Difference between Insertion sort and Selection sort
Last Updated :
30 Mar, 2023
Insertion sort and selection sort are two popular sorting algorithms, and their main difference lies in how they select and place elements in a sorted sequence.
Selection Sort:
- In selection sort, the input array is divided into two parts: a sorted part and an unsorted part.
- The algorithm repeatedly finds the minimum element in the unsorted part and swaps it with the leftmost element of the unsorted part, thus expanding the sorted part by one element.
- Selection sort has a time complexity of O(n^2) in all cases.
Insertion Sort:
- In insertion sort, the input array is also divided into two parts: a sorted part and an unsorted part.
The algorithm picks up an element from the unsorted part and places it in the correct position in the sorted part, shifting the larger elements one position to the right.
Insertion sort has a time complexity of O(n^2) in the worst case, but can perform better on partially sorted arrays, with a best-case time complexity of O(n).
Main differences:
- Selection sort scans the unsorted part to find the minimum element, while insertion sort scans the sorted part to find the correct position to place the element.
Selection sort requires fewer swaps than insertion sort, but more comparisons.
Insertion sort is more efficient than selection sort when the input array is partially sorted or almost sorted, while selection sort performs better when the array is highly unsorted.
In summary, both algorithms have a similar time complexity, but their selection and placement methods differ. The choice between them depends on the characteristics of the input data and the specific requirements of the problem at hand.
Advantages of Insertion Sort:
- Simple and easy to understand and implement.
- Efficient for small data sets or nearly sorted data.
- In-place sorting algorithm, meaning it doesn’t require extra memory.
- Stable sorting algorithm, meaning it maintains the relative order of equal elements in the input array.
Disadvantages of Insertion Sort:
- Inefficient for large data sets or reverse-ordered data, with a worst-case time complexity of O(n^2).
- Insertion sort has a lot of swaps, which can make it slow on modern computers.
Advantages of Selection Sort:
- Simple and easy to understand and implement.
- Efficient for small data sets or nearly sorted data.
- In-place sorting algorithm, meaning it doesn’t require extra memory.
Disadvantages of Selection Sort:
- Inefficient for large data sets, with a worst-case time complexity of O(n^2).
- Selection sort has a lot of comparisons, which can make it slow on modern computers.
- Unstable sorting algorithm, meaning it may not maintain the relative order of equal elements in the input array.
In this article, we will discuss the difference between the Insertion sort and the Selection sort:
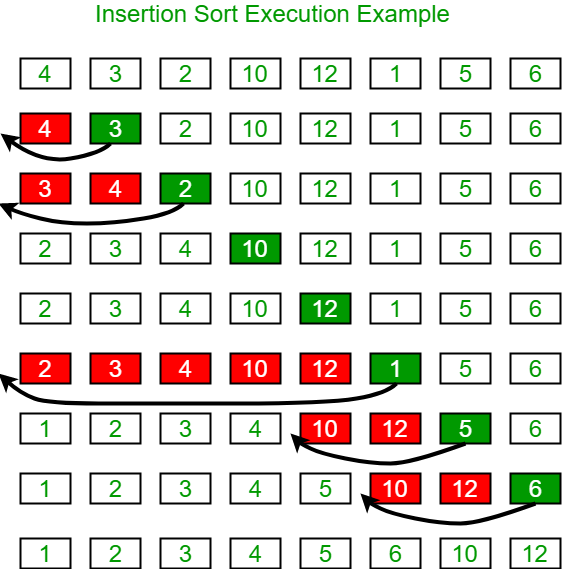
Insertion sort is a simple sorting algorithm that works similar to the way you sort playing cards in your hands. The array is virtually split into a sorted and an unsorted part. Values from the unsorted part are picked and placed at the correct position in the sorted part.
Algorithm:
To sort an array of size n in ascending order:
- Iterate from arr[1] to arr[n] over the array.
- Compare the current element (key) to its predecessor.
- If the key element is smaller than its predecessor, compare it to the elements before. Move the greater elements one position up to make space for the swapped element.
Below is the image to illustrate the Insertion Sort:
Below is the program for the same:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
void insertionSort(int arr[], int n)
{
int i, key, j;
for (i = 1; i < n; i++) {
key = arr[i];
j = i - 1;
while (j >= 0 && arr[j] > key) {
arr[j + 1] = arr[j];
j = j - 1;
}
arr[j + 1] = key;
}
}
void printArray(int arr[], int n)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
cout << arr[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 12, 11, 13, 5, 6 };
int N = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
insertionSort(arr, N);
printArray(arr, N);
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.util.*;
class GFG
{
static void insertionSort(int arr[], int n)
{
int i, key, j;
for (i = 1; i < n; i++)
{
key = arr[i];
j = i - 1;
while (j >= 0 && arr[j] > key)
{
arr[j + 1] = arr[j];
j = j - 1;
}
arr[j + 1] = key;
}
}
static void printArray(int arr[], int n)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
System.out.print(arr[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int arr[] = { 12, 11, 13, 5, 6 };
int N = arr.length;
insertionSort(arr, N);
printArray(arr, N);
}
}
|
Python3
def insertionSort(arr, n):
i = 0
key = 0
j = 0
for i in range(1,n,1):
key = arr[i]
j = i - 1
while (j >= 0 and arr[j] > key):
arr[j + 1] = arr[j]
j = j - 1
arr[j + 1] = key
def printArray(arr, n):
i = 0
for i in range(n):
print(arr[i],end = " ")
print("\n",end = "")
if __name__ == '__main__':
arr = [12, 11, 13, 5, 6]
N = len(arr)
insertionSort(arr, N)
printArray(arr, N)
|
C#
using System;
class GFG
{
static void insertionSort(int[] arr, int n)
{
int i, key, j;
for (i = 1; i < n; i++)
{
key = arr[i];
j = i - 1;
while (j >= 0 && arr[j] > key)
{
arr[j + 1] = arr[j];
j = j - 1;
}
arr[j + 1] = key;
}
}
static void printArray(int[] arr, int n)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
Console.Write(arr[i] + " ");
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
static public void Main()
{
int[] arr = new int[] { 12, 11, 13, 5, 6 };
int N = arr.Length;
insertionSort(arr, N);
printArray(arr, N);
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
function insertionSort(arr,n)
{
let i, key, j;
for (i = 1; i < n; i++)
{
key = arr[i];
j = i - 1;
while (j >= 0 && arr[j] > key)
{
arr[j + 1] = arr[j];
j = j - 1;
}
arr[j + 1] = key;
}
}
function printArray(arr,n)
{
let i;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
document.write(arr[i] + " ");
}
document.write("<br>");
}
let arr=[12, 11, 13, 5, 6];
let N = arr.length;
insertionSort(arr, N);
printArray(arr, N);
</script>
|
The selection sort algorithm sorts an array by repeatedly finding the minimum element (considering ascending order) from the unsorted part and putting it at the beginning. The algorithm maintains two subarrays in a given array.
- The subarray is already sorted.
- The remaining subarray is unsorted.
In every iteration of the selection sort, the minimum element (considering ascending order) from the unsorted subarray is picked and moved to the sorted subarray.
Below is an example to explains the above steps:
arr[] = 64 25 12 22 11
// Find the minimum element in arr[0...4]
// and place it at beginning
11 25 12 22 64
// Find the minimum element in arr[1...4]
// and place it at beginning of arr[1...4]
11 12 25 22 64
// Find the minimum element in arr[2...4]
// and place it at beginning of arr[2...4]
11 12 22 25 64
// Find the minimum element in arr[3...4]
// and place it at beginning of arr[3...4]
11 12 22 25 64
Below is the program for the same:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
void swap(int* xp, int* yp)
{
int temp = *xp;
*xp = *yp;
*yp = temp;
}
void selectionSort(int arr[], int n)
{
int i, j, min_idx;
for (i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {
min_idx = i;
for (j = i + 1; j < n; j++)
if (arr[j] < arr[min_idx])
min_idx = j;
swap(&arr[min_idx], &arr[i]);
}
}
void printArray(int arr[], int size)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < size; i++) {
cout << arr[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 64, 25, 12, 22, 11 };
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
selectionSort(arr, n);
cout << "Sorted array: \n";
printArray(arr, n);
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.util.*;
class GFG
{
static void selectionSort(int arr[], int n)
{
int i, j, min_idx;
for (i = 0; i < n - 1; i++)
{
min_idx = i;
for (j = i + 1; j < n; j++)
if (arr[j] < arr[min_idx])
min_idx = j;
int temp = arr[min_idx];
arr[min_idx]= arr[i];
arr[i] = temp;
}
}
static void printArray(int arr[], int size)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < size; i++) {
System.out.print(arr[i]+ " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int arr[] = { 64, 25, 12, 22, 11 };
int n = arr.length;
selectionSort(arr, n);
System.out.print("Sorted array: \n");
printArray(arr, n);
}
}
|
Python3
def selectionSort(arr, n):
for i in range(n - 1):
min_idx = i
for j in range(i + 1, n):
if (arr[j] < arr[min_idx]):
min_idx = j
arr[min_idx], arr[i] = arr[i], arr[min_idx]
def printArray(arr, size):
for i in range(size):
print(arr[i], end = " ")
print()
if __name__ == "__main__":
arr = [64, 25, 12, 22, 11]
n = len(arr)
selectionSort(arr, n)
print("Sorted array: ")
printArray(arr, n)
|
C#
using System;
public class GFG
{
static void selectionSort(int []arr, int n)
{
int i, j, min_idx;
for (i = 0; i < n - 1; i++)
{
min_idx = i;
for (j = i + 1; j < n; j++)
if (arr[j] < arr[min_idx])
min_idx = j;
int temp = arr[min_idx];
arr[min_idx]= arr[i];
arr[i] = temp;
}
}
static void printArray(int []arr, int size)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < size; i++) {
Console.Write(arr[i]+ " ");
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
int []arr = { 64, 25, 12, 22, 11 };
int n = arr.Length;
selectionSort(arr, n);
Console.Write("Sorted array: \n");
printArray(arr, n);
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
function selectionSort(arr, n)
{
let i, j, min_idx;
for(i = 0; i < n - 1; i++)
{
min_idx = i;
for(j = i + 1; j < n; j++)
if (arr[j] < arr[min_idx])
min_idx = j;
let temp = arr[min_idx];
arr[min_idx]= arr[i];
arr[i] = temp;
}
}
function printArray(arr, size)
{
let i;
for(i = 0; i < size; i++)
{
document.write(arr[i] + " ");
}
document.write("<br>");
}
let arr = [ 64, 25, 12, 22, 11 ];
let n = arr.length;
selectionSort(arr, n);
document.write("Sorted array: <br>");
printArray(arr, n);
</script>
|
Output:
Sorted array:
11 12 22 25 64
Tabular Difference between Insertion Sort and Selection Sort:
|
|
Insertion Sort |
Selection Sort |
| 1. |
Inserts the value in the presorted array to sort the set of values in the array. |
Finds the minimum / maximum number from the list and sort it in ascending / descending order. |
| 2. |
It is a stable sorting algorithm. |
It is an unstable sorting algorithm. |
| 3. |
The best-case time complexity is Ω(N) when the array is already in ascending order. It have Θ(N2) in worst case and average case. |
For best case, worst case and average selection sort have complexity Θ(N2). |
| 4. |
The number of comparison operations performed in this sorting algorithm is less than the swapping performed. |
The number of comparison operations performed in this sorting algorithm is more than the swapping performed. |
| 5. |
It is more efficient than the Selection sort. |
It is less efficient than the Insertion sort. |
| 6. |
Here the element is known beforehand, and we search for the correct position to place them. |
The location where to put the element is previously known we search for the element to insert at that position. |
| 7. |
The insertion sort is used when:
- The array is has a small number of elements
- There are only a few elements left to be sorted
|
The selection sort is used when
- A small list is to be sorted
- The cost of swapping does not matter
- Checking of all the elements is compulsory
- Cost of writing to memory matters like in flash memory (number of Swaps is O(n) as compared to O(n2) of bubble sort)
|
| 8. |
The insertion sort is Adaptive, i.e., efficient for data sets that are already substantially sorted: the time complexity is O(kn) when each element in the input is no more than k places away from its sorted position |
Selection sort is an in-place comparison sorting algorithm |
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...