Sort elements by frequency | Set 4 (Efficient approach using hash)
Last Updated :
02 Jun, 2023
Print the elements of an array in the decreasing frequency if 2 numbers have the same frequency then print the one which came first.
Examples:
Input : arr[] = {2, 5, 2, 8, 5, 6, 8, 8}
Output : arr[] = {8, 8, 8, 2, 2, 5, 5, 6}
Input : arr[] = {2, 5, 2, 6, -1, 9999999, 5, 8, 8, 8}
Output : arr[] = {8, 8, 8, 2, 2, 5, 5, 6, -1, 9999999}
We have discussed different approaches in below posts :
Sort elements by frequency | Set 1
Sort elements by frequency | Set 2
Sorting Array Elements By Frequency | Set 3 (Using STL)
All of the above approaches work in O(n Log n) time where n is total number of elements. In this post, a new approach is discussed that works in O(n + m Log m) time where n is total number of elements and m is total number of distinct elements.
The idea is to use hashing.
- We insert all elements and their counts into a hash. This step takes O(n) time where n is number of elements.
- We copy the contents of hash to an array (or vector) and sort them by counts. This step takes O(m Log m) time where m is total number of distinct elements.
- For maintaining the order of elements if the frequency is the same, we use another hash which has the key as elements of the array and value as the index. If the frequency is the same for two elements then sort elements according to the index.
The below image is a dry run of the above approach:
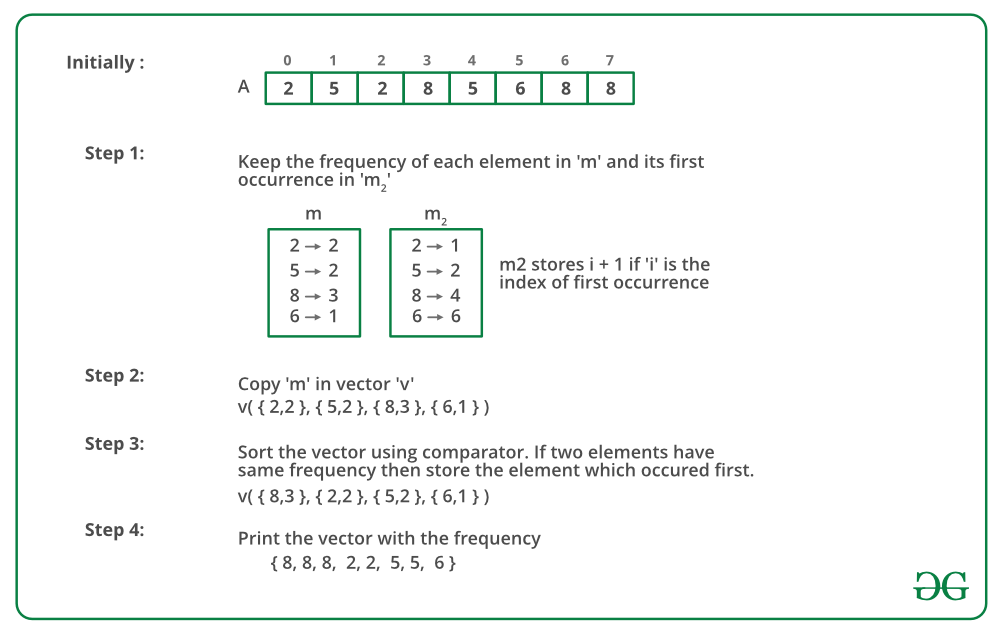
We do not need to declare another map m2, as it does not provide the proper expected result for the problem.
instead, we need to just check for the first values of the pairs sent as parameters in the sortByVal function.
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
bool sortByVal(const pair<int, int>& a,
const pair<int, int>& b)
{
if (a.second == b.second)
return a.first < b.first;
return a.second > b.second;
}
vector<int>sortByFreq(int a[], int n)
{
vector<int>res;
unordered_map<int, int> m;
vector<pair<int, int> > v;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
m[a[i]]++;
}
copy(m.begin(), m.end(), back_inserter(v));
sort(v.begin(), v.end(), sortByVal);
for (int i = 0; i < v.size(); ++i)
while(v[i].second--)
{
res.push_back(v[i].first);
}
return res;
}
int main()
{
int a[] = { 2, 5, 2, 6, -1, 9999999, 5, 8, 8, 8 };
int n = sizeof(a) / sizeof(a[0]);
vector<int>res;
res = sortByFreq(a, n);
for(int i = 0;i < res.size(); i++)
cout<<res[i]<<" ";
return 0;
}
|
Python3
from functools import cmp_to_key
def sortByVal(a,b):
if (a[1] == b[1]):
return a[0] - b[0]
return b[1] - a[1]
def sortByFreq(a, n):
res = []
m = {}
v = []
for i in range(n):
if(a[i] in m):
m[a[i]] = m[a[i]]+1
else:
m[a[i]] = 1
for key,value in m.items():
v.append([key,value])
v.sort(key = cmp_to_key(sortByVal))
for i in range(len(v)):
while(v[i][1]):
res.append(v[i][0])
v[i][1] -= 1
return res
a = [ 2, 5, 2, 6, -1, 9999999, 5, 8, 8, 8 ]
n = len(a)
res = []
res = sortByFreq(a, n)
for i in range(len(res)):
print(res[i],end = " ")
|
Java
import java.util.*;
class SortByValue implements Comparator<Map.Entry<Integer, Integer> >
{
public int compare(Map.Entry<Integer, Integer> o1,
Map.Entry<Integer, Integer> o2)
{
if (o1.getValue() == o2.getValue())
return o1.getKey() - o2.getKey();
return o2.getValue() - o1.getValue();
}
}
class GFG
{
static Vector<Integer> sortByFreq(int a[], int n)
{
HashMap<Integer, Integer> m = new HashMap<>();
Vector<Integer> v = new Vector<>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
int x = a[i];
if (m.containsKey(x))
m.put(x, m.get(x) + 1);
else
m.put(x, 1);
}
Vector<Map.Entry<Integer, Integer> > v1 =
new Vector<>(m.entrySet());
Collections.sort(v1, new SortByValue());
for (int i = 0; i < v1.size(); i++)
for (int j = 0; j < v1.get(i).getValue(); j++)
v.add(v1.get(i).getKey());
return v;
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int a[] = { 2, 5, 2, 6, -1, 9999999, 5, 8, 8, 8 };
int n = a.length;
Vector<Integer> v = sortByFreq(a, n);
for (int i = 0; i < v.size(); i++)
System.out.print(v.get(i) + " ");
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
function sortByVal(a,b)
{
if (a[1] == b[1])
return a[0] - b[0];
return b[1] - a[1];
}
function sortByFreq(a, n)
{
let res = [];
let m = new Map();
let v = [];
for (let i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
if(m.has(a[i]))
m.set(a[i],m.get(a[i])+1);
else
m.set(a[i],1);
}
for(let [key,value] of m){
v.push([key,value]);
}
v.sort(sortByVal)
for (let i = 0; i < v.length; ++i)
while(v[i][1]--)
{
res.push(v[i][0]);
}
return res;
}
let a = [ 2, 5, 2, 6, -1, 9999999, 5, 8, 8, 8 ];
let n = a.length;
let res = [];
res = sortByFreq(a, n);
for(let i = 0;i < res.length; i++)
document.write(res[i]," ");
</script>
|
C#
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
class SortByValue : IComparer<KeyValuePair<int, int>>
{
public int Compare(KeyValuePair<int, int> o1, KeyValuePair<int, int> o2)
{
if (o1.Value == o2.Value)
return o1.Key - o2.Key;
return o2.Value - o1.Value;
}
}
class GFG
{
static List<int> sortByFreq(int[] a, int n)
{
Dictionary<int, int> m = new Dictionary<int, int>();
List<int> res = new List<int>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
int x = a[i];
if (m.ContainsKey(x))
m[x]++;
else
m.Add(x, 1);
}
List<KeyValuePair<int, int>> v =
new List<KeyValuePair<int, int>>(m);
v.Sort(new SortByValue());
foreach (KeyValuePair<int, int> kvp in v)
{
for (int i = 0; i < kvp.Value; i++)
res.Add(kvp.Key);
}
return res;
}
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
int[] a = { 2, 5, 2, 6, -1, 9999999, 5, 8, 8, 8 };
int n = a.Length;
List<int> res = sortByFreq(a, n);
foreach (int i in res)
Console.Write(i + " ");
}
}
|
Output
8 8 8 2 2 5 5 -1 6 9999999
Time Complexity: O(n) + O(m Log m) where n is total number of elements and m is total number of distinct elements
Auxiliary Space: O(n)
This article is contributed by Aarti_Rathi and Ankur Singh and improved by Ankur Goel.
Simple way to sort by frequency.
The Approach:
Here In This approach we first we store the element by there frequency in vector_pair format(Using Mapping stl map) then sort it according to frequency then reverse it and apply bubble sort to make the condition true decreasing frequency if 2 numbers have the same frequency then print the one which came first. then print the vector.
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
void the_helper(int a[],vector<pair<int,int>>&res,int n){
map<int,int>mp;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)mp[a[i]]++;
for(auto it:mp)res.push_back({it.second,it.first});
sort(res.begin(),res.end());
}
int main() {
int a[] = {2, 5, 2, 6, -1, 9999999, 5, 8, 8, 8};
vector<pair<int,int>>res;
the_helper(a,res,10);
reverse(res.begin(),res.end());
for(int i=0;i<res.size();i++){
if(res[i].first==res[i+1].first){
for(int j=i;j<res.size();j++){
if(res[i].second>res[j].second&&res[i].first==res[j].first){
swap(res[i],res[j]);
}
}
}
}
for(int i=0;i<res.size();i++){
for(int j=0;j<res[i].first;j++)cout<<res[i].second<<" ";
}
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.util.*;
class Pair{
int first;
int second;
public Pair(int first, int second){
this.first = first;
this.second = second;
}
}
public class Main{
public static void the_helper(int[] a, List<Pair> res, int n){
Map<Integer, Integer> mp = new HashMap<>();
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
if(mp.containsKey(a[i]))
mp.put(a[i], mp.get(a[i])+1);
else
mp.put(a[i], 1);
}
for(Map.Entry<Integer, Integer> entry : mp.entrySet()){
res.add(new Pair(entry.getValue(), entry.getKey()));
}
res.sort((x, y) -> x.first - y.first);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] a = {2, 5, 2, 6, -1, 9999999, 5, 8, 8, 8};
List<Pair> res = new ArrayList<>();
the_helper(a, res, 10);
Collections.reverse(res);
for(int i = 0; i < res.size()-1; i++){
if(res.get(i).first == res.get(i+1).first){
for(int j = i; j < res.size(); j++){
if(res.get(i).second > res.get(j).second && res.get(i).first == res.get(j).first){
Pair temp = res.get(j);
res.set(j, res.get(i));
res.set(i, temp);
}
}
}
}
System.out.println();
for(Pair p : res){
for(int i = 0; i < p.first; i++){
System.out.print(p.second + " ");
}
}
}
}
|
Python3
import collections
def the_helper(a, res, n):
mp = collections.defaultdict(int)
for i in range(n):
mp[a[i]] += 1
for key, val in mp.items():
res.append((val, key))
res.sort()
if __name__ == '__main__':
a = [2, 5, 2, 6, -1, 9999999, 5, 8, 8, 8]
res = []
the_helper(a, res, len(a))
res.reverse()
for i in range(len(res) - 1):
if res[i][0] == res[i+1][0]:
for j in range(i+1, len(res)):
if res[i][0] == res[j][0] and res[i][1] > res[j][1]:
res[i], res[j] = res[j], res[i]
for i in range(len(res)):
for j in range(res[i][0]):
print(res[i][1], end=' ')
|
C#
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
public class Program {
public static void the_helper(int[] a, List<Tuple<int,int>> res, int n) {
Dictionary<int,int> mp = new Dictionary<int,int>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (mp.ContainsKey(a[i])) {
mp[a[i]]++;
} else {
mp[a[i]] = 1;
}
}
foreach (var it in mp) {
res.Add(new Tuple<int,int>(it.Value, it.Key));
}
res.Sort();
}
public static void Main() {
int[] a = { 2, 5, 2, 6, -1, 9999999, 5, 8, 8, 8 };
List<Tuple<int,int>> res = new List<Tuple<int,int>>();
the_helper(a, res, 10);
res.Reverse();
for (int i = 0; i < res.Count; i++) {
if (i < res.Count - 1 && res[i].Item1 == res[i+1].Item1) {
for (int j = i; j < res.Count; j++) {
if (res[i].Item2 > res[j].Item2 && res[i].Item1 == res[j].Item1) {
var temp = res[i];
res[i] = res[j];
res[j] = temp;
}
}
}
}
for(int i=0;i<res.Count;i++){
for (int j = 0; j < res[i].Item1; j++) {
Console.Write(res[i].Item2 + " ");
}
}
}
}
|
Javascript
class pair{
constructor(first, second){
this.first = first;
this.second = second;
}
}
function the_helper(a, res, n){
mp = new Map();
for(let i = 0; i<n; i++){
if(mp.has(a[i]))
mp.set(a[i], mp.get(a[i])+1);
else
mp.set(a[i], 1);
}
mp.forEach(function(value, key){
res.push(new pair(value, key));
})
res.sort(function(a, b){
return a.first - b.first;
});
}
let a = [2, 5, 2, 6, -1, 9999999, 5, 8, 8, 8];
let res = [];
the_helper(a, res, 10);
res.reverse();
for(let i = 0; i < res.length-1; i++){
if(res[i].first == res[i+1].first){
for(let j = i; j < res.length; j++){
if(res[i].second > res[j].second && res[i].first == res[j].first){
let temp = res[j];
res[j] = res[i];
res[i] = temp;
}
}
}
}
console.log("\n");
for(let i = 0; i < res.length; i++){
for(let j = 0; j < res[i].first; j++){
console.log(res[i].second + " ");
}
}
|
Output
8 8 8 2 2 5 5 -1 6 9999999
Time Complexity: O(n^2) I.e it take O(n) for getting the frequency sorted vector but for sorting in decreasing frequency if 2 numbers have the same frequency then print the one which came first we use bubble sort so it take O(n^2).
Auxiliary Space: O(n),for vector.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...