The advantages of electricity compared to other electronic products are mobility and flexibility. Electrical energy can be transported anywhere through several wires and converted into light, heat, or movement according to the user’s needs.
A circuit or grid is a network of interconnected electrical components that together form a closed path so that electric current can flow continuously.
Mathematically, we know how to solve problems as functions representing the names of the fields. We are particularly interested in presidents who meet certain standards of judgment. So here we focus mainly on the events that leaders represent over time. However, it is also possible to have spatial symbols with different dimensions, such as 2D images and 3D MRI scans. We can also have “spacetime” characters; you can think of video as a 3D signal with two dimensions and a physical time. Electromagnetic waves or sound waves propagating in space are often parameterized as four-dimensional signals with three spatial dimensions and one-time dimensions. Further, we discuss the working of signals and their types.
In this article, we will be going through Signals, First, we will start with the Definition of Signals, and then we will go through different types of signals and parameters, After that we will go through what is digital signal processing and then go through signals and notation where we will go through Basic, Functional, periodic and Geometric Signals. At last, we will conclude our Article with some of its Applications and FAQs.
Signal
A signal is a function of one or more variables that indicate some (usually physical) phenomenon. Signal Serves as Carriers of information between communication devices. They can Convey Different types of information depending on the Application required. These signals can be of different forms.
Examples of Signals
- Human voice
- Voltage in electrical circuits
- Room temperature controlled by a thermostat system
- Position, speed, and acceleration of an aircraft
- Accelerometers measured with accelerometers in mobile phones
- Force measured with force sensors in robotic systems
- Electromagnetic waves used to transmit information in wireless computer networks
- Digital photographs • Digital Music Recording.
Types of Signals
There Are Different Types of Signals Which are given Below:
- Analog Signals
- Digital Signals
- Real and Complex Signals
- Deterministic and Random Signals
- Periodic and Non-periodic Signals
1. Analog Signals
This signals are continues (e.g., a real variable) and infinitely varying with time parameter or can take any value within a given range.
- This signals are represented by the sine wave
- Example Like audio signals, temperature readings, sound waves or television waves.

Analog Signal Graph
2. Digital Signals
A signal that is a function of discrete variables (e.g., an integer variable) is said to be discrete time and this are represent in binary form (0s and 1s).
- More robust against noise.
- Commonly used in computer systems and telecommunications.

Digital Signal Graph
3. Real and Complex Signals
If the value of the signal x(t) is a real number, the signal x(t) is also a real signal; If the value of the signal x(t) is a complex number, the signal x(t) is complex. signal. In general, the complex signal x(t) is a function of the form
x(t)= x1(t) + jx2(t) ———————-(1.1)
where x1(t) and x2(t) are real symbols, j = V-1.
Please note that in equation (1.1) t represents a constant variable or the difference between the two.
4. Deterministic and Random Signals
A deterministic signal is one whose value is always specified exactly. Therefore, the decision signal can be modeled by knowing time t. A random signal is one that takes a significant amount of time and needs to be characterized.
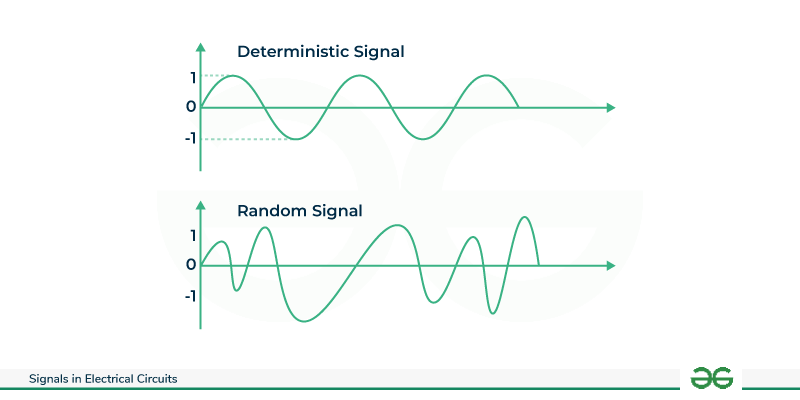
Deterministic and Random Signal Graph
5. Periodic and Non-periodic Signals
A continuous signal is a signal of infinite duration that repeats the same pattern over and over again.
One-sided or time-limited signals can never be periodic. Any continuous-time signal which is not periodic signal is known as non-periodic (or aperiodic) signal.

Periodic Signal Graph

Aperiodic signal Graph
Signal Parameters

Signal Paramter Graph
Digital Signal Processing
Analog signals have been the subject of many studies in the past. In recent years, digital signals have begun to attract more and more attention. As for numbers, they can be processed by the same logic circuits used in digital computers.
Below figure shows two good ideas for signal processing. Digital processing of analog signals requires that we use an analog to digital converter (ADC) to sample the analog signal before processing and a digital-to-analog converter (DAC) to convert the processed digital signal back to Analog form.
.png)
Analog to Digital
Few technologies change the world as much as those that act as digital barriers. For example, until recently, music recording technology was comparable throughout, and music’s most important product was used to make LP (long-play) records. Digital discs replaced all of this in just a few years, making long playing records almost obsolete. Analog and digital signals are the subject of this and many other applications.
Signals and Notation
Different Signals and Notation are Given Below :
- Basic Signals
- Periodic Signals
- Functional signals
- Geometric signals
1. Basic Signals
- Unit Step
- Unit Impulse Signals
- Unit Ramp signal
- Unit parabolic signal
1.1. Unit Step
The continuous time function u(t) is defined as a positive function for its discrete time counterpart, the unit step is discontinuous at t=0.

Unit Step
1.2. Unit Impulse Signals
The continuous-time unit impulse function 8(t) is related to the unit step in a manner analogous to the relationship between the discrete-time unit impulse and step functions. Specifically, the continuous-time unit step function is obtained by performing the running integral of the unit impulse function..
We can think of a pulse as a long, narrow pulse for a region, as shown in Figure. The width of the rectangular pulse is as small as ε → 0. Therefore, its height 1/ε → ∞ is a very large value. The impact chamber can therefore be thought of as a rectangular pulse whose width will be infinitely small, its height will be infinitely large, and all areas are still together. Therefore, only when t= 0 is δ(t) = 0 undefined. Therefore the unit blow is represented by the symbol spear.

Unit Impulse Signals
1.3. Unit Ramp Signal
This signal is define as it starts from t=0 and always increasingly Linearly.
The function r(t) means that the signal will start at time zero and immediately assume a slope, and depending on the given time characteristics (e.g. positive or negative good, good), the signal will follow a straight and curved path. Right or left, here it is on the right.
.png)
Unit Ramp Signal
Therefore the ramp function r(t) is a critical function that exists only on the positive side and is zero on the negative side. And can be expressed in the form of an equation as shown below .
1.4. Unit Parabolic Signal
The amplitude increases with the square of time.

Unit Parabolic Signal
2. Periodic Signals
Sinusoidal Signals
A continuous time sine wave signal can be displayed
x(t) =A cos (ωt + θ )
where A is the amplitude (real ), ω is the radian frequency in radians per second, and θ is the phase angle in radians.
.png)
Sinusoidal Signals
3. Functional Signals
- Sinc Function
- Signum Function
- Continuous-Time Complex Exponential
3.1. Sinc Function
Since time oscillates sinusoidally and the ideal 1/t decreases with time, sinc(t) exhibits decreasing oscillations. At t = 0 the sinc function takes the indefinite form 0/0. These signal plays a very
important role in Fourier analysis, communication systems, and signal processing.

Sinc Functions
3.2. Signum Function
Another function that is closely related to the unit step function is the named function. The sIgn represented by the symbol function is defined as follows :

Signum Function
3.3. Continuous-Time Complex Exponential
- Real exponential signals: c and a are real. Where C and a are, in general, complex numbers

Continuous-Time Complex Exponential Graph
If a Is positive, x(t) grows exponentially as t increases, and this form is used to describe many different physical processes, including communication in atomic explosions and complex chemistry Reaction.
If either a is negative, then x(t) is a decay exponent; This signal is also used to describe many phenomena, including the radio decay process and the response systems of RC circuits and damped machines.
General Complex Exponential Signals
- Therefore, when r = 0 the real and imaginary parts of the complex exponential are sinusoids.
- r > 0 they correspond to the sinusoidal signal multiplied by the growth exponent, and for
- r < 0 they correspond to the sinusoidal signal multiplied by the decay exponent.

General Complex Exponential Signals Graph
4. Geometric signals
- Rectangular signal and Triangular signal
Rectangular Signal and Triangular Signal
The rectangular pulse rect(t) and triangular pulse tri(t) are defined as Both are properly symmetrical and have unit area and unit height.
.png)
Rectangular and Trianagular Signal
Applications of Signals in Electrical Circuits
Applications of Signals in Electrical Circuits are given below :
Communication Systems
- Signals are serving as data in communication signals.
- In Telephone and wireless communication is based on the signal Transmission.
Audio Systems
- Analog signals are present during the audio system and represent changes in audio parameters.
- The signal is still used in audio dispensation and storage today.
Signal Processing
- Filtering and processing are the most important for some applications like audio and video processing.
- Adjustment and Judgment techniques are used to control the signals.
Radar and Sonar Systems
- Radar and sonar systems use signals to sense and locate objects.
- When the output object is interrupted or intermittent by any other object after that the return signal is analyzed to obtain information.
Medical Imaging
- To detect the human body so many new medical imaging technologies (such as MRI and CT scans) use the signals
- Signals are in the form of electromagnetic waves. So, they are manipulated to produce diagnostic images
Comparison between Analog and Digital Signal
|
Features
|
Analog Signal
|
Digital Signal
|
|
Representation
|
It has Continuous waveforms and infinite number of values.
|
This is discrete and finite values.
|
|
Representation medium
|
such as voltage, current and sound waves.
|
In Binary digits
|
|
Waveform
|
Smooth and continuous curve
|
Step-wise changes
|
|
Accuracy
|
Sensitive to noise and interface.
|
Less Sensitive to noise and interface.
|
|
Processing
|
Complex processing
|
Easy processing and flexible.
|
|
Bandwidth
|
Bandwidth consumption is variable.
|
Bandwidth consumption is fixed.
|
|
Device Compatibility
|
This are compatible with traditional devices such as analog cameras, analog audio systems etc.
|
This are compatible with modern devices such as computers, smartphones etc.
|
|
Power consumption
|
Use more power.
|
Use less Power.
|
|
Example
|
Temperature, flow measurement etc.
|
Motor start, trip etc.
|
Conclusion
In the circuit, signals follow the script that controls the operation of electronic devices. Whether analog signals or digital signals, periodic or aperiodic signals, deterministic and random signals, we can say that the signals are information systems for communication, control and processing. As technology advances, understanding and controlling signals becomes important. From simple sine to digital model, signals still form the basis of innovation in electrical engineering.
FAQs on Signals
What role do signals play in communication?
Signals are act as messengers in communication. They smooth the progress of data transfer in telephone and wireless communications.
How are audio signals used?
In audio systems, analog signals represent changes in sound parameters, while digital signals ar e used in daily
What are the major classifications of the signal?
Answer; (i) Discrete time signal (ii) Continuous time signal
What are the types of Fourier series?
Different Types of Fourier Series are
- Exponential Fourier series
- Trigonometric Fourier series
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...