Number of days after which tank will become empty
Last Updated :
31 Oct, 2022
Given a tank with capacity C liters which is completely filled in starting. Everyday tank is filled with l liters of water and in the case of overflow extra water is thrown out. Now on i-th day i liters of water is taken out for drinking. We need to find out the day at which tank will become empty the first time.
Examples:
Input : Capacity = 5
l = 2
Output : 4
At the start of 1st day, water in tank = 5
and at the end of the 1st day = (5 - 1) = 4
At the start of 2nd day, water in tank = 4 + 2 = 6
but tank capacity is 5 so water = 5
and at the end of the 2nd day = (5 - 2) = 3
At the start of 3rd day, water in tank = 3 + 2 = 5
and at the end of the 3rd day = (5 - 3) = 2
At the start of 4th day, water in tank = 2 + 2 = 4
and at the end of the 4th day = (4 - 4) = 0
So final answer will be 4
We can see that tank will be full for starting (l + 1) days because water taken out is less than water being filled. After that, each day water in the tank will be decreased by 1 more liter and on (l + 1 + i)th day (C – (i)(i + 1) / 2) liter water will remain before taking drinking water.
Now we need to find a minimal day (l + 1 + K), in which even after filling the tank by l liters we have water less than l in tank i.e. on (l + 1 + K – 1)th day tank becomes empty so our goal is to find minimum K such that,
C – K(K + 1) / 2 <= l
We can solve above equation using binary search and then (l + K) will be our answer. Total time complexity of solution will be O(log C)
C++
Java
public class Tank_Empty {
static int getCumulateSum(int n)
{
return (n * (n + 1)) / 2;
}
static int minDaysToEmpty(int C, int l)
{
if (C <= l)
return C;
int lo = 0;
int hi = (int)1e4;
int mid;
while (lo < hi) {
mid = (lo + hi) / 2;
if (getCumulateSum(mid) >= (C - l))
hi = mid;
else
lo = mid + 1;
}
return (l + lo);
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
int C = 5;
int l = 2;
System.out.println(minDaysToEmpty(C, l));
}
}
|
Python3
C#
using System;
class GFG
{
static int getCumulateSum(int n)
{
return (n * (n + 1)) / 2;
}
static int minDaysToEmpty(int C,
int l)
{
if (C <= l)
return C;
int lo = 0;
int hi = (int)1e4;
int mid;
while (lo < hi)
{
mid = (lo + hi) / 2;
if (getCumulateSum(mid) >= (C - l))
hi = mid;
else
lo = mid + 1;
}
return (l + lo);
}
static public void Main ()
{
int C = 5;
int l = 2;
Console.WriteLine(minDaysToEmpty(C, l));
}
}
|
Javascript
Output:
4
Alternate Solution :
It can be solved mathematically with a simple formula:
Let’s Assume C>L. Let d be the amount of days after the Lth when the tank become empty.During that time, there will be (d-1)refills and d withdrawals.
Hence we need to solve this equation :
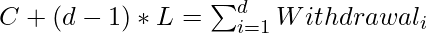
Sum of all withdrawals is a sum of arithmetic progression,therefore :
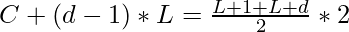
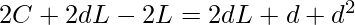
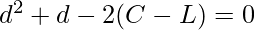
Discriminant = 1+8(C-L)>0,because C>L.
Skipping the negative root, we get the following formula:
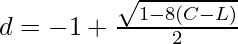
Therefore, the final answer is:
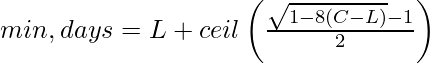
C++
Java
import java.lang.*;
class GFG {
static int minDaysToEmpty(int C, int l)
{
if (l >= C) return C;
double eq_root = (Math.sqrt(1 + 8 *
(C - l)) - 1) / 2;
return (int)(Math.ceil(eq_root) + l);
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
System.out.println(minDaysToEmpty(5, 2));
System.out.println(minDaysToEmpty(6514683, 4965));
}
}
|
Python3
import math
def minDaysToEmpty(C, l):
if (l >= C): return C
eq_root = (math.sqrt(1 + 8 * (C - l)) - 1) / 2
return math.ceil(eq_root) + l
print(minDaysToEmpty(5, 2))
print(minDaysToEmpty(6514683, 4965))
|
C#
using System;
class GFG
{
static int minDaysToEmpty(int C,
int l)
{
if (l >= C) return C;
double eq_root = (Math.Sqrt(1 + 8 *
(C - l)) - 1) / 2;
return (int)(Math.Ceiling(eq_root) + l);
}
static public void Main ()
{
Console.WriteLine(minDaysToEmpty(5, 2));
Console.WriteLine(minDaysToEmpty(6514683,
4965));
}
}
|
PHP
<?php
function minDaysToEmpty($C, $l)
{
if ($l >= $C)
return $C;
$eq_root = (int)sqrt(1 + 8 *
($C - $l) - 1) / 2;
return ceil($eq_root) + $l;
}
echo minDaysToEmpty(5, 2), "\n";
echo minDaysToEmpty(6514683,
4965), "\n";
?>
|
Javascript
<script>
function minDaysToEmpty(C, l)
{
if (l >= C) return C;
let eq_root = (Math.sqrt(1 + 8 *
(C - l)) - 1) / 2;
return (Math.ceil(eq_root) + l);
}
document.write(minDaysToEmpty(5, 2) + "</br>");
document.write(minDaysToEmpty(6514683, 4965));
</script>
|
Output :
4
8573
Thanks to Andrey Khayrutdinov for suggesting this solution.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...