century CE):
- Mahendravarman I, one of the Pallava rulers, played a crucial role in the transition from Jainism to Hinduism.
- The Pallavas became strong patrons of Hinduism and contributed to the promotion of Sanskrit and Tamil literature.
- Architectural Achievements (6th – 8th Century CE):
- The Pallavas were renowned for their architectural achievements, particularly the rock-cut temples and monolithic rathas (chariots) at Mamallapuram (Mahabalipuram).
- Mahendravarman I and Narasimhavarman I (Mamalla) were key rulers associated with these architectural marvels.
- Maritime Activities and Trade (7th – 8th Century CE):
- The Pallavas actively engaged in maritime activities, contributing to trade and cultural exchanges with Southeast Asian countries.
- This period saw the expansion of Pallava influence to regions beyond Tamil Nadu, including Andhra Pradesh and parts of Karnataka.
- Chola Invasions and Decline (9th Century CE):
- The Pallavas faced invasions from the Chola dynasty in the 9th century, leading to the decline of their power.
- Rajasimha (Narasimhavarman II) was a notable ruler during this period.
The Extent of the Pallava Dynasty
The Pallava Dynasty was the most significant and efficient dynasty of the south India. They became more strong during the reign of Mahendravarman I (571–630 CE).
- The capital of the Pallava dynasty is Kanchipuram.
- Their territory was stretched from the north side of Andhra Pradesh to River Kaveri in the south side.
- The Pallavas reduced the power of Cholas and made them a marginal state in the seventh century.
- The Pallava king Narasimhavarman occupied Badami regions after defeating the Chalukyas.
- To suppress the Kalabhra uprising, Pandyas, Chalukyas, and Pallavas worked together.
Administration under the Pallavas
Administration under the Pallavas was well-organized and followed the system of monarchy. The king was the head of the whole kingdom. Amatyas were the council ministers who usually helped the king to maintain administrative matters.
- Pallavas promoted agriculture in their administration.
- They encouraged people to do sea trade. Collected huge wealth and taxes.
- Spent the wealth and taxes to build the temple architecture.
- Pallava kingdom was divided into Kottams or Nadu.
- Land grants were very common to Brahmans (Brahmadeya).
- Temples and Brahmans were exempted from taxation.
- A group of villages were called ‘Nadu’ and more than one Nadus were called ‘Nagaram’ together.
- A group of Nagarams were called as ‘Manadalam’.
- Sabhas consist of Brahmin landowners.
- The land owner looked after the irrigation, agriculture, roads, and temples.
- “Ur” were the Non-Bhmin land owners.
Society and Religion of the Pallavas
The Pallavas were the followers of Hinduism but they were tolerant of other religions. They worshipped of Lord Shiva and Lord Vishnu. However, Buddhism and Jainism lost their popularity during this time.
- They had a four–fold rigid caste system.
- Brahmana occupied all the dominant positions.
- Pallava were orthodox Brahman Hindus.
- The Bhakti Movement was promoted under Pallavas.
- Shaiva and Vaishnav sages promoted as they worship lord Shiba and Vishnu.
- Shaiva sage poets were called Nayanars.
- Important Nayanars were Thirunavukkarasar or Appar, Sundarar or Sundarmurti, Sambandar, Manikkavsagar.
- Vaishnav sage poets were called Alvars.
- Important Alvars were Perialvar, Andal-poetess, Nammalvar, Kulashekhar.
- Saivism and Vaishnavism became more popular in their time.
Literary Works of the Pallavas
The Pallavas were great supporters of education and literature. Kanchi had been developed as a great centre of education, culture and trade. Here are some details:
- Kanchi was their capital which was an ancient center of learning.
- Kanchi’s Ghatika was the famous education center which attracted students from all over India and abroad.
- Mayurasarman was the founder of the Kadamba dynasty who studied Vedas in Kanchi.
- Dinganaga came to Kanchi to pursue study. He was a Buddhist writer.
- Kanchi was the home of Dharmapala. Later he became the President of Nalanda University.
- Bharavi was a great Sanskrit scholar related to this dynasty.
- Dandin was a Sanskrit writer who was a part of the court of Narasimhavarman II.
- The Sanskrit play Mattavilasa Prahasana was written by Pallava king Mahendravarman I.
- They also promoted the Tamil literature with music and dance.
- Religious hymns were sung at this time with music and dance.
The Pallavas Art and Architecture
Early stage of Dravidian art and architecture flourished under the Pallavas. The Pallava dynasty majorly known for the rock-cut architecture. It involves carving large rocks into various shapes and sizes to build temples.
- The Pallavas made so many contributions to Indian art and architecture.
- Religious revival was common and architectural activity was considered as status.
- Pallavas were the main contributor and creator of the Dravidian style architecture.
- So many cave temples were created at this time.
- Pancha Ratha are monolithic stone chariots based on Mahabharata.
- The Pallavas also aided in the advancement of sculpture.
- Beautiful sculptures were curved on the walls of the Mandapas.
- The classical art “Descent of Ganges or the Penance of Arjuna” is a masterpiece. Present in Mamallapuram.
- Pallavas’ were the patronage of music, dance, and painting.
- The paintings in the Sittannavasal caves were painted the Pallava period.
Important Kings – The Pallavas (275CE – 897CE)
The Pallavas ruled the South Indian subcontinent from 275CE to 897CE who were the most influential rulers of the region. Here are some important kings as mentioned below:
- Defeated by Pulkeshin II, King of the Chalukya kingdom.
- Major Title Used In His Times: Gunabhara, Satyasandha, Chettakari (temple-maker) Chitrakarapuli (painter), Vichitrachitta and Mattavilasa.
- Mandagapathu inscription tells about the beginning of making a rock-cut temple.
- He was a versatile genius having expertise in painting, music, and literature.
- He composed a satirical drama named Mattavilasa Prahasanam in Sanskrit.
- Music inscriptions at Kudumiamalai were made by him.
|
- Narshimhavarman I defeated the Chalukya King Pulkeshin II.
- Major Battle: Battle of Manimangalam.
- The war was encrypted in the Kuram copper plate inscriptions.
- Got the title of Mamalla (great wrestler).
- The founded the great city of Mahabalipuram.
- On conquering Badami, he assumed the title of ‘Vatapikonda’.
- He sent a naval expedition to Sri Lanka.
- He restored the throne of Sri Lankan prince- Manavarma.
- Chinese traveller and Buddhist monk Hieun Tsang visited in his times.
|
- He was known Rajsimha.
- He assumed titles of Shankarbhakta, Agmapriya etc.
- Sent embassies to China.
- So many temples and specifically Kailasanatha temple were built during his times.
- Dandin, the great Sanskrit scholar lived in his court.
- Patronized Perundevannar who translated Mahabharata in Tamil.
|
Decline of the Pallavas
Attack and temporary occupation of Kanchi by Vikramaditya II regarded as the beginning of the end of Pallavas.
- Pallava kingdom was attacked by the Pandyas and the Rashtrakutas.
- Rashtrakuta King Dantidurga defeated Nandivarman.
- The last Pallava king was named as Aparajitavarman.
- Aditya I defeated Aparjitavarman and captured the Kanchi region. From here Chola dynasty started.
- Other notable rulers: Nandivarman, Parmeshwarvarman I and Parmeshwarvarmn II.
Related Articles:
FAQs on The Pallavas (275CE-897CE)
What is the origin of Pallavas?
Pallavas were the indigenous subordinates of the Satavahanas in the Deccan.
Who defeated Pallava dynasty?
Aditya I defeated Aparjitavarman. After that he took control of the Kanchi.
What language did Pallavas speak?
Pallavas spoke in Tamil, Prakrit and Sanskrit.
Which temple did Pallavas built?
Kailasanathar Temple at Kanchipuram, the Shore Temple and the Pancha Rathasof Mahabalipuram were built by Pallavas.
What is the symbol of Pallavas?
The symbol of Pallavas was the Lion (Simha) and the Bull (Nandi).
Who was the founder of the Pallava Dynasty?
The founder of the Pallava Dynasty was Simhavishnu. He is credited with establishing the dynasty around the 3rd century CE in the Tondaimandalam region, which is in present-day Northern Tamil Nadu, India.
Who was the greatest ruler of the Pallava Dynasty?
One of the most renowned rulers of the Pallava Dynasty was Narasimhavarman I (Mamalla), known for military successes, naval achievements, and significant contributions to architecture, including the Shore Temple at Mamallapuram.
What is the name of the capital of Pallavas?
The capital of the Pallava Dynasty was Kanchipuram, also known as Kanchi or Conjeevaram.
What are the temples built by Pallavas?
Some notable temples built by the Pallavas include the Shore Temple in Mahabalipuram, Kailasanatha Temple, Vaikunta Perumal Temple, and Pancha Rathas in Kanchipuram, showcasing their significant contributions to South Indian temple architecture.
What is the meaning of Pallavas?
The term “Pallava” is derived from Sanskrit and means “a creeper or branch.”
What is the period of Pallava Chola?
The Pallava dynasty, spanning from 275 CE to 897 CE, held sway over a substantial part of the Deccan, referred to as Tondaimandalam. Their influence played a pivotal role in shaping the history and heritage of southern India.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...