PostgreSQL – Change Column Type
Last Updated :
28 Aug, 2020
In this article, we will discuss the step by step process of changing the data type of a column using the ALTER TABLE statement in PostgreSQL.
Syntax:
ALTER TABLE table_name
ALTER COLUMN column_name [SET DATA] TYPE new_data_type;
Let’s analyze the above syntax:
- First, specify the name of the table to which the column you want to change belongs in the ALTER TABLE clause.
- Second, give the name of column whose data type will be changed in the ALTER COLUMN clause.
- Third, provide the new data type for the column after the TYPE keyword. It is possible to use either SET DATA TYPE or TYPE.
Example:
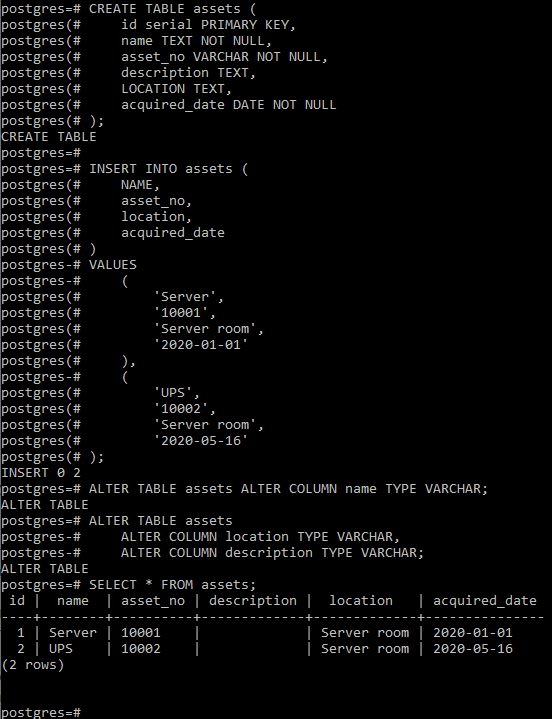
Let’s create a table (say, assets) and insert a few rows into it for the demonstration using the below statement:
CREATE TABLE assets (
id serial PRIMARY KEY,
name TEXT NOT NULL,
asset_no VARCHAR NOT NULL,
description TEXT,
LOCATION TEXT,
acquired_date DATE NOT NULL
);
INSERT INTO assets (
NAME,
asset_no,
location,
acquired_date
)
VALUES
(
'Server',
'10001',
'Server room',
'2020-01-01'
),
(
'UPS',
'10002',
'Server room',
'2020-05-16'
);
Now we will change the data type of the name column to VARCHAR, using the below statement:
ALTER TABLE assets ALTER COLUMN name TYPE VARCHAR;
Now we change the data type of description and location columns from TEXT to VARCHAR using the below statement:
ALTER TABLE assets
ALTER COLUMN location TYPE VARCHAR,
ALTER COLUMN description TYPE VARCHAR;
Now we check the table for the changes made using the below statement:
SELECT * FROM assets;
Output:
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...