A Python dictionary is a data structure that stores the value in key:value pairs.
Example:
As you can see from the example, data is stored in key:value pairs in dictionaries, which makes it easier to find values.
Python3
Dict = {1: 'Geeks', 2: 'For', 3: 'Geeks'}
print(Dict)
|
Output:
{1: 'Geeks', 2: 'For', 3: 'Geeks'}
Python Dictionary Syntax
dict_var = {key1 : value1, key2 : value2, …..}
What is a Dictionary in Python?
Dictionaries in Python is a data structure, used to store values in key:value format. This makes it different from lists, tuples, and arrays as in a dictionary each key has an associated value.
Note: As of Python version 3.7, dictionaries are ordered and can not contain duplicate keys.
How to Create a Dictionary
In Python, a dictionary can be created by placing a sequence of elements within curly {} braces, separated by a ‘comma’.
The dictionary holds pairs of values, one being the Key and the other corresponding pair element being its Key:value.
Values in a dictionary can be of any data type and can be duplicated, whereas keys can’t be repeated and must be immutable.
Note – Dictionary keys are case sensitive, the same name but different cases of Key will be treated distinctly.
The code demonstrates creating dictionaries with different types of keys. The first dictionary uses integer keys, and the second dictionary uses a mix of string and integer keys with corresponding values. This showcases the flexibility of Python dictionaries in handling various data types as keys.
Python3
Dict = {1: 'Geeks', 2: 'For', 3: 'Geeks'}
print("\nDictionary with the use of Integer Keys: ")
print(Dict)
Dict = {'Name': 'Geeks', 1: [1, 2, 3, 4]}
print("\nDictionary with the use of Mixed Keys: ")
print(Dict)
|
Output
Dictionary with the use of Integer Keys:
{1: 'Geeks', 2: 'For', 3: 'Geeks'}
Dictionary with the use of Mixed Keys:
{'Name': 'Geeks', 1: [1, 2, 3, 4]}
Dictionary Example
A dictionary can also be created by the built-in function dict(). An empty dictionary can be created by just placing curly braces{}.
Different Ways to Create a Python Dictionary
The code demonstrates different ways to create dictionaries in Python. It first creates an empty dictionary, and then shows how to create dictionaries using the dict() constructor with key-value pairs specified within curly braces and as a list of tuples.
Python3
Dict = {}
print("Empty Dictionary: ")
print(Dict)
Dict = dict({1: 'Geeks', 2: 'For', 3: 'Geeks'})
print("\nDictionary with the use of dict(): ")
print(Dict)
Dict = dict([(1, 'Geeks'), (2, 'For')])
print("\nDictionary with each item as a pair: ")
print(Dict)
|
Output:
Empty Dictionary:
{}
Dictionary with the use of dict():
{1: 'Geeks', 2: 'For', 3: 'Geeks'}
Dictionary with each item as a pair:
{1: 'Geeks', 2: 'For'}
Complexities for Creating a Dictionary:
- Time complexity: O(len(dict))
- Space complexity: O(n)
Nested Dictionaries
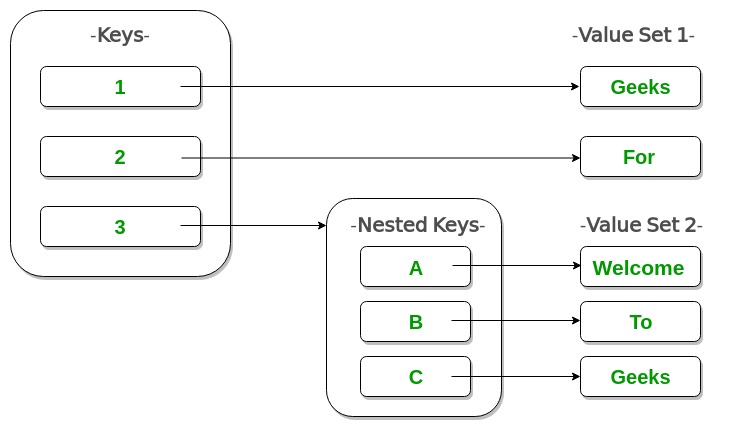
Example: The code defines a nested dictionary named ‘Dict’ with multiple levels of key-value pairs. It includes a top-level dictionary with keys 1, 2, and 3. The value associated with key 3 is another dictionary with keys ‘A,’ ‘B,’ and ‘C.’ This showcases how Python dictionaries can be nested to create hierarchical data structures.
Python3
Dict = {1: 'Geeks', 2: 'For',
3: {'A': 'Welcome', 'B': 'To', 'C': 'Geeks'}}
print(Dict)
|
Output:
{1: 'Geeks', 2: 'For', 3: {'A': 'Welcome', 'B': 'To', 'C': 'Geeks'}}
More on Python Nested Dictionary
Adding Elements to a Dictionary
The addition of elements can be done in multiple ways. One value at a time can be added to a Dictionary by defining value along with the key e.g. Dict[Key] = ‘Value’.
Updating an existing value in a Dictionary can be done by using the built-in update() method. Nested key values can also be added to an existing Dictionary.
Note- While adding a value, if the key-value already exists, the value gets updated otherwise a new Key with the value is added to the Dictionary.
Example: Add Items to a Python Dictionary with Different DataTypes
The code starts with an empty dictionary and then adds key-value pairs to it. It demonstrates adding elements with various data types, updating a key’s value, and even nesting dictionaries within the main dictionary. The code shows how to manipulate dictionaries in Python.
Python3
Dict = {}
print("Empty Dictionary: ")
print(Dict)
Dict[0] = 'Geeks'
Dict[2] = 'For'
Dict[3] = 1
print("\nDictionary after adding 3 elements: ")
print(Dict)
Dict['Value_set'] = 2, 3, 4
print("\nDictionary after adding 3 elements: ")
print(Dict)
Dict[2] = 'Welcome'
print("\nUpdated key value: ")
print(Dict)
Dict[5] = {'Nested': {'1': 'Life', '2': 'Geeks'}}
print("\nAdding a Nested Key: ")
print(Dict)
|
Output:
Empty Dictionary:
{}
Dictionary after adding 3 elements:
{0: 'Geeks', 2: 'For', 3: 1}
Dictionary after adding 3 elements:
{0: 'Geeks', 2: 'For', 3: 1, 'Value_set': (2, 3, 4)}
Updated key value:
{0: 'Geeks', 2: 'Welcome', 3: 1, 'Value_set': (2, 3, 4)}
Adding a Nested Key:
{0: 'Geeks', 2: 'Welcome', 3: 1, 'Value_set': (2, 3, 4), 5:
{'Nested': {'1': 'Life', '2': 'Geeks'}}}
Complexities for Adding Elements in a Dictionary:
- Time complexity: O(1)/O(n)
- Space complexity: O(1)
Accessing Elements of a Dictionary
To access the items of a dictionary refer to its key name. Key can be used inside square brackets.
Access a Value in Python Dictionary
The code demonstrates how to access elements in a dictionary using keys. It accesses and prints the values associated with the keys ‘name’ and 1, showcasing that keys can be of different data types (string and integer).
Python3
Dict = {1: 'Geeks', 'name': 'For', 3: 'Geeks'}
print("Accessing a element using key:")
print(Dict['name'])
print("Accessing a element using key:")
print(Dict[1])
|
Output:
Accessing a element using key:
For
Accessing a element using key:
Geeks
There is also a method called get() that will also help in accessing the element from a dictionary. This method accepts key as argument and returns the value.
Complexities for Accessing elements in a Dictionary:
- Time complexity: O(1)
- Space complexity: O(1)
Example: Access a Value in Dictionary using get() in Python
The code demonstrates accessing a dictionary element using the get() method. It retrieves and prints the value associated with the key 3 in the dictionary ‘Dict’. This method provides a safe way to access dictionary values, avoiding KeyError if the key doesn’t exist.
Python3
Dict = {1: 'Geeks', 'name': 'For', 3: 'Geeks'}
print("Accessing a element using get:")
print(Dict.get(3))
|
Output:
Accessing a element using get:
Geeks
Accessing an Element of a Nested Dictionary
To access the value of any key in the nested dictionary, use indexing [] syntax.
Example: The code works with nested dictionaries. It first accesses and prints the entire nested dictionary associated with the key ‘Dict1’. Then, it accesses and prints a specific value by navigating through the nested dictionaries. Finally, it retrieves and prints the value associated with the key ‘Name’ within the nested dictionary under ‘Dict2’.
Python3
Dict = {'Dict1': {1: 'Geeks'},
'Dict2': {'Name': 'For'}}
print(Dict['Dict1'])
print(Dict['Dict1'][1])
print(Dict['Dict2']['Name'])
|
Output:
{1: 'Geeks'}
Geeks
For
Deleting Elements using ‘del’ Keyword
The items of the dictionary can be deleted by using the del keyword as given below.
Example: The code defines a dictionary, prints its original content, and then uses the ‘del’ statement to delete the element associated with key 1. After deletion, it prints the updated dictionary, showing that the specified element has been removed.
Python3
Dict = {1: 'Geeks', 'name': 'For', 3: 'Geeks'}
print("Dictionary =")
print(Dict)
del(Dict[1])
print("Data after deletion Dictionary=")
print(Dict)
|
Output
Dictionary ={1: 'Geeks', 'name': 'For', 3: 'Geeks'}
Data after deletion Dictionary={'name': 'For', 3: 'Geeks'}
Dictionary Methods
Here is a list of in-built dictionary functions with their description. You can use these functions to operate on a dictionary.
| Method |
Description |
| dict.clear() |
Remove all the elements from the dictionary |
| dict.copy() |
Returns a copy of the dictionary |
| dict.get(key, default = “None”) |
Returns the value of specified key |
| dict.items() |
Returns a list containing a tuple for each key value pair |
| dict.keys() |
Returns a list containing dictionary’s keys |
| dict.update(dict2) |
Updates dictionary with specified key-value pairs |
| dict.values() |
Returns a list of all the values of dictionary |
| pop() |
Remove the element with specified key |
| popItem() |
Removes the last inserted key-value pair |
| dict.setdefault(key,default= “None”) |
set the key to the default value if the key is not specified in the dictionary |
| dict.has_key(key) |
returns true if the dictionary contains the specified key. |
For Detailed Explanations: Python Dictionary Methods
Multiple Dictionary Operations in Python
The code begins with a dictionary ‘dict1’ and creates a copy ‘dict2’. It then demonstrates several dictionary operations: clearing ‘dict1’, accessing values, retrieving key-value pairs and keys, removing specific key-value pairs, updating a value, and retrieving values. These operations showcase how to work with dictionaries in Python.
Python3
dict1 = {1: "Python", 2: "Java", 3: "Ruby", 4: "Scala"}
dict2 = dict1.copy()
print(dict2)
dict1.clear()
print(dict1)
print(dict2.get(1))
print(dict2.items())
print(dict2.keys())
dict2.pop(4)
print(dict2)
dict2.popitem()
print(dict2)
dict2.update({3: "Scala"})
print(dict2)
print(dict2.values())
|
Output:
{1: 'Python', 2: 'Java', 3: 'Ruby', 4: 'Scala'}
{}
Python
dict_items([(1, 'Python'), (2, 'Java'), (3, 'Ruby'), (4, 'Scala')])
dict_keys([1, 2, 3, 4])
{1: 'Python', 2: 'Java', 3: 'Ruby'}
{1: 'Python', 2: 'Java'}
{1: 'Python', 2: 'Java', 3: 'Scala'}
dict_values(['Python', 'Java', 'Scala'])
We have covered all about dictionaries in Python, discussed its definition, and uses, and saw different dictionary methods with examples. The dictionary is an important data structure for storing data in Python. It is very different from tuples and lists.
Read More Data Structures in Python
Also Read:
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...