Recursive Insertion Sort
Last Updated :
13 Sep, 2023
Insertion sort is a simple sorting algorithm that works the way we sort playing cards in our hands.
Below is an iterative algorithm for insertion sort
Algorithm
// Sort an arr[] of size n
insertionSort(arr, n)
Loop from i = 1 to n-1.
a) Pick element arr[i] and insert
it into sorted sequence arr[0..i-1]
Example:
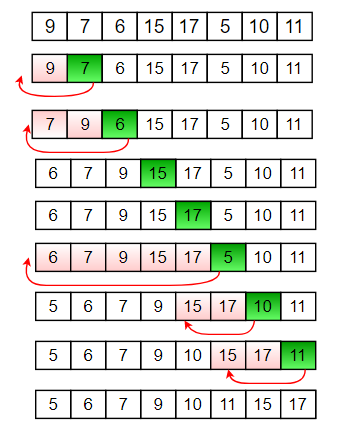
Refer Insertion Sort for more details.
How to implement it recursively?
Recursive Insertion Sort has no performance/implementation advantages, but can be a good question to check one’s understanding of Insertion Sort and recursion.
If we take a closer look at Insertion Sort algorithm, we keep processed elements sorted and insert new elements one by one in the sorted array.
Recursion Idea.
- Base Case: If array size is 1 or smaller, return.
- Recursively sort first n-1 elements.
- Insert last element at its correct position in sorted array.
Below is implementation of above idea.
C++
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void insertionSortRecursive(int arr[], int n)
{
if (n <= 1)
return;
insertionSortRecursive( arr, n-1 );
int last = arr[n-1];
int j = n-2;
while (j >= 0 && arr[j] > last)
{
arr[j+1] = arr[j];
j--;
}
arr[j+1] = last;
}
void printArray(int arr[], int n)
{
for (int i=0; i < n; i++)
cout << arr[i] <<" ";
}
int main()
{
int arr[] = {12, 11, 13, 5, 6};
int n = sizeof(arr)/sizeof(arr[0]);
insertionSortRecursive(arr, n);
printArray(arr, n);
return 0;
}
|
C
#include <stdio.h>
void insertionSortRecursive(int arr[], int n)
{
if (n <= 1)
return;
insertionSortRecursive(arr, n - 1);
int last = arr[n - 1];
int j = n - 2;
while (j >= 0 && arr[j] > last) {
arr[j + 1] = arr[j];
j--;
}
arr[j + 1] = last;
}
void printArray(int arr[], int size)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < size; i++)
printf("%d ", arr[i]);
printf("\n");
}
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 12, 11, 13, 5, 6 };
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
insertionSortRecursive(arr, n);
printArray(arr, n);
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.util.Arrays;
public class GFG
{
static void insertionSortRecursive(int arr[], int n)
{
if (n <= 1)
return;
insertionSortRecursive( arr, n-1 );
int last = arr[n-1];
int j = n-2;
while (j >= 0 && arr[j] > last)
{
arr[j+1] = arr[j];
j--;
}
arr[j+1] = last;
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int arr[] = {12, 11, 13, 5, 6};
insertionSortRecursive(arr, arr.length);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));
}
}
|
Python3
def insertionSortRecursive(arr,n):
if n<=1:
return
insertionSortRecursive(arr,n-1)
last = arr[n-1]
j = n-2
while (j>=0 and arr[j]>last):
arr[j+1] = arr[j]
j = j-1
arr[j+1]=last
def printArray(arr,n):
for i in range(n):
print(arr[i],end=" ")
arr = [12,11,13,5,6]
n = len(arr)
insertionSortRecursive(arr, n)
printArray(arr, n)
|
C#
using System;
class GFG
{
static void insertionSortRecursive(int []arr,
int n)
{
if (n <= 1)
return;
insertionSortRecursive(arr, n - 1);
int last = arr[n - 1];
int j = n - 2;
while (j >= 0 && arr[j] > last)
{
arr[j + 1] = arr[j];
j--;
}
arr[j + 1] = last;
}
static void Main()
{
int []arr = {12, 11, 13, 5, 6};
insertionSortRecursive(arr, arr.Length);
for(int i = 0; i < arr.Length; i++)
Console.Write(arr[i] + " ");
}
}
|
PHP
<?php
function insertionSortRecursive(&$arr, $n)
{
if ($n <= 1)
return;
insertionSortRecursive($arr, $n - 1);
$last = $arr[$n - 1];
$j = $n - 2;
while ($j >= 0 && $arr[$j] > $last)
{
$arr[$j + 1] = $arr[$j];
$j--;
}
$arr[$j + 1] = $last;
}
function printArray(&$arr, $n)
{
for ($i = 0; $i < $n; $i++)
echo $arr[$i]." ";
}
$arr = array(12, 11, 13, 5, 6);
$n = sizeof($arr);
insertionSortRecursive($arr, $n);
printArray($arr, $n);
?>
|
Javascript
<script>
function insertionSortRecursive(arr,n)
{
if (n <= 1)
return;
insertionSortRecursive( arr, n-1 );
let last = arr[n-1];
let j = n-2;
while (j >= 0 && arr[j] > last)
{
arr[j+1] = arr[j];
j--;
}
arr[j+1] = last;
}
let arr=[12, 11, 13, 5, 6];
insertionSortRecursive(arr, arr.length);
for(let i=0;i<arr.length;i++)
{
document.write(arr[i]+" ");
}
</script>
|
Output :
5 6 11 12 13
Time Complexity: O(n2)
Auxiliary Space: O(n)
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wObxd4Kx8sE
about the topic discussed above
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...