Modes of Propagation in Optical Fiber
Last Updated :
10 Apr, 2024
In the realms of connectivity and telecommunications, Fiber Optic Network basically specifies and analyses the modes of propagation on optical fiber. Certainly, optical fibers are the reason for existence of modern day communication systems cause they are carrying immense volumes of data through photons.
This article delves in depth into the main modes of fiber propagation, which comprises for instance showing what terminology means, discussing its importance and demonstrating its structure through drawings.
Primary Terminologies
Optical Fiber: An optical fiber is a lightweight, thin, and flexible electrical conductive material made of a glass or plastic material that is principally designed for data transfer in telecommunications networks.
Modes of Propagation: The modes of propagation are classical waveforms of light that travel via different paths within an optical fiber. Whichever mode we are dealing with, it can either transit us to a multimode propagation or to a single-mode transience.
Multimode Propagation: We can speak of multipath propagation when light rays (beams) pass through the optical fiber simultaneously, being transmitted via different channels to the receiver part (end-piece) of the connection.
Single-Mode Propagation: A single waveguide construction implies that the light travels through the interior of the fiber along one central axis, and as a result, when it is transmitted across long distances the light experiences very little dispersion to ensure the accuracy of signal transmission.
Images for Illustration
To demonstrate the ideas of multimode and single propagation diagrams can be generated in draw.io or Google Drawings by using drawing tools. This illustration would explain the optical fiber structure, the power paths of multimode and single-mode propagation, and the distinction in dispersion and signal precision across multi-mode and single-mode modes.
Implementing Necessary Steps towards Understanding Ways of Communication
1. Optical Fiber Structure
An optical fiber is a thin, durable and flexible strand of glass or plastic, used to communicate as light pulses over much longer distances than electrical based line.

Optical Fiber Structure
- Core: This is the particle that transmits light through it. It is usually made from a glass of high purity and has the index of refraction higher the cladding.
- Cladding: It is densest at the core and its refractive index there is slightly lower. Its goal is achieved due to a total refraction that prevents light from spreading outward.
- Protective Coating: The last layer, which is also the closest to the core, protects the fiber from various environmental influences and adds the necessary mechanical strength.
Internal reflection of light is indicated by the beam throughout the shaft. Incident light entering the core at angle greater than the critical angle (which is determined by the refractive indices of core and cladding coefficient) bounces internally forever to preserve the photon’s trajectory.
2. Multimode Propagation
- In multimode propagation, several light beams fulfill the role of the core and follow their respective paths. This could results in modal dispersion; when these rays come at the end of the receiving place at times depending on their different path lengths.

Multimode Propagation
- Mode dispersion is the limiting factor in multimode fiber transmission because signal interferences from different modes of the fiber lead to signal distortions reduce the bandwidth and transmission distance.
3. Single-Mode Propagation
- Single-mode propagation resulting in a ray of light traveling the core’s primary axis is the purpose here. In this situation, the ratio of core diameter to multimode fiber diameter is smaller.
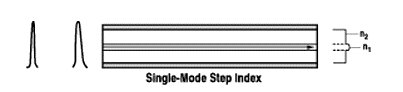
Single-Mode Propagation
- One of the most distinctive features of single-mode fibers is their minimal dispersion, which in turn leads to intense bandwidth and the capability to transmit signals over a long distance without relatively noticeable signal degradation. They are designed in such a way as to they mainly focus on the transmission over great distances while ensuring that there will be no quality loss of signals.
4. Comparison and Applications
- Bandwidth: Single-mode fibers have the advantage of higher throughput over multimode due to their ability to confine all light intensity to one focused light ray.
- Distance: Single mode fibers is very effective for long transmissions since the dispersion becomes minimized and signal loss is significantly decreased, while multimode fibers are used to cover the need in local area networks.
- Cost: However, single-mode fibers are relatively harder to produce and set up comparatively to multimode fibers since they demand high accuracy and are equipped with special parts.
- Applications: The sole-mode fiber is installed as a long-distance telecommunication system designed for backbones, while the multi-mode fiber is just for the short range located in those places like LANs, data center, campus applications, etc.
Conclusion
Knowing the modes of propagation in optical fiber is an essential requirement to have efficient and reliable communication systems. This article explores the definitions of important terms, illustrations of each concept, and talks about the traits of multimode and single mode propagation in order to increase readers’ knowledge of optical fiber technology in computer networks and communications.
Modes of Propagation in Optical Fiber – FAQs
What are the primary differences between multimode and single-mode propagation in optical fibers?
Modal propagation style is a state in which many light rays travel through the core of the fiber, causing modal dispersion, a limited bandwidth, and distance. What differs is that single-mode propagation uses only one light ray along the core’s central axis to minimize dispersion and facilitate high bandwidth and long-distance communications.
How does modal dispersion affect data transmission in multimode optical fibers?
A phenomenon called modal dispersion takes place in multimode fibers as different rays try out different paths and arrive at the end with different timing. This scattering leads to a narrower bandwidth and less distance of transmission for multimode fibers, decreasing the data transmission quality and speed.
What are the key factors to consider when choosing between multimode and single-mode optical fibers for a communication system?
Factors that need to be considered include: transmission distance, bandwidth requirements, cost-effectiveness, and application specific needs. While single mode fibers are great for long distance transmission applications with high bandwidth requirements, multimode fibers are appropriate for relatively short distance and LAN (local area network) uses.
How does the core size of an optical fiber affect its mode of propagation?
A narrow core of an optical fiber determines the propagation mode. Larger core’s of the fibers mainly function as a multimode core, permitting an engagement of a number of light rays in communication and corresponding to higher bandwidth but limited transmission distances. On the other hand, it is compact ’core’ that constitutes the major difference between large-core multimode fibers and smaller-core single-mode fibers which ensure that only one single ray of propagation goes far away for a long transmission.
Can optical fibers support different modes of propagation simultaneously?
Optical fibers can handle several modes of propagation, particularly in a multimode fiber. Unlike the waveguide transmission mode of direct current, the electromagnetic wave propagation in a radio frequency signal is a simultaneous process, which can cause modulation dispersion on signal quality and reliability while traveling longer distances. On the other hand, single-mode fibers are like the first directional laser beams and they are designed for the precise single-ray propagation which is intended to eliminates the dispersion and optimize the long-distance communication.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...