SQL Query to find an employee whose salary is equal to or greater than a specific number
Last Updated :
07 Apr, 2021
In this article, we will discuss the overview of SQL query and our main focus will be on how to Find an Employee whose salary is equal to or greater than a specific number in SQL with the help of examples. Let’s discuss it one by one.
Introduction :
SQL (Structured Query Language ) is used to maintain structured data in relational databases and this is a standard that is used to manipulate data in databases. SQL is further classified into DDL(Data Definition Language), DML(Data Manipulation Language), DCL (Data Control Language) based on purpose in a database we use commands related to these. Queries in SQL allow us to interact with databases. Queries in DBMS helps in the creation, deletion, updating, and retrieval of data from a database.
Step-1: Creating a sample table –
Creating this table employee step_by_step in MySQL.
| emp_id |
emp_name |
emp_sex |
emp_age |
emp_salary |
|
90001
|
ROBERT |
MALE |
35
|
100000
|
|
90002
|
KISNEY |
MALE |
30
|
80000
|
|
90003
|
ANDRIA |
FEMALE |
45
|
300000
|
|
90004
|
JESSICA |
FEMALE |
40
|
250000
|
|
90005
|
DANNY |
MALE |
38
|
150000
|
Step-2: Creating a database –
Creating a database using the query as follows.
Syntax :
CREATE DATABASE database_name;
Creating a database company as follows.
CREATE DATABASE company;
Output :

Step-3: Using the database –
Using the database company using the following SQL query as follows.
syntax: USE database_name;
Output :

Step-4: Adding a table –
Adding a table employee into a database company using the following SQL query as follows.
Syntax :
CREATE TABLE table_name
( column_name1 data_type1 ,
column_name2 data_type2 ,
column_name3 data_type3 ,
.
.
column_nameN data_typeN , );
SQL Query for Creating a table as follows.
Creating a table employee
with
columns (emp_id,emp_name,emp_sex,emp_age,emp_salary)
into a database company:
Output :

Step-5: Verifying column and data types –
Columns and their data types by DESCRIBE query as follows.
Syntax :
DESCRIBE table_name;
SQL Query for verifying Columns and their data types as follows.
DESCRIBE employee;
Output :

Step-6: Inserting rows into a table employee –
Here, Inserting rows into a table employee as follows.
Syntax :
INSERT INTO table_name
VALUES(column1_data,column2_data,......columnN_data);
Inserted data of 5 employees in the table and created the table employee as follows.
Output :

Step-7: Verifying Inserted data –
Check the inserted data in the database using the select query as follows.
SELECT * FROM employee;
Output :

Examples :
Here, we will see the examples to understand the query as follows.
Example-1 :
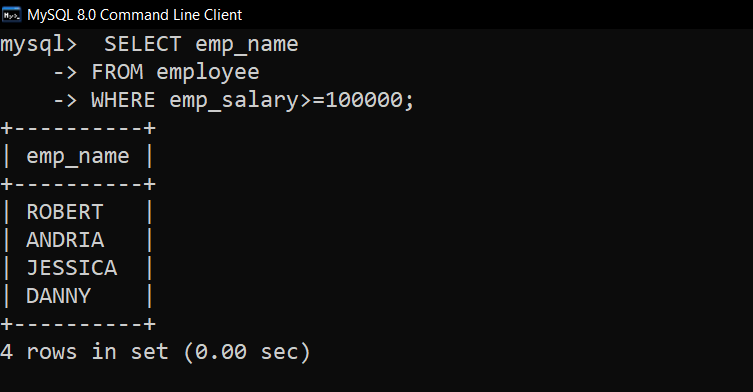
Query to find the employee names whose salary is greater than or equal to 1,00,000.
SQL Query –
SELECT emp_name
FROM employee
WHERE emp_salary>=100000;
Output :
Example-2 :
Query to find all details of employees whose salary is greater than or equal to 2,00,000.
SQL Query –
SELECT emp_name
FROM employee
WHERE emp_salary>=200000;
Output :

Example-3 :
Query to find an employee whose salary is 3,00,000.
SQL Query –
SELECT emp_name
FROM employee
WHERE emp_salary=300000;
Output :

Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...