response.json() – Python requests
Last Updated :
06 Mar, 2024
Python requests are generally used to fetch the content from a particular resource URL. Whenever we make a request to a specified URL through Python, it returns a response object. Now, this response object would be used to access certain features such as content, headers, etc. This article revolves around how to check the response.json() out of a response object. It is one of the most used methods in the requests module.
How to use response.json() using Python requests?
response.json() is a part of the requests module in Python so, firstly we have to install the requests module in Python. response.json() is widely used to fetch data from APIs. In this article, we will explore how to use response.json() to load JSON data into Python objects.
Parsing Python requests Response JSON Content
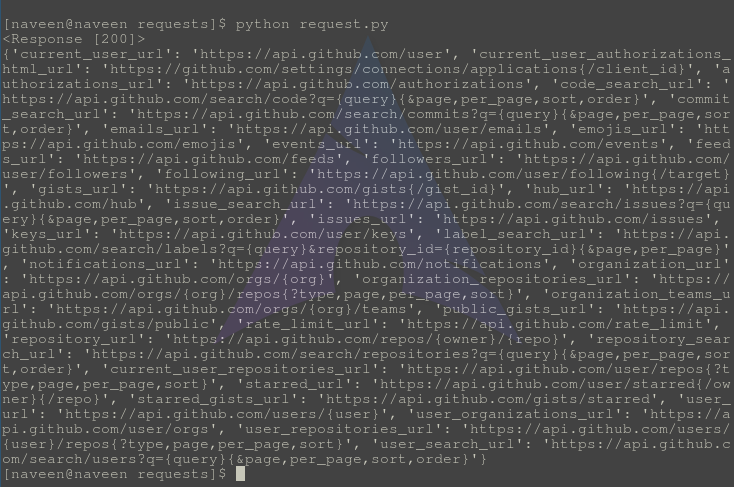
In the below code, firstly we imported the requests module and then fetch the data from an API using requests.get() method and store in variable ‘response’. When we print the response it prints ‘<Response [200]>’ which is the HTTP code that indicates success. To print the JSON data fetched we have used json() method which prints the JSON data in the Python dictionary format as seen in the output. In this way, we can pas parse JSON responses in Python.
Python3
import requests
print(response)
print(response.json())
|
Output:
Convert Request Response to Dictionary in Python
In the below code, we will parse the JSON data and print that data same as we access the keys and values of a dictionary. After making the get request to an API we store the JSON data in a variable “API_Data” using the response.json() method. Then we iterate over the JSON data using for loop and print the data by using the keys.
Python3
import requests
API_Data = response.json()
for key in API_Data:{
print(key,":", API_Data[key])
}
|
Output:
 How to Pretty Print a JSON Object From Python Requests
How to Pretty Print a JSON Object From Python Requests
In the below code, we will pretty print the JSON object that we got from an API using request.get() method. For that after converting the JSON object to the dictionary and stored into “response_dict” we will apply the json.dumps() method on data stored in “response_dict”. We will apply indentation on data by passing the argument “indent=4” and sorting the keys by setting “sort_keys=True” and then printing the data. We can see in the output that data is sorted in increasing order and with indentation.
Python3
import requests
import json
response_dict = response.json()
print(json.dumps(response_dict, indent=4, sort_keys=True))
|
Output:

Advanced Concepts:
There are many libraries to make an HTTP request in Python, which are httplib, urllib, httplib2, treq, etc., but requests are one of the best with cool features. If any attribute of requests shows NULL, check the status code using the below attribute.
requests.status_code
If status_code doesn’t lie in the range of 200-29. You probably need to check the method begin used for making a request + the URL you are requesting for resources.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...