A square function is also a quadratic function. A square function is represented as f(x) = x2. The graph of the square function is in the shape of a parabola or U- shaped. Based on the coefficient of x2 (highest degree in a square function), the graph may be U- shaped or Inverted U- shaped.
In this article we have covered, the definition of a square function, the graph of a square function, the domain and range of a square function and others in detail.
What is a Square Function?
A square function is a function that multiplies a number by Itself. In general, the square function is denoted by,
y = x2
where,
A square function can be an even function because the square of the positive number is equal to the square of the negative number., i.e. x2 = (-x)2. A square function is a quadratic function of the form,
y = (x + a)2
Quadratic functions have the highest degree of ‘2’. Quadratic function means squaring of variable x along with a constant value. The general form of a quadratic function is,
y = ax2 + bx + c
where,
- a is coefficient of x2
- b is coefficient of x
- c is constant
Coefficient of x2 should not be equal to zero i.e., a ≠ 0
Quadratic function is a quadratic equation of the form,
ax2 + bx +c = 0
To find the roots of a quadratic equation,
[Tex]x=\frac{-b\pm \sqrt{b^2-4ac}}{2a}[/Tex]
Graph of a Square Function
Graph of a square function is Concave up or Concave down. It means the graph of the square function will be either open upwards or inverted(downwards).
For Example, take f(x) = ax2
Graph of the square function depends on the coefficient of x2,
- If the coefficient (a) is positive (a > 0) then the graph is concave up, f(x) has the minimum value.
- If the coefficient (a) is negative (a<0) then the graph is concave down, f(x) has the maximum value.

For example: Let us consider a square function y = x2
Substitute different x values in y,
y = 32 = 9
y = (-3)2 = 9
y = 12= 1
y = (-1)2= 1
y = 02 = 0
Take these calculated values in table as shown below,
x
| y
|
|---|
|
-3
|
9
|
|
-1
|
1
|
|
0
|
0
|
|
1
|
1
|
|
3
|
9
|
Plot these points and join them on the graph as shown below, having x-axis and y-axis,
.png)
Graph
Compare y = ax2 with y = x2,
as a = 1 which is a > 0, So the graph is concave up and f(x) has minimum value of (x, y) = (0, 0).
This minimum point is called vertex. The line that passes through this vertex is called the Axis of symmetry.
Axis of Symmetry: It is the line that divides the graph into two equal parts.
For y = x2, axis of symmetry is,
Take x-coordinate of vertex,
x = 0 is the axis of symmetry
Domain of a Square Function
Domain is set of ‘x’ values or input values of a function. The domain of the square function is set of Real numbers (It means positive integers, negative integers, irrational numbers and fractions).
Domain of Square Function = ℝ (Real Numbers)
Range of a Square Function
Range is set of ‘y’ values or output values of a function. The range of the square function is Non -negative Real numbers.
Range = (0, +∞)
Properties of Square Function
Some of the properties of the square function are:
- Even Function: Square function is an even function i.e., f(-x) = f(x)
For example, f(x) = x2
Substitute x = -x in f(x),
f(-x) = (-x)2 = x2
Then, f(-x) = f(x)
- Non-Negative Number: Square of any real number is always an Non-negative number. For any non real number “a”, the square is, a ≥ 0
- Symmetry about y-axis: Graph of square function is same on both side of the y-axis.
- Increasing and Decreasing: The graph of the square function is decreasing on the negative values of ‘x'(moving from negative infinity to negative numbers of ‘x’ ) and Increasing on the positive values of ‘x’.
- Parabola: Shape of the square function is like a parabola.
- Quadratic: Square function is also a quadratic function.
- Inverse Relation: Take a number ‘x’, square the number (x2) and then take square root of the number, [Tex]\sqrt{x^{2}}=x[/Tex], which gives the original number. So the opposite of square root function is the Square function.
Conclusion
Square function forms an inverse relation with square root function. It is the basis of quadratic relationship. The graph of the square function is like a parabola. It also tell us whether the function is an even function or not, non negative output, increasing on positive inputs and decreasing on negative inputs which are properties of square function. Square function is used in mathematics like algebra, calculus, geometry, and physics, and applications in areas such as optimization and engineering.
Examples on Square Function
Example 1: Graph the square function y = (x + 1)2?
Solution:
Given square function,
y = (x+1)2
Substitute different x values in y to plot the given function,
Substitute x = -2 in y,
y = (-2+1)2
y = 1
Substitute x = -1 in y,
y = (-1+1)2
y = 0
Substitute x=0 in y,
y = (0+1)2
y = 1
Substitute x=1 in y,
y = (1+1)2
y = 4
Take these point in table of values as shown below,
x
| y = (x+1)2
|
|---|
|
-2
|
1
|
|
-1
|
0
|
|
0
|
1
|
|
1
|
4
|
Plot these points on the graph and then join these points as shown below,

Graph of y=(x+1)2
The graph of y = (x+1)2 is concave up,
Vertex is (x, y) = (-1, 0)
Axis of symmetry is
x = -1
Example 2: Graph the square function y=(-2x-1)2 , find the x-intercept, y-intercept, domain and range?
Solution:
Given square function,
y = (-2x – 2)2
Substitute different x values in y to plot the given function,
Substitute x=-2 in y,
y = (-2(-2)-2)2
y = (4-2)2
y = 4
Substitute x = -1 in y,
y = {-2(-1) – 2}2
y = 0
Substitute x = 0 in y,
y = {-2(0) – 2}2
y = 4
Substitute x = 1 in y,
y = {-2(1) – 2}2
y = 16
Take these point in table of values as shown below,
Plot these points on the graph and then join these points as shown below,
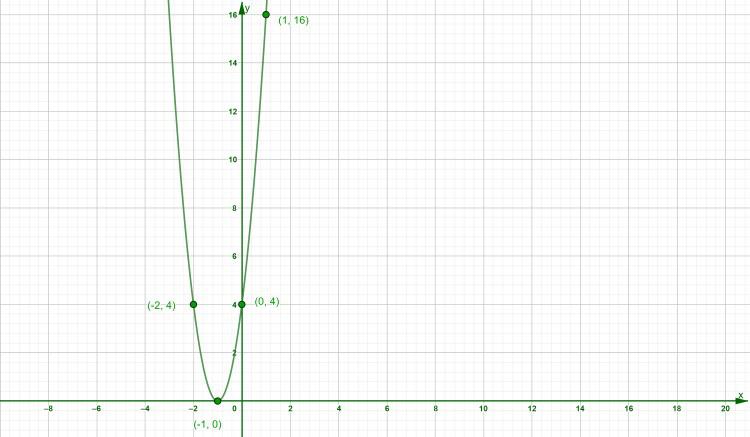
Graph of y=(-2x-2)2
x-intercept: It is the value of x at y = 0.
Substitute y = 0 in y = (-2x – 2)2
0 = (-2x – 2)2
-2x – 2 = 0
2x = -2
x = -2/2
x = -1
x-intercept is (x, y)= (-1,0)
y-intercept: It is the value of y at x=0,
Substitute x = 0 in y = (-2x-2)2 ,
y = (-2(0)-2)2
y = (0-2)2
y = 4
y-intercept is (x, y) = (0, 4)
Use (a+b)2= a2+b2+2ab
(-2x-2)2= (-2x)2+ (-2)2+2(-2x)(-2)
(-2x-2)2 = 4x2+4+8x
Given square function is the parabola of the form ax2+bx+c with vertex (xv , yv ),
If a< 0, range is [Tex]f(x)\leq y_v[/Tex]
If a> 0, range is [Tex]f(x)\geq y_v[/Tex]
Here a=1,
Substitute y=0 in y=(-2x-2)2,
(-2x-2)2=0
-2x-2 = 0
2x = -2
x = -1
Vertex is (xv , yv ) = (-1,0) [which is shown in the graph],
as a = 4 > 0
Domain is set of x values,
Domain = (-∞, +∞)
Example 3: Check whether y = x2 + x is square function or not.
Solution:
Given,
Substitute x = -x in f(x),
f(-x) = (-x)2 + (-x)
f(-x) = x2– x
As,
f(x) is not equals to f(-x)
y = x2+x is not a square function
Example 4: Find the domain of the square function y=(x+1)2
Solution:
Given square function y = (x+1)2,
The function has no undefined points,
Domain is set of x values,
Domain is Real numbers
Example 5: Find the range of the square function y=(x+1)2.
Solution:
Given square function y=(x+1)2,
Using formula,
(a+b)2 = a2+b2+2ab
(x+1)2= x2+12+2(x)(1)
(x+1)2= x2+2x+1
Given square function is the parabola of the form ax2+bx+c with vertex (xv, yv),
If a< 0, range is f(x) <= yv
If a> 0, range is f(x) >= yv
Here a=1,
Substitute y=0 in y=(x+1)2,
(x+1)2 = 0
x+1 = 0
x = -1
Vertex is (xv , yv) = (-1, 0)
Range is set of y values,
Range is f(x) >= yv
Substitute yv = 0 in above,
Range is y > = 0
Practice Questions on Square Function
Question 1: Graph the square function y = (-x+7)2
Question 2: Find the x and y intercept of the square function y = (3x+4)2
Question 3: Find the domain and range of the square function y = (2x-21)2.
Question 4: Find the domain and range of the square function y = (x-12)2.
FAQs on Square Function
What is a square function?
A square function is also called a quadratic function is a function in which the highest degree of independent variable(x) is 2 and is generally represented as: y = (ax + b)2
What is the formula for a squared function?
A square function is represented as: f(x) = ax2 + bx + c.
What is an example of squared function?
Square function also called Quadratic function is defined as: f(x) = ax2 + bx + c, where a ≠ 0. Some examples of quadratic functions are: f(x) = 2x2 + 4x – 5, f(x) = (x + 11)2, etc.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...