Modes of Radio Wave Propagation in Wireless Communication
Last Updated :
23 Mar, 2023
Radio Waves are types of electromagnetic Radiation. they are produced by the acceleration of electromagnetic charges. Radio waves play an important role in communication, navigation, weather forecasting, medical imaging technology, etc. These waves have the longest wavelength in the electromagnetic spectrum
Propagation of Radio Waves
Radio waves can propagate through air, water, various solid objects, vacuum and etc. The ability of radio waves to propagate through various materials depends on the wavelength and the frequency of the radio waves.
Modes of Radio Wave Propagation
There are three main modes of propagation of radio waves: ground wave, sky wave, and space wave.
Sky Wave Propagation: This mode of propagation occurs when the signal is transmitted by the transmitting antenna (Tx) is reflected by the ionosphere layer (sky) and received by the receiving antenna (Rx) is known as sky wave propagation. The ionosphere is the layer of the earth’s upper atmosphere that contains ionized gases and plasma. It protects the earth from harmful radiation.
- Sky wave propagation occurs in the ionosphere.
- The range of frequencies that can be used for sky wave propagation is typically between 3 and 30 MHz.
- The range of sky wave propagation is affected by the angle at which the radio waves enter the ionosphere, the height of the ionosphere, and the density of the ionosphere.
The critical frequency in Hz : 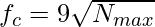 here, Nmax is the maximum electron density per m3
here, Nmax is the maximum electron density per m3
The skip distance is given as : 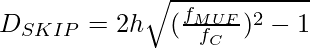
Here, DSKIP is skip distance
h is the height at which reflection happens
fMUF is a maximum usable frequency
fc is the critical frequency
.png)
Skywave Propagation of Radio Waves
Space Wave Propagation of Radio Waves: This mode of propagation occurs when the transmitting wave travels directly to the receiving antenna directly without any reflection, refraction, and deflection phenomenon. It is also called direct wave propagation or line-of-sight transmission.
- Space wave propagation is commonly used for short-range radio communication
- Space wave propagation is also used for satellite communication,
- The maximum range is approximately 40 kilometers for radio waves at 100 MHz.
- Space wave propagation is used in a wide variety of applications, including television broadcasting, mobile phones, wireless LANs, and remote sensing.
The distance between two antennae is : 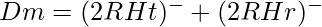
Here, R is the radius of the earth
Ht is the height of the transmission antenna
Hr is the height of the receiver antenna
.png)
Space Wave Propagation of Radio Waves
Ground Wave Propagation: This mode of propagation occurs when the transmitting waves travel along the earth’s surface and are received at the receiving antenna is known as the Ground wave propagation. The range of the Ground wave Propagation depends on the frequency of the transmitted wave, the power of the transmitter, and the properties of the earth’s surface and the earth’s atmosphere.
- Ground wave propagation requires a lower-power transmitter than other methods of radio wave propagation.
- It is used for medium-range communication such as 100km to 1000km.
- mostly the frequency used for the ground wave propagation lies between 3khz to 3Mhz.
.png)
Ground wave Propagation of the Radio Waves
Tropospheric Scatter Propagation: Tropospheric scatter propagation is a form of radio communication that uses the scattering of radio waves off the Earth’s troposphere to reach distant locations. This propagation method works by bouncing the signal off small atmospheric irregularities, such as water droplets or dust particles, which scatter the signal in different directions.
- Tropospheric scatter propagation is most effective at frequencies between 100 MHz and 1 GHz.
- Can provide reliable communication over distances of hundreds of kilometers.
- This method of communication is typically used for long-distance point-to-point links, such as military and emergency communications
.png)
Tropospheric Scatter Propagation
There are several modes of radio wave propagation in wireless communication, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. Here are some of the most common modes:
Ground wave propagation: This mode of propagation is used for long-distance communication, especially over land. The radio waves follow the curvature of the earth’s surface and are able to travel a considerable distance without being obstructed by buildings or other obstacles. The advantage of ground wave propagation is its ability to cover long distances without the need for repeaters or other equipment. However, the disadvantage is that the signal strength decreases rapidly with distance, and the quality of the signal can be affected by changes in the terrain or atmospheric conditions.
Sky wave propagation: This mode of propagation is used for long-distance communication over the ocean or other large bodies of water. The radio waves are reflected off the ionosphere and can be received by antennas on the ground hundreds or even thousands of miles away. The advantage of sky wave propagation is its ability to cover vast distances without the need for repeaters or other equipment. However, the disadvantage is that the signal strength can be affected by changes in the ionosphere, which can be caused by solar activity or other factors.
Line-of-sight propagation: This mode of propagation is used for short-range communication, typically within a few miles. The radio waves travel in a straight line from the transmitter to the receiver and require an unobstructed line of sight between the two. The advantage of line-of-sight propagation is its ability to provide a strong, reliable signal over short distances. However, the disadvantage is that obstacles such as buildings, trees, or hills can block the signal, limiting its range.
Tropospheric propagation: This mode of propagation is used for medium-range communication, typically between 30 and 300 miles. The radio waves are reflected or refracted by the atmosphere, allowing them to follow the curvature of the earth’s surface. The advantage of tropospheric propagation is its ability to provide a reliable signal over medium distances without the need for repeaters or other equipment. However, the disadvantage is that the signal can be affected by atmospheric conditions such as rain, fog, or thunderstorms.
Scatter propagation: This mode of propagation is used for communication over short to medium ranges in areas with obstacles such as mountains or buildings. The radio waves are scattered off these obstacles, allowing them to reach the receiver. The advantage of scatter propagation is its ability to provide a reliable signal in areas where other modes of propagation may be obstructed. However, the disadvantage is that the signal can be affected by changes in the terrain or the position of the obstacles.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...