PostgreSQL – RENAME COLUMN
Last Updated :
17 Jan, 2023
In PostgreSQL, the RENAME COLUMN clause is used with the ALTER TABLE statement to rename one or more columns in a table.
Syntax:
ALTER TABLE table_name
RENAME COLUMN column_name TO new_column_name;
Let’s analyze the above syntax:
- First, specify the table, which contains the column you want to rename, after the ALTER TABLE clause.
- Second, provide the column name after the RENAME COLUMN clause.
- Third, give the new column name after the TO keyword.
Let’s take some examples of using the ALTER TABLE RENAME COLUMN to get a better understanding. Example 1: First, let’s create two new tables namely customers and customer_groups using the below statement:
CREATE TABLE customer_groups (
id serial PRIMARY KEY,
name VARCHAR NOT NULL
);
CREATE TABLE customers (
id serial PRIMARY KEY,
name VARCHAR NOT NULL,
phone VARCHAR NOT NULL,
email VARCHAR,
group_id INT,
FOREIGN KEY (group_id) REFERENCES customer_groups (id)
);
Then we create a new view named customer_data based on the customers and customer_groups tables as follows:
CREATE VIEW customer_data
AS SELECT
c.id,
c.name,
g.name customer_group
FROM
customers c
INNER JOIN customer_groups g ON g.id = c.group_id;
Now we will use the ALTER TABLE RENAME COLUMN statement to rename the email column of the customers table to contact_email:
ALTER TABLE customers
RENAME COLUMN email TO contact_email;
Now verify the changes made using the below statement:
SELECT * FROM customers;
Output: 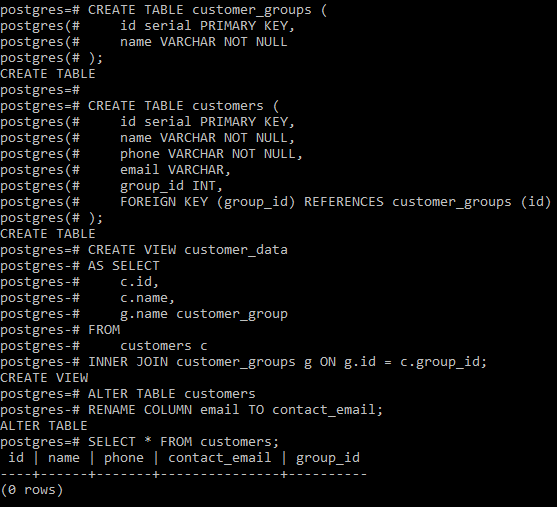 Example 2: These statements rename two columns name and phone of the customers table to customer_name and contact_phone respectively:
Example 2: These statements rename two columns name and phone of the customers table to customer_name and contact_phone respectively:
ALTER TABLE customers
RENAME COLUMN name TO customer_name;
ALTER TABLE customers
RENAME COLUMN phone TO contact_phone;
Now verify the changes made using the below statement:
SELECT * FROM customers;
Output: 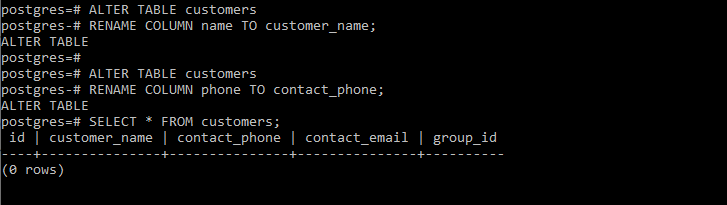
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...