MYSQLdb Connection in Python
Last Updated :
23 Nov, 2021
In this article, I have discussed how to connect to MySQL database remotely using python. For any application, it is very important to store the database on a server for easy data access. It is quite complicated to connect to the database remotely because every service provider doesn’t provide remote access to the MySQL database. Here I am using python’s MySQLdb module for connecting to our database which is at any server that provides remote access.
What is MYSQLdb?
MySQLdb is an interface for connecting to a MySQL database server from Python. It implements the Python Database API v2.0 and is built on top of the MySQL C API.
Packages to Install
mysql-connector-python
mysql-python
If using anaconda
conda install -c anaconda mysql-python
conda install -c anaconda mysql-connector-python
else
pip install MySQL-python
pip install MySQL-python-connector
Import-Package
import MYSQLdb
How to connect to a remote MySQL database using python?
Before we start you should know the basics of SQL. Now let us discuss the methods used in this code:
- connect(): This method is used for creating a connection to our database it has four arguments:
- Server Name
- Database User Name
- Database Password
- Database Name
- cursor(): This method creates a cursor object that is capable of executing SQL queries on the database.
- execute(): This method is used for executing SQL queries on the database. It takes a sql query( as string) as an argument.
- fetchone(): This method retrieves the next row of a query result set and returns a single sequence, or None if no more rows are available.
- close() : This method close the database connection.
Free remote mysql database providers:
1.www.freemysqlhosting.net
2.www.heliohost.org
Python3
import MySQLdb
def mysqlconnect():
try:
db_connection= MySQLdb.connect
("Hostname","dbusername","password","dbname")
except:
print("Can't connect to database")
return 0
print("Connected")
cursor=db_connection.cursor()
cursor.execute("SELECT CURDATE();")
m = cursor.fetchone()
print("Today's Date Is ",m[0])
db_connection.close()
mysqlconnect()
|
Connected
Today's Date Is 2017-11-14
Python3
import mysql.connector as mysql
db = mysql.connect(host="localhost",user="root",password="tiger",database="python")
cursor = db.cursor()
cursor.execute("DROP TABLE IF EXISTS EMPLOYEE")
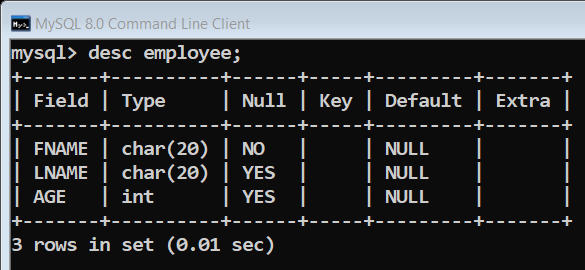
sql = "CREATE TABLE EMPLOYEE ( FNAME CHAR(20) NOT NULL, LNAME CHAR(20), AGE INT )"
cursor.execute(sql)
db.close()
|
Output:
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...