Pentagon is a two-dimensional, closed geometric shape characterized by five straight sides and five angles. A Pentagon is one of various types of polygons, which constitute a family of two-dimensional geometric shapes formed by connecting straight lines to enclose a region.
In this article, we will discuss Pentagon in detail, including its shape, parts, types, angles, and formulas, as well as some real-life examples of a Pentagon.
What is Pentagon?
A pentagon is a type of polygon that is characterized by having five straight sides and five interior angles. When the term is used, it typically refers to a regular pentagon, where all sides are of equal length and all interior angles are equal, each measuring 108 degrees. The sum of the interior angles of any pentagon is always 540 degrees
Pentagon Meaning
Pentagon is defined as a five-sided polygon. It has five straight sides and a total of five interior angles, that add up to 540°. A Pentagon is classified as a two-dimensional, flat, or plane figure with five sides. These sides are interconnected, forming a closed shape. Hence, a Pentagon is characterized by having exactly 5 sides.
When all the sides and angles of a pentagon are of equal length and measure, it is referred to as a regular Pentagon; otherwise, it is termed an irregular pentagon.
Pentagon Shape
The term “Pentagon” originates from the Greek words “Penta,” which means “five,” and “gonia,” which means “angles.” Thus, a Pentagon is a geometric figure defined by having five sides and five interior angles.
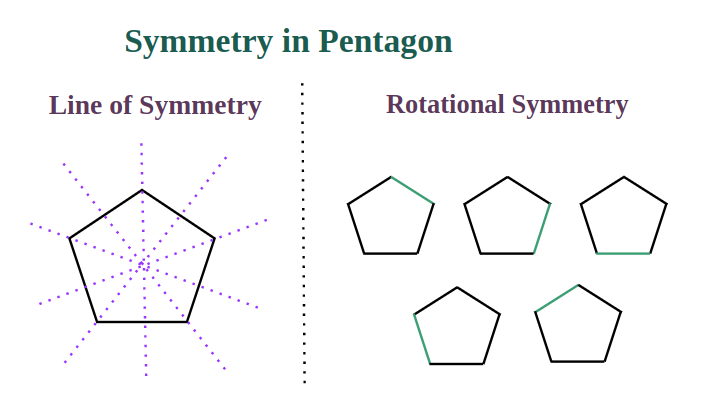
In the case of a regular pentagon, all five sides are equal in length, all five interior angles measure 108 degrees, and the shape possesses both reflectional and rotational symmetry about its center, resulting in five lines of symmetry.
Pentagon Examples in Real-life
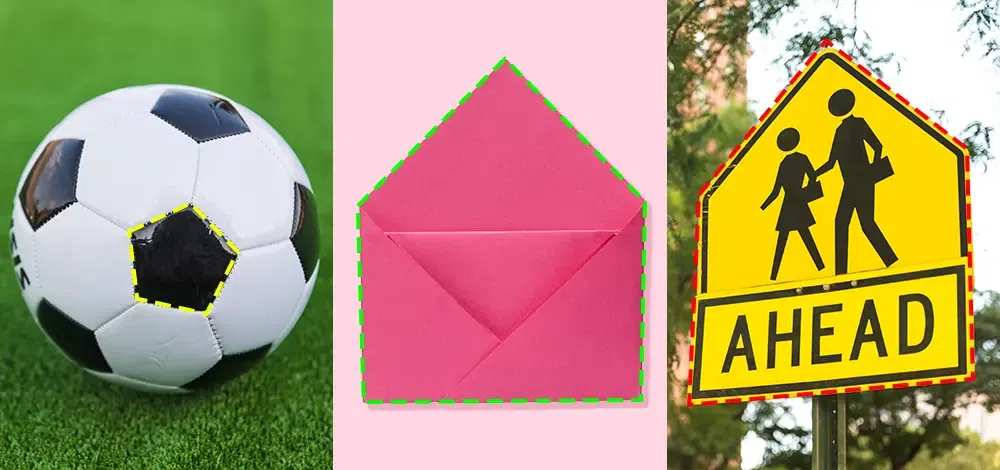
- A diamond can resemble a pentagon with its five sides and five corners.
- The headquarters of the United States Department of Defense is famously known as the Pentagon due to its architectural resemblance to a pentagon shape.
- A football is constructed from several black and white pentagonal patches of five-sided shape.
- Echinoderms like sea stars exhibit a pentagonal symmetry in their body structure.

Parts of Pentagon
Some of the most common parts of pentagon are:
| Term |
Definition |
| Side |
One of the five line segments that together form the pentagon shape. A Pentagon has a total of five sides. |
| Vertex |
A point where two sides of the shape meet. It’s also referred to as a corner. For example, a rectangle has four vertices, forming 90° angles at each corner. |
| Diagonal |
A straight line that connects two non-adjacent vertices. It’s a line drawn between two corners of a 2D figure that are not next to each other. Diagonals of a Pentagon is equal to n × (n − 3) ÷ 2 = 5 × (5 − 3) ÷ 2 = 5. |
Angles in Pentagon
An angle is created when two sides of the Pentagon intersect at a common point known as the Angle’s vertex. In this section, we will explore different types of angles within a pentagon, including
- Interior Angle
- Exterior Angle
Let’s discuss both these angles in details.

Interior Angle of Pentagon
An Interior Angle is the angle formed by two adjacent sides of the shape on the inside. When two straight lines intersect within the shape, they create Interior Angles.
A Pentagon can be thought of as composed of three triangles. Therefore, the Total Sum of Angles in a Pentagon is equivalent to the sum of angles in three triangles, which is 3 times the sum of angles in one triangle (180 degrees). This results in a sum of 540 degrees for the Interior Angles of a Pentagon.
Sum of Interior Angles in any Polygon = 180° × (n − 2)
Where ‘n’ represents the number of sides. In the case of a Pentagon with 5 sides, this formula will be:
Sum of Interior Angles of a Pentagon = 180° × (5 − 2) = 3 × 180° = 540°.
Note: Each Interior Angle of Regular Pentagon is equal to 540° ÷ n = 540° ÷ 5 = 108°.
Exterior Angle of Pentagon
An Exterior Angle is the angle formed by two adjacent sides of the shape on the outside. It measures the angle at a specific vertex but on the exterior of the shape.
The Sum of Exterior Angles in a Pentagon is equal to 360°. To prove that the sum of exterior angles of a polygon is 360°, we can follow these steps:
We know the formula for the sum of interior angles of a regular polygon with ‘n’ sides, which is 180° × (n − 2).
Each interior angle in the polygon can be calculated as: 180° × (n-2)/n .
It’s a known fact that each exterior angle in a polygon is supplementary to its corresponding interior angle.
So, Each exterior angle can be expressed as: [180°n – 180°n + 360°]/n, which simplifies to 360°/n.
To find the Total Sum of Exterior Angles for the polygon, we multiply the number of sides ‘n’ by the measure of each exterior angle (360°/n).
Applying this to a pentagon with 5 sides (n = 5), we observe that the sum of exterior angles for the pentagon is 5 x (360°/5) = 360°
Note: Each exterior angle of a regular pentagon is equal to 360° ÷ n = 360° ÷ 5 = 72°.
Types of Pentagon
Pentagons can be classified into four types depending on their sides, angles, and vertices.
- Based on Length of Side
- Regular Pentagon
- Irregular Pentagon
- Based on Measure of Angle
- Convex Pentagon
- Concave Pentagon
- Some other Types of Pentagon
- Equilateral Pentagon
- Cyclic Pentagon
Regular and Irregular Pentagons
A Regular polygon contains all its sides are of equal length, and all its angles have the same measure. This symmetry ensures that the polygon looks the same from any angle or side. In the case of a Regular Pentagon, it always appears identical.
On the other hand, an Irregular Pentagon lacks this symmetry because it possesses varying side lengths and angles. As a result, the shape may look different when observed from different angles or sides.

Read More: Regular Polygons
Convex and Concave Pentagon
A Convex Pentagon is a polygon in which all its vertices point outwards, creating a shape that does not pointing inwards. In a Convex Pentagon, no internal angles are greater than 180°.
In other words, a Concave Pentagon contains a bowl-like structure between some sides and it has at least one vertex pointing inward. In a Concave Pentagon, at least one internal angle is greater than 180°.

Read More : Convex Polygons
Equilateral Pentagon
An Equilateral Pentagon is a geometric shape where all five sides are of the same length. While the angles within this type of pentagon can vary within a specific range, it is referred to as “equilateral and equiangular” when all sides and angles are equal.

Cyclic Pentagon
A Cyclic Pentagon is a polygon in geometry where all of its vertices are positioned on the circumference of a circle. This characteristic of having its vertices on the circle’s boundary is what defines it as a “cyclic” pentagon. A classic example of a cyclic pentagon is a regular pentagon.
Properties of Pentagon
A Pentagon is a 2D shape featuring five sides and five interior angles. Its key properties include:
The sum of the interior angles in a Pentagon is always 540°.
For a Regular Pentagon:
- All five sides are of equal length.
- All interior angles are congruent, measuring 108° each.
- All exterior angles are also congruent, with a measurement of 72°.
- Regular pentagons have five lines of symmetry, dividing the shape into congruent parts.
- They also possess five rotational symmetries.
- Five diagonals intersect at a common point within the pentagon.
- The ratio of the diagonal’s length to the side’s length in a regular pentagon is the golden ratio, (1 + √5)/2.
Line of Symmetry
The number of lines of symmetry in a regular polygon is equivalent to the number of its sides. These symmetrical lines extend from a vertex to the midpoint of the opposite side, creating a total of 5 lines that divide the pentagon into congruent halves. A regular pentagon has five lines of symmetry: one horizontal, one vertical, and three diagonal.
Area of Pentagon
Formula for finding the area of a Regular Pentagon is as follows:
Area = (5/2) × Side Length × Apothem Length
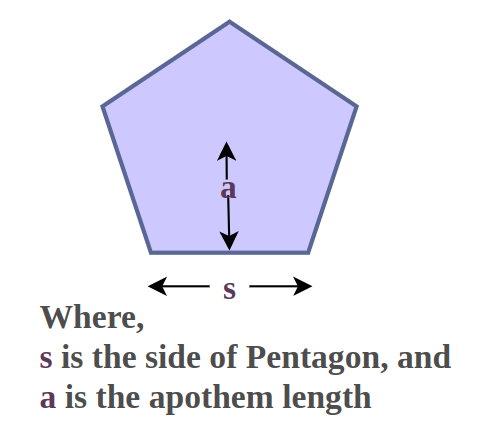
This formula multiplies half of the perimeter (5/2) by the apothem length. It is a key formula to calculate the area of a regular pentagon using its side and apothem measurements.
Apothem is a straight line drawn from the center of a polygon to one of its sides, and it is perpendicular to that side or a segment from the center to the midpoint of a side.
If only the side length of a pentagon is given, then
Area = 5 × side length2 / (4 tan 36°) Square units
If only the radius of a pentagon is given, then
Area = (5/2) × radius2 sin 72° Square units
Area of Irregular Pentagon
To calculate the area of an Irregular Pentagon, we can divide it into smaller triangles or quadrilaterals, calculate the individual areas of these smaller shapes, and then sum them up to find the total area of the Irregular Pentagon.
Read more : Area of Pentagon
Perimeter of Pentagon
It is the total distance covered around the edge of the Pentagon. The formula of perimeter or circumference of a pentagon is written as,
Perimeter = (side 1 + side 2 +side 3 + side 4 + side 5)
To find the Perimeter of a Regular Pentagon, it involves multiplying the length of a single side by five, as all sides in a Regular Pentagon are of equal length.
In the case of an Irregular Pentagon, determining the Perimeter requires adding together the lengths of all five sides since they are not same in length.
People Also Read:
Solved Examples on Pentagon
Example 1: Determine the area of a Regular Pentagon, if Ayushi measures one of its side is 10 cm long, and the apothem (a segment from the center to the midpoint of a side) is 8 cm in length.
Solution:
Given Data,
Length of Apothem = 8 cm
Side Length = 10 cm
Area = ½ × perimeter × apothem.
In this case, the perimeter is 5 times the length of one side, which is 10 cm. So, the formula becomes:
Area = ½ × 5 × 10 × 8.
Solving this equation:
Area = ½ × 5 × 10 × 8 = ½ × 400 = 200 square cm.
Hence, the area of the Regular Pentagon is 200 square cm.
Example 2: Determine the area of Regular Pentagon, if it has the side length of 20 cm and an apothem of 15 cm.
Solution:
Given Data,
Side Length = 20 cm
Length of apothem = 15 cm
Area = ½ × perimeter × apothem.
In this case, the perimeter is 5 times the length of one side, which is 20 cm. So, the formula becomes:
Area = ½ × 5 × 20 × 15.
Solving this equation:
Area = ½ × 5 × 20 × 15 = ½ × 1500 = 750 square cm.
Hence, the area of the Regular Pentagon is 750 square cm.
Example 3: If the perimeter of a Regular Pentagon is 400 cm, find out the length of each side.
Solution:
The perimeter of the Regular Pentagon is 400 cm.
The perimeter of a Regular Pentagon is equal to the product of the number of sides and the length of each side. In this case, there are 5 sides, so:
Perimeter = 5 × Side
Now, we can solve for the length of each side:
400 cm = 5 × Side
To find the length of each side, divide both sides of the equation by 5:
Side = 400 cm / 5 = 80 cm
So, the length of each side of the Regular Pentagon is 80 cm.
Practice Problems on Pentagon
Q1. If the side length of a perimeter is 22 cm, what would be the perimeter of the Pentagon?
Q2. If the perimeter of a Regular Pentagon is 360 cm, what would be the length of each side?
Q3. Find the area of a Pentagon with a side length of 8 cm.
Q4. A Regular Pentagon has a side length 22 cm and length of apothem as 46 cm. What would be its area and perimeter?
Q5. How many triangles can a Pentagon be divided into?
Summary – Pentagon
A Pentagon is a two-dimensional geometric figure with five straight sides and five interior angles that sum up to 540 degrees. It’s part of the polygon family, distinguished by its closed shape formed by connecting five line segments. Pentagons can be regular, where all sides and angles are equal—each interior angle being 108 degrees—or irregular, with varying side lengths and angles. The term “Pentagon” derives from Greek, indicating its five-angled nature. In real life, pentagons are seen in various forms, such as the architectural design of the Pentagon building, the shape of a football, and the body structure of echinoderms like sea stars. A Pentagon consists of sides, vertices, and diagonals, the latter calculated by the formula n (n−3)÷2, yielding five for a pentagon. It includes interior angles, contributing to the shape’s internal sum of 540 degrees, and exterior angles that together reflect the polygon’s external orientation.
FAQs on Pentagon
What is Pentagon in Geometry?
A Pentagon is a two-dimensional, closed geometric shape characterized by five straight sides and five angles.
How Many Sides of Pentagon?
There are 5 sides in a Pentagon.
How Many Lines of Symmetry in Pentagon?
A regular pentagon, which has all sides of equal length and all angles of equal measure, has 5 lines of symmetry.
Can a Pentagon be a Parallelogram?
No, a Pentagon is not a parallelogram. A pentagon is a five-sided polygon, and a parallelogram is a four-sided polygon.
Write the difference between Regular and Irregular Pentagon?
When all the sides and angles of a pentagon are of equal length and measure, it is referred to as a Regular Pentagon; otherwise, it is termed an Irregular Pentagon.
What is the value of interior angle of Pentagon?
Each interior angle of Regular Pentagon is equal to 540° ÷ n = 540° ÷ 5 = 108°.
Can a Pentagon be Concave?
Polygons, including pentagons show convex or concave characteristics. A polygon, such as a pentagon, is a convex when all its interior angles measure less than 180°. On the other hand, it is classified as concave if it possesses one or more interior angles exceeding 180°.
What are Some Real Life Examples of Pentagon Shapes?
- A diamond can resemble a pentagon with its five sides and five corners.
- The headquarters of the United States Department of Defense is famously known as the Pentagon due to its architectural resemblance to a pentagon shape.
- A football is constructed from several black and white pentagonal patches of five-sided shape.
- Echinoderms like sea stars exhibit a pentagonal symmetry in their body structure.
What is Sum of Interior Angles of Pentagon?
The sum of the interior angles of a pentagon, regardless of whether it is regular or irregular, is 540 degrees. This can be calculated using the formula for the sum of interior angles of a polygon: (n−2) × 180°, where n is the number of sides.
What is Sum of Exterior Angles of Pentagon?
The sum of the exterior angles of any polygon, including a pentagon, is always 360 degrees.
How to Calculate the Pentagon Formula?
- The number of diagonals in a polygon with ‘n’ sides can be calculated as n × (n – 3) ÷ 2 = 5 × (5 − 3) ÷ 2 = 5.
- The sum of the interior angles in a polygon can be calculated as 180° × (n – 2) = 180° × (5 − 2) = 540°. In a regular pentagon, each exterior angle measures 360° ÷ n = 360° ÷ 5 = 72°.
- In a regular pentagon, each interior angle measures 540° ÷ n = 540° ÷ 5 = 108°.
- The area of a regular pentagon can be calculated using the formula: 1/2 × Perimeter × Apothem.
- The perimeter of the pentagon is the sum of its five sides.
How can we Calculate the Sum of Pentagon Angles?
To find the sum of interior angles of a Pentagon, for example, we will use the formula: S = ( n-2) x 180°; here, n = 5. As a result, (5-2) x1 80° = 3 x 180° = 540°.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...