Plant Ecology Notes
Last Updated :
29 Dec, 2023
Plant ecology deals with the scientific relationship of plants with their environment. In other words, in plant ecology, we study the interaction of plants with the biotic and abiotic factors of the environment. The biotic factors are the living things (organisms) that are associated with plants and the abiotic factors are non-living things (like temperature, water, light, air, gases), etc. Photosynthesis, a chemical process that sustains plant life, is a key feature of plant ecology. The environmental conditions and a plant’s interaction with the environment influence “fitness,” or the ability to flourish.

What is Ecology?
Ecology is a discipline of science that explores the interactions between organisms. Ernst Heckel uses the term “oekologie” in 1866. Hans Reiter, a naturalist, introduced the term ecology in 1868. Ecology, according to Ernst Haeckel, is the study of the reciprocal relationship between organisms and their environment. The term ecology comes from the Greek word oikos, which means “home.” Ecology is made from the words Eco (environment) + logos (research). Eugene Odum is the father of ecology.
Plant Ecology
Plant ecology, is the combination of physiological and morphological “adaptation” is particularly important for plants, as they are fixed in their habitat and the conditions for life are determined by the varieties and numbers of the organisms of the ecosystem and not by the individual plant alone.
The path from stress ecology to ecosystems runs via whole plant ecology and synecology because morphology, i.e. the structure of plants, and the responses of populations are not primarily metabolic.
The diagram, shows the relations between ecophysiology, whole plant physiology and synecology (Ecology of vegetation cover), and ecosystem science where other organisms, not only plants, are increasingly considered.

- At the level of organism ,we consider the plant as a whole and the relations between its organ from the root to the leaf, flower and seed. At the level of whole plant ecology new, not metabolic characteristics are added: although these are genetically determined, they may be modified within limits. These include plant structures including size and life cycle (phenology, life span, strategies for reproduction and distribution).
- Cellular metabolism and structural characteristics are not only the basis for the spatial and temporal patterns of plant species, dealth with in synecology but also the basis of elementary cycles in ecosystems, which are characterised by the diversity of species and forms of organisation. These include indirect interactions between individual plants and other plants species.
- The science of geobotany relates to global aspects in plant ecology, which are included in the term global changes, where the direct and indirect influences of man through land use, changes in land used and the subsequent changes in climate are becoming increasingly felt.
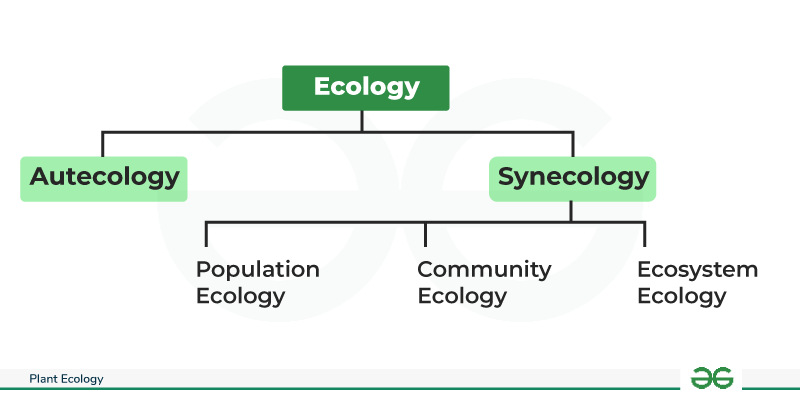
The study of plant ecology is divided into two major divisions: Autecology and Synecology
Autecology
Autecology consider conditions and responses of individual plant species with their habitat. Plants occupied every terrestrial habitat ranging from tropical climates to eternal ice, from moors to deserts and extremely saline habitat.
Synecology
Synecology is the next higher level of plant ecology, extending to populations based on the strategies of propogation and distribution. It doesnot consider the fate of a single individual but the dynamic spatial and temporal behaviour of populations growth, homoestasis and decline.
Abiotic and Biotic Environment Factors Causes Stress on Plants

Biotic Factor of Plant Ecology
A biotic component of an ecosystem is a live component. The term “biotic” is produced by combining the phrases “bio” (life) and “ic” (like). As a result, the phrase refers to all biological organisms in an ecosystem that are life-like. The biotic components of the ecosystem are all living beings. Plants, animals, and microorganisms are examples of biotic factors. Biotic factors, resulting from interactions with other organism for ex- effect of symbiosis or parasitism.
Other organisms are part of the biotic community. Comparable environments in a region have comparable species makeup. However, each species is spread based on its own responses to physical and biotic environmental changes. A community’s species makeup is governed by local species availability, unique historical events, and chance.
Abiotic Components of Plant Ecology
Non-living ecosystem components are referred to as abiotic components. These are the inorganic and organic components and compounds found in the organism’s surroundings or habitat. Physical variables such as temperature, soil, and so on are also considered abiotic components.
These physical parameters are divided into two categories: Climatic factors and Edaphic factors
- Rain, temperature, light, solar energy, wind current, humidity, and moisture were all climatic elements.
- The sun’s radiant energy is the only important energy source for any biosphere.
Global Aspects of Plant Ecology
The plant ecological aspects of global change may be formulated as-
- The interaction between climate and land ecosystems, the effects on terrestrial ecosystems of changes in climate and land use, the effects on the climate of feedback reactions resulting from changes in terrestrial ecosystem.
- Considering these aspects, plant ecology is part of other scientific subjects areas particularly geo-ecology which considers anthropogenic pollutants, in addition to natural material changes.
- Also, biogeochemistry examines material cycles between, atmosphere, air or land. These global material cycles are regulated by organisms particularly with respect to changes at boundary layer between atmosphere and land.
Also Read:
FAQs on Plant Ecology
1. What are the Four main Branches of Plant Ecology?
Plant ecology can also be divided by levels of organization including plant ecophysiology, plant population ecology, community ecology, ecosystem ecology, landscape ecology and biosphere ecology.
2. What is Plant Ecology Major?
Plant ecology is the study of plant interactions with their environment, at the level of individuals, and of how plant-plant interactions mediate environmental interactions at the level of populations, communities, and ecosystems.
3. Why Plant Ecology is Important?
All plants and animals have roles in the environment as they sharing limited natural resources such as air, minerals, space. Lack of ecological studies may be the cause of deprivation and looting of these natural resources. The entire living organism needs energy such as nutrition, light, radiation etc.
4. What is the Role of Plant Ecology?
Plants define forest and grassland systems, shaping hydrologic systems and nutrient cycling, providing the basis for food systems and shelter for wildlife, and often driving local economies.
5. What are the Environmental Factors of Plant Ecology?
Light, water, temperature, humidity, ventilation, fertilization, and soil are chief factors affecting plant growth, and any one of these factors in incorrect proportions will prevent proper plant growth indoors. Light is probably the most essential factor for house plant growth.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...