PostgreSQL – Create Auto-increment Column using SERIAL
Last Updated :
28 Aug, 2020
In PostgreSQL, a sequence is a special kind of database object that generates a sequence of integers. A sequence is often used as the primary key column in a table.
The SERIAL pseudo-type can be used to generate a sequence while creating a new table.
Syntax:
CREATE TABLE table_name(
id SERIAL
);
In the above syntax by setting the SERIAL pseudo-type to the id column, PostgreSQL performs the following:
- First, create a sequence object and set the next value generated by the sequence as the default value for the column.
- Second, add a NOT NULL constraint to the id column because a sequence always generates an integer, which is a non-null value.
- Third, assign the owner of the sequence to the id column; as a result, the sequence object is deleted when the id column or table is dropped.
The above syntax is equivalent to the below statement:
CREATE SEQUENCE table_name_id_seq;
CREATE TABLE table_name (
id integer NOT NULL DEFAULT nextval('table_name_id_seq')
);
ALTER SEQUENCE table_name_id_seq
OWNED BY table_name.id;
PostgreSQL provides three serial pseudo-types SMALLSERIAL, SERIAL, and BIGSERIAL with the following characteristics:
| Name |
Storage Size |
Range |
| SMALLSERIA |
2 bytes |
1 to 32, 767 |
| SERIAL |
4 bytes |
1 to 2, 147, 483, 647 |
| BIGSERIAL |
8 bytes |
1 to 9, 223, 372, 036, 854, 775, 807 |
Now let’s look into an example for better understanding.
Example:
The following statement creates the animals table with the id column as the SERIAL column:
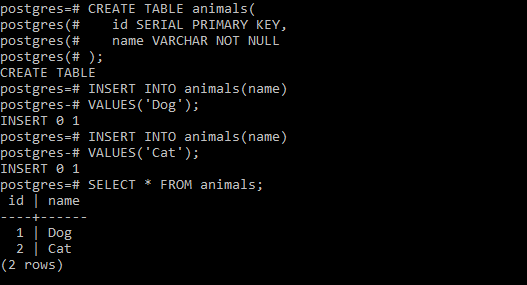
CREATE TABLE animals(
id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
name VARCHAR NOT NULL
);
Now we will insert a single value to the animal table as below:
INSERT INTO animals(name)
VALUES('Dog');
We repeat the above statement wit5h a different value as below:
INSERT INTO animals(name)
VALUES('Cat');
PostgreSQL inserted two rows into the animals table with the values for the id column are 1 and 2. To verify so use the below statement:
SELECT * FROM animals;
Output:
Example 2:
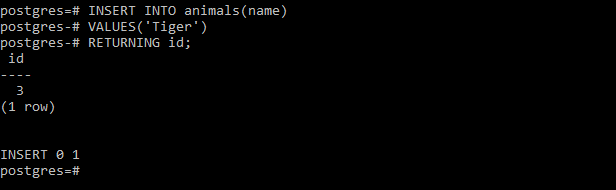
The following statement inserts a new row into the animals table and returns the value generated for the id column:
INSERT INTO animals(name)
VALUES('Tiger')
RETURNING id;
Output:
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...