Surface Mount Technology
Last Updated :
17 Oct, 2023
Surface Mount Technology (SMT) is used in the electronic industry to assemble and solder electronic components directly onto the surface of printed circuit boards. Unlike through-hole technology, where components have leads inserted into drilled holes, SMT components have small leads or no leads, relying on solder paste and a reflow soldering process to establish electrical connections.
What is Surface Mount Technology (SMT)?
Surface Mount Technology is a method for assembling electronic components onto printed circuit boards (PCBs). Unlike traditional through-hole technology, where components have leads inserted through holes in the PCB, SMT involves mounting components directly onto the surface of the PCB. The SMT offers advantages such as smaller form factors and improved manufacturing efficiency and compatibility with the automated assembly processes.
SMT Manufacturing Process
The SMT manufacturing process involves the following key steps:
1. Component Placement
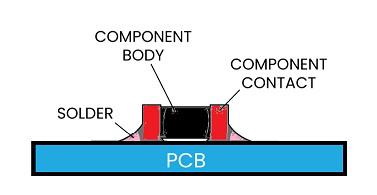
The Tiny electronic components including resistors, capacitors, and printed antennas mentioned earlier are picked and placed on PCB using the specialized robotic machinery. These components are provided in the form of the Surface Mount Devices (SMDs).
2. Solder Paste Application
The Solder paste a sticky mixture of the solder alloy particles and flux is applied to the PCB’s pads using the stencil. The solder paste is positioned in the locations where components will be placed and soldered.
3. Component Soldering
The PCB with solder paste applied is passed through a reflow oven. The heat in oven melts the solder paste is allowing the components to adhere to the pads on PCB. As the assembly cools and the solder solidifies forming strong electrical connections.
4. Inspection and Testing
The assembly undergoes visual inspection and testing to identify defects soldering issues or incorrect placements. Automated optical inspection and X-ray techniques are often used for the thorough examination.
Evolution and Reasons
The SMT evolved as a response to the demand for miniaturization, improved performance, and higher production speeds in the electronics industry. As electronic devices became smaller and more complex, traditional through-hole assembly methods became limiting due to larger component sizes and increased assembly time.
Effects
The adoption of SMT has led to significant advancements in electronics manufacturing, including:
- The Miniaturization of the electronic devices.
- The Enhanced performance due to shorter signal paths.
- To Increased production efficiency and reduced manufacturing costs.
Types of Surface Mount Components
1. Surface Mount Devices (SMDs)
These are small leadless electronic components such as resistors, capacitors and integrated circuits. They are soldered directly onto PCB’s surface.
2. Surface Mount Connectors:
These connectors like USB ports or HDMI connectors are directly mounted onto PCB is enabling easy interfacing with the other devices.
Properties and Characteristics
- Miniaturization: The SMT allows for the smaller component sizes and denser PCB layouts.
- Higher Frequencies: The Shorter traces reduce signal interference and enable higher-frequency operation.
- Improved Thermal Performance: The Direct contact between components and PCB aids in the better heat dissipation.
- Automated Assembly: The Robotic machines automate component placement and increasing production efficiency.
Applications
SMT is used in a wide range of electronics, including:
- Consumer electronics: The Mobile phones, laptops and TVs.
- Automotive electronics: The Engine control units and infotainment systems.
- Industrial equipment: The PLCs control panels.
- Medical devices: Imaging equipment and monitoring devices.
Example
Consider a mobile phone’s PCB assembly. Surface mount components are densely placed on PCB’s surface is allowing for compact and lightweight design.
Difference Between terms SMT and SMD
|
Definition
|
The method for the assembling electronic components onto the PCBs without inserting leads through holes.
|
The individual electronic components designed for the mounting directly onto the PCB surfaces.
|
|
Scope
|
The Encompasses the entire process of the assembling components onto PCB surface including placement, inspection and testing.
|
The Refers specifically to components that are mounted onto PCB surface using the SMT techniques.
|
|
Process Stages
|
Involves component placement solder paste application or reflow soldering and potentially cleaning.
|
The Focuses on individual components’ physical design and form such as resistors and integrated circuits.
|
|
Key Importance
|
The Methodology for the assembling electronics.
|
The Components designed for the direct surface mounting components designed for the direct surface mounting.
|
Advantages
- Space Efficiency: The Components are placed on both sides of PCB maximizing space utilization.
- Cost-Effective: To Automated assembly reduces labor costs and enhances production speed.
- Better Signal Integrity: The Shorter traces result in the reduced signal interference.
Disadvantages
- Rework Challenges: The Removing and replacing SMT components can be difficult due to their small size.
- Initial Investment: The Setting up SMT production lines requires substantial investment in equipment.
Conclusion
Surface Mount Technology has transformed the electronics industry by enabling the miniaturization and streamlining manufacturing processes. From smartphones to the industrial machinery SMT is the driving force behind the production of the modern electronic devices and Understanding its working , properties and applications empowers engineers and enthusiasts to design and build innovative electronics that meet the demands of digital era.
FAQs on Surface Mount
Q.1: Are SMT components more reliable than through-hole components?
Answer:
The SMT components are generally considered more reliable due to their compact design and reduced susceptibility to mechanical stress.
Q.2: Can SMT components be used for high-power applications?
Answer:
Yes, SMT components can handle high-power applications with the proper thermal management.
Q.3: Are there size limitations for SMT components?
Answer:
While SMT enables miniaturization extremely small components can pose challenges during the assembly and inspection.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...