starts_with() and ends_with() in C++20 with Examples
Last Updated :
28 Jan, 2021
In this article, we will be discussing starts_with() and ends_with() with examples in C++20.
starts_with()
This function efficiently checks if a string begins with the given prefix or not. This function written in both std::basic_string and in std::basic_string_view.
Syntax:
template <typename PrefixType> bool starts_with(PrefixType prefix)
In the above syntax the prefix can be:
- string
- string view
- single character or C-style string with null-terminated character
starts_with() with different types of Prefix:
bool starts_with(std::basic_string_view<Char T, Traits> x) const noexcept;
bool starts_with(CharT x) const noexcept;
bool starts_with(const CharT *x) const;
All the three overloaded forms of the function effectively return std::basic_string_view<Char T, Traits>(data(), size()).starts_with(x);
Parameters: It requires a single character sequence or a single character to compare to the start of the string.
Return Value: It returns the boolean true or false indication the following:
- True: If string starts with the prefix.
- False: If string does not start with the prefix.
Program 1:
Below program to demonstrates the concept of starts_with() in C++:
C++
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <string_view>
using namespace std;
template <typename PrefixType>
void if_prefix(const std::string& str,
PrefixType prefix)
{
cout << "'" << str << "' starts with '"
<< prefix << "': "
<< str.starts_with(prefix)
<< endl;
}
int main()
{
string str = { "geeksforgeeks" };
if_prefix(str, string("geek"));
if_prefix(str, string_view("geek"));
if_prefix(str, 'g');
if_prefix(str, "geek\0");
if_prefix(str, string("for"));
if_prefix(str, string("Geek"));
if_prefix(str, 'x');
return 0;
}
|
Output:

This function efficiently checks if a string ends with the given suffix or not. This function written in both std::basic_string and in std::basic_string_view.
Syntax:
template <typename SuffixType> bool starts_with(SuffixType suffix)
In the above syntax the suffix can be:
- string
- string view
- single character or C-style string with null-terminated character.
ends with() different types of Suffix:
constexpr bool ends_with(std::basic_string_view<Char T, Traits> sv) const noexcept;|
constexpr boll ends_with(CharT c) const noexcept;
constexpr bool ends_with(const CharT* s) const;
All the three overloaded forms of the function effectively return std::basic_string_view<Char T, Traits>(data(), size()).ends_with(x);
Parameters: It requires a single character sequence or a single character to compare to the end of the string.
Return Value: It returns the boolean true or false indicating the following:
- True: If string ends with the suffix.
- False: If string does not end with the suffix.
Program 2:
Below program to demonstrates the concept of ends_with() in C++:
C++
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <string_view>
using namespace std;
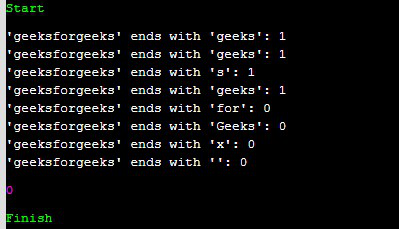
template <typename SuffixType>
void if_suffix(const std::string& str,
SuffixType suffix)
{
cout << "'" << str << "' ends with '" << suffix << "': " << str.ends_with(suffix) << std::endl;
}
int main()
{
string str = { "geeksforgeeks" };
if_suffix(str, string("geeks"));
if_suffix(str, string_view("geeks"));
if_suffix(str, 's');
if_suffix(str,
"geeks\0");
if_suffix(str, string("for"));
if_suffix(str, string("Geeks"));
if_suffix(str, 'x');
if_suffix(str, '\0');
}
|
Output:
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...