SAS | How to specify a list of Variables?
Last Updated :
23 Jul, 2019
Suppose you have a list of variables. You don’t want to type the name of each variable every time to define them within the function or array. You are looking for a shortcut to accomplish this task.
Create a dataset with a list of variables
data dummy;
input a1 a3 a4 a2 a6$ bs$ a5;
cards;
2 1 3 5 aa xy 2
2 5 4 1 ab xz 4
2 7 3 9 ac wx 3
;
run;
|
Output:
How to specify a list of variables
A single dash (-) refers to specify consecutive numbered variables. For example: a1-a4;
A double dash (–) refers to specify variables based on the order of the variables as they appear/entered in the file, regardless of the name of the variables.
data dummy1 (drop= a1
set dummy;
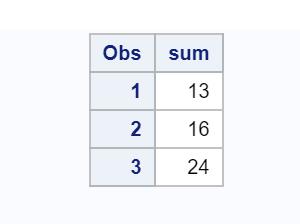
sum = sum(of a1-a4);
sum1 = sum(of a1
run;
|
Output:

In the above program, a1-a4 includes a1, a2, a3 and a4, whereas a1--a4 includes a1, a3 and a4 only as they appear the same way in file.
How to specify all NUMERIC variables
data dummy1 (drop= a1
set dummy;
sum = sum(of _numeric_);
run;
|
Output:
How to use double dash in array
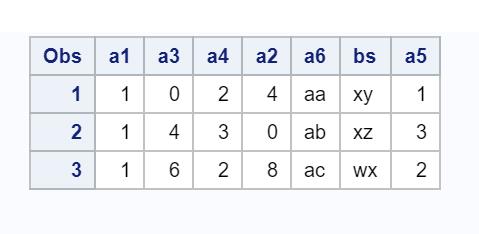
The below-defined program will subtract one from values in variables a1, a3 and a4.
data dummy1;
set dummy;
array vars a1
do over vars;
vars = vars - 1;
end;
run;
|
Output:

How to use numeric variables in array
The below-defined program will subtract one from values in numeric variables.
data dummy1;
set dummy;
array vars _numeric_;
do over vars;
vars = vars - 1;
end;
run;
|
Output:
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...