Five Levels of Ecology
Last Updated :
18 Mar, 2024
The five levels of ecology indicate various ecological levels of organization which is necessary for the survival of life on the earth. An ecosystem also displays interactions on ecological levels between different organisms. The energy flow occurs within ecological levels as bigger organisms eat up smaller organisms. In this article, we will cover the five levels of ecology in order from smallest to largest.
Five Levels of Ecology Definition
Ecology studies various living organisms, their abiotic environment, and how organisms interact with each other and their environment. The ecology can be divided into five levels of ecology – organisms, population, community. ecosystem, and biosphere.
What are the Ecological Level of Organization?
Alexander Von Humboldt is famous as the “Father of Ecology”. Ecology comes from the Greek word “Oekologie” which consists of two parts- “Oikos” ( house or a place to live) and “Logos”( to study). Ernst Haeckel, a German scientist, gave the term “Ecology” in 1866.
The term “ecological level of organisations” defines how the entire biological world, at the individual organism level and above it, is arranged into a particular hierarchy and helps us to study ecology from various aspects. There are five levels of ecological organisations. The 5 levels of ecology in order from smallest to largest can be visualised as a pyramid and they are mentioned as follows-
Organism/Individuals—-> Population —-> Community —-> Ecosystem —-> Biosphere

Organisms/ Individuals
Definition: An organism is a living being with all the characteristics that are essential for the existence of life such as growth, development, capability to respond to any stimulus, reproduction etc.
This is the smallest level of ecology. It is also considered as the fundamental unit of the entire ecology. Organisms can be unicellular ( organisms with only one cell such as Bacteria) and multicellular (organisms with more than one cell such as Humans). Besides this, on the basis of complexity of internal body organisation, organisms can be classified into prokaryotes and eukaryotes.
Prokaryotes are the organisms that do not possess a well developed nucleus. On the other hand, eukaryotes are the organisms which possess well developed nucleus and other cellular organelles.
Also Read: Difference Between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
Population
Definition: Population means a group which consists of organisms of the same species that live in a particular geographical area at the same time and they compete with each other for the resources.
Interbreeding is also seen among the individuals of a population. For Example: A population of wild dogs. All the dogs belong to the same species which live in the same place. They fight against each other for the food and also mate with each other for reproduction.
Also Read: Population Ecology – Definition, Characteristics, Importance, Effects
Defintion: Community refers to various populations that live in the same geographical area at the same time and they are dependent on each other for their survival which means these populations interact with each other.
A community can consists of plants, animals, bacteria, fungi. Various types of interactions can be seen in a community such as competition ( different species of various population compete among each other for food and other resources), predation ( a species or population can consume another population or species), symbiosis (interaction between two species which benefits only one species or can be beneficial for both the species).
Also Read: Community Ecology Definition & Examples
Ecosystem
Definition: An ecosystem refers to one or more communities which interact with their abiotic (non-living factors such as soil, wind, temperature, water etc) physical and chemical environment.
Example- Forest ecosystem, Aquatic ecosystem, Desert ecosystem etc.
Also Read: What is Ecosystem? Definition, Structure, Types, and Functions
Biosphere
It is the largest or highest level of ecological organisation. Biosphere actually means collection of all the ecosystems that can be found on our Earth. It consists of the lithosphere or the outer part of our Earth, troposphere or the lowest layer of atmosphere and the hydrosphere or the entire water resource on our earth. In one word, biosphere refers to the region of Earth where life can be found.
Also Read: What is Biosphere?
What are the 5 Ecological Levels Interactions?
Ecological levels of interactions can be defined as how the organisms of the same species or different species interact with each other in a specific community. Interactions can be of different types-
| Ecological Interactions |
Description |
| Competition |
This occurs when an individual organism or an entire population compete with each other for resources and food. |
| Predation |
It occurs when an individual organism hunts another organism to fulfil its nutritional requirements. |
| Commensalism |
This is the interaction between two individuals where one individual is benefited but the other is neither benefited nor harmed. |
| Parasitism |
This is the interaction between two individuals where the host is harmed and the organism that depends on the host or the parasite gets benefited. |
| Mutualism |
Here, both the individuals involved in this interaction are benefited. |
Also Read: Population Interactions
Examples of Ecological Interactions
Examples of various ecological interactions are given below:
- Two Birds are fighting for a particular worm. (Competition)
- A lion killing a deer for its food. (Predation)
- Birds make their nests on the tree. Here, the tree is not affected by the bird but the bird gets shelter. (Commensalism)
- Lice found on the head of the human. (Parasitism)
- Pollination by bees. Here, bees get food from the flower and the flower is pollinated by the bees. (Mutualism)
Energy Flow Between Ecological Levels
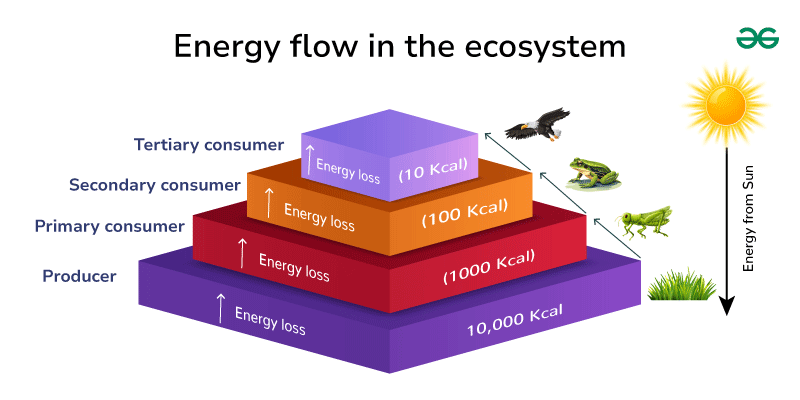
Energy flow means the flow of energy between different living organisms in an ecosystem. The flow of energy is unidirectional. It always occurs from the producers or green plants to the herbivores and from the herbivores, the energy flows to the carnivores. 10 % of energy is lost as heat in each tropic level. Energy flow between ecological levels is very important for maintaining ecological balance.
Conclusion – Five Levels of Ecology
Ecology is the study of various living organisms and how they interact with their environment. To study ecology more minutely, five main levels of ecological organisation have been introduced. These levels help us to know how various living organisms are dependent on each other and as well as to their environment.
Also Read:
FAQs on Five Levels of Ecology
Name the Seven Types of Ecology.
Ecology can be of various types. The seven main types of ecology are Terrestrial ecology, Aquatic ecology, Microbial ecology, Evolutionary ecology, Taxonomic ecology, Population ecology and Behavioral Ecology.
What is the Major Unit of Ecology?
The ecosystem is the major unit of ecology. An ecosystem refers to one or more communities which interact with their abiotic environment.
What is the Highest Level of Ecology?
Five main ecological levels of organisation can be seen in ecology. Among these, the Biosphere is known as the highest level of ecological organisation.
Name the Five Ecological Level of Organisations in order.
The five ecological levels of organisations are arranged according to their size. From smallest to largest, the level of ecological organisations are- organisms—Population—-Community—-Ecosystem—-Biosphere.
Who was the Father of Ecology?
Alexander Von Humboldt is known as the father of ecology. He was a Prussian Botanist.
What is Ecology Level?
Ecology level refers to the hierarchical organization of ecological studies, ranging from individual organisms to the biosphere, encompassing the study of interactions between organisms and their environment at various scales.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...