Longest Consecutive Subsequence
Last Updated :
23 Mar, 2024
Given an array of integers, find the length of the longest sub-sequence such that elements in the subsequence are consecutive integers, the consecutive numbers can be in any order.
Examples:
Input: arr[] = {1, 9, 3, 10, 4, 20, 2}
Output: 4
Explanation: The subsequence 1, 3, 4, 2 is the longest subsequence of consecutive elements
Input: arr[] = {36, 41, 56, 35, 44, 33, 34, 92, 43, 32, 42}
Output: 5
Explanation: The subsequence 36, 35, 33, 34, 32 is the longest subsequence of consecutive elements.
Naive Approach:
The idea is to first sort the array and find the longest subarray with consecutive elements. After sorting the array and removing the multiple occurrences of elements, run a loop and keep a count and max (both initially zero). Run a loop from start to end and if the current element is not equal to the previous (element+1) then set the count to 1 else increase the count. Update max with a maximum of count and max.
Follow the steps below to solve the problem:
- Intialise ans and countConsecutive with 0.
- Sort the arr[].
- Store the distinct elements in dist[] array by traversing over the arr[].
- Now, traverse on the dist[] array to find the count of consecutive elements and maintain the answer variable.
Below is the implementation of above approach:
C++
// C++ program to find longest
// contiguous subsequence
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Returns length of the longest
// contiguous subsequence
int findLongestConseqSubseq(int arr[], int n)
{
int ans = 0, count = 0;
// sort the array
sort(arr, arr + n);
vector<int> v;
v.push_back(arr[0]);
// insert repeated elements only once in the vector
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
if (arr[i] != arr[i - 1])
v.push_back(arr[i]);
}
// find the maximum length
// by traversing the array
for (int i = 0; i < v.size(); i++) {
// Check if the current element is equal
// to previous element +1
if (i > 0 && v[i] == v[i - 1] + 1)
count++;
// reset the count
else
count = 1;
// update the maximum
ans = max(ans, count);
}
return ans;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 1, 2, 2, 3 };
int n = sizeof arr / sizeof arr[0];
cout << "Length of the Longest contiguous subsequence "
"is "
<< findLongestConseqSubseq(arr, n);
return 0;
}
// Java program to find longest
// contiguous subsequence
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
static int findLongestConseqSubseq(int arr[], int n)
{
// Sort the array
Arrays.sort(arr);
int ans = 0, count = 0;
ArrayList<Integer> v = new ArrayList<Integer>();
v.add(10);
// Insert repeated elements
// only once in the vector
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
if (arr[i] != arr[i - 1])
v.add(arr[i]);
}
// Find the maximum length
// by traversing the array
for (int i = 0; i < v.size(); i++) {
// Check if the current element is
// equal to previous element +1
if (i > 0 && v.get(i) == v.get(i - 1) + 1)
count++;
else
count = 1;
// Update the maximum
ans = Math.max(ans, count);
}
return ans;
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int arr[] = { 1, 9, 3, 10, 4, 20, 2 };
int n = arr.length;
System.out.println(
"Length of the Longest "
+ "contiguous subsequence is "
+ findLongestConseqSubseq(arr, n));
}
}
// This code is contributed by parascoding
// C# program to find longest
// contiguous subsequence
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG {
static int findLongestConseqSubseq(int[] arr, int n)
{
// Sort the array
Array.Sort(arr);
int ans = 0, count = 0;
List<int> v = new List<int>();
v.Add(10);
// Insert repeated elements
// only once in the vector
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
if (arr[i] != arr[i - 1])
v.Add(arr[i]);
}
// Find the maximum length
// by traversing the array
for (int i = 0; i < v.Count; i++) {
// Check if the current element is
// equal to previous element +1
if (i > 0 && v[i] == v[i - 1] + 1)
count++;
else
count = 1;
// Update the maximum
ans = Math.Max(ans, count);
}
return ans;
}
// Driver code
static void Main()
{
int[] arr = { 1, 9, 3, 10, 4, 20, 2 };
int n = arr.Length;
Console.WriteLine(
"Length of the Longest "
+ "contiguous subsequence is "
+ findLongestConseqSubseq(arr, n));
}
}
// This code is contributed by divyeshrabadiya07
<script>
// JavaScript program to find longest
// contiguous subsequence
// Returns length of the longest
// contiguous subsequence
function findLongestConseqSubseq(arr, n) {
let ans = 0, count = 0;
// sort the array
arr.sort(function (a, b) { return a - b; })
var v = [];
v.push(arr[0]);
//insert repeated elements only once in the vector
for (let i = 1; i < n; i++) {
if (arr[i] != arr[i - 1])
v.push(arr[i]);
}
// find the maximum length
// by traversing the array
for (let i = 0; i < v.length; i++) {
// Check if the current element is equal
// to previous element +1
if (i > 0 && v[i] == v[i - 1] + 1)
count++;
// reset the count
else
count = 1;
// update the maximum
ans = Math.max(ans, count);
}
return ans;
}
// Driver code
let arr = [1, 2, 2, 3];
let n = arr.length;
document.write(
"Length of the Longest contiguous subsequence is "
+findLongestConseqSubseq(arr, n)
);
// This code is contributed by Potta Lokesh
</script>
# Python3 program to find longest
# contiguous subsequence
# Returns length of the longest
# contiguous subsequence
def findLongestConseqSubseq(arr, n):
ans = 0
count = 0
# Sort the array
arr.sort()
v = []
v.append(arr[0])
# Insert repeated elements only
# once in the vector
for i in range(1, n):
if (arr[i] != arr[i - 1]):
v.append(arr[i])
# Find the maximum length
# by traversing the array
for i in range(len(v)):
# Check if the current element is
# equal to previous element +1
if (i > 0 and v[i] == v[i - 1] + 1):
count += 1
# Reset the count
else:
count = 1
# Update the maximum
ans = max(ans, count)
return ans
# Driver code
arr = [1, 2, 2, 3]
n = len(arr)
print("Length of the Longest contiguous subsequence is",
findLongestConseqSubseq(arr, n))
# This code is contributed by avanitrachhadiya2155
OutputLength of the Longest contiguous subsequence is 3
Time complexity: O(Nlog(N)), Time to sort the array is O(Nlog(N)).
Auxiliary space: O(N). Extra space is needed for storing distinct elements.
Longest Consecutive Subsequence using Hashing:
The idea is to use Hashing. We first insert all elements in a Set. Then check all the possible starts of consecutive subsequences.
Illustration:
Below image is the dry run for example arr[] = {1, 9, 3, 10, 4, 20, 2}:
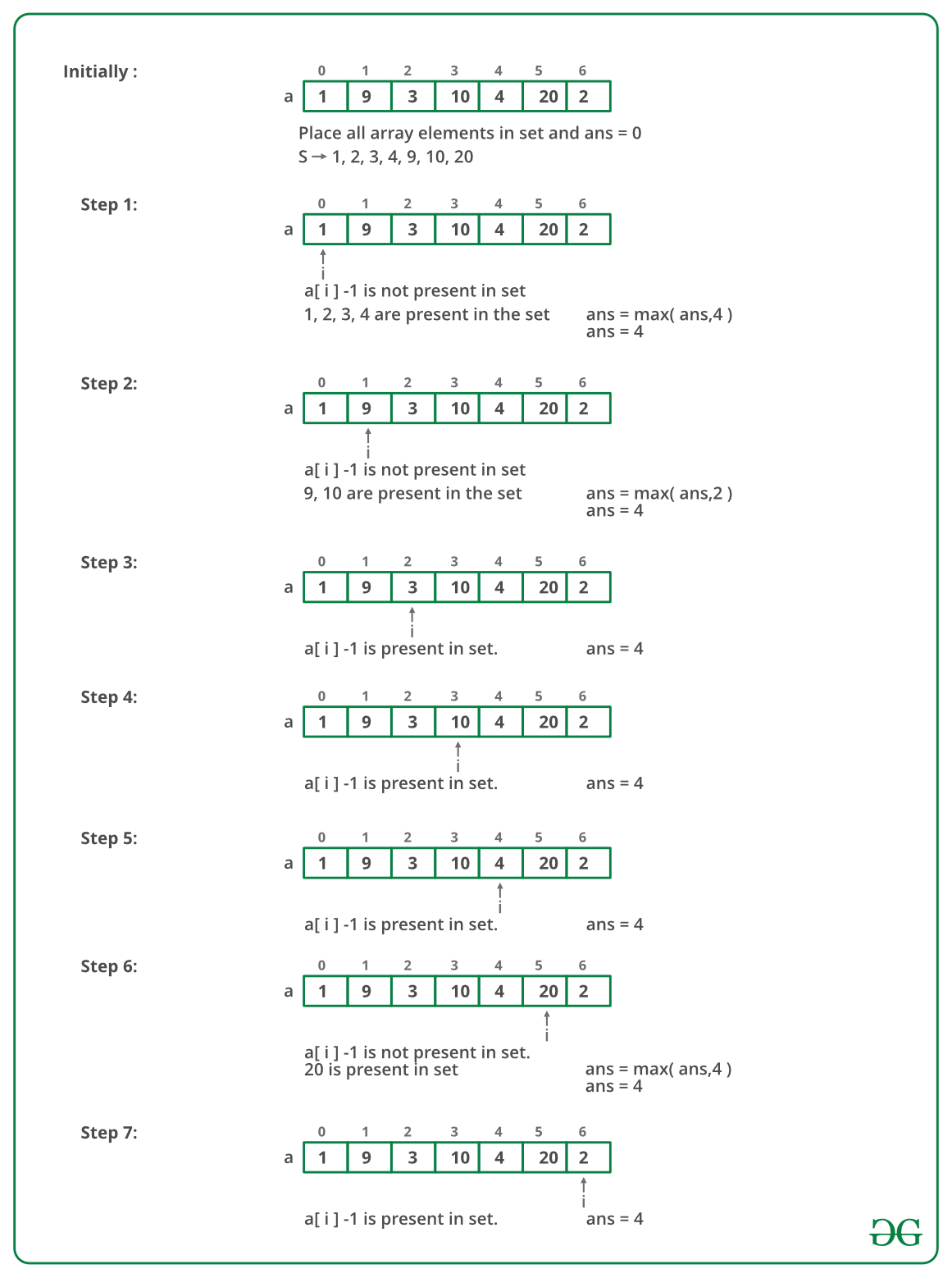
Follow the steps below to solve the problem:
- Create an empty hash.
- Insert all array elements to hash.
- Do the following for every element arr[i]
- Check if this element is the starting point of a subsequence. To check this, simply look for arr[i] – 1 in the hash, if not found, then this is the first element of a subsequence.
- If this element is the first element, then count the number of elements in the consecutive starting with this element. Iterate from arr[i] + 1 till the last element that can be found.
- If the count is more than the previous longest subsequence found, then update this.
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
// C++ program to find longest
// contiguous subsequence
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Returns length of the longest
// contiguous subsequence
int findLongestConseqSubseq(int arr[], int n)
{
unordered_set<int> S;
int ans = 0;
// Hash all the array elements
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
S.insert(arr[i]);
// check each possible sequence from
// the start then update optimal length
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
// if current element is the starting
// element of a sequence
if (S.find(arr[i] - 1) == S.end()) {
// Then check for next elements
// in the sequence
int j = arr[i];
while (S.find(j) != S.end())
j++;
// update optimal length if
// this length is more
ans = max(ans, j - arr[i]);
}
}
return ans;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 1, 9, 3, 10, 4, 20, 2 };
int n = sizeof arr / sizeof arr[0];
cout << "Length of the Longest contiguous subsequence "
"is "
<< findLongestConseqSubseq(arr, n);
return 0;
}
// Java program to find longest
// consecutive subsequence
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class ArrayElements {
// Returns length of the longest
// consecutive subsequence
static int findLongestConseqSubseq(int arr[], int n)
{
HashSet<Integer> S = new HashSet<Integer>();
int ans = 0;
// Hash all the array elements
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
S.add(arr[i]);
// check each possible sequence from the start
// then update optimal length
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
// if current element is the starting
// element of a sequence
if (!S.contains(arr[i] - 1)) {
// Then check for next elements
// in the sequence
int j = arr[i];
while (S.contains(j))
j++;
// update optimal length if this
// length is more
if (ans < j - arr[i])
ans = j - arr[i];
}
}
return ans;
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String args[])
{
int arr[] = { 1, 9, 3, 10, 4, 20, 2 };
int n = arr.length;
System.out.println(
"Length of the Longest consecutive subsequence is "
+ findLongestConseqSubseq(arr, n));
}
}
// This code is contributed by Aakash Hasija
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
// C# program to find longest consecutive subsequence
public class ArrayElements {
// Returns length of the
// longest consecutive subsequence
public static int findLongestConseqSubseq(int[] arr,
int n)
{
HashSet<int> S = new HashSet<int>();
int ans = 0;
// Hash all the array elements
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
S.Add(arr[i]);
}
// check each possible sequence from the start
// then update optimal length
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
// if current element is the starting
// element of a sequence
if (!S.Contains(arr[i] - 1)) {
// Then check for next elements in the
// sequence
int j = arr[i];
while (S.Contains(j)) {
j++;
}
// update optimal length if this length
// is more
if (ans < j - arr[i]) {
ans = j - arr[i];
}
}
}
return ans;
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
int[] arr = new int[] { 1, 9, 3, 10, 4, 20, 2 };
int n = arr.Length;
Console.WriteLine(
"Length of the Longest consecutive subsequence is "
+ findLongestConseqSubseq(arr, n));
}
}
// This code is contributed by Shrikant13
<script>
// Javascript program to find longest
// contiguous subsequence
// Returns length of the longest
// contiguous subsequence
function findLongestConseqSubseq(arr, n) {
let S = new Set();
let ans = 0;
// Hash all the array elements
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++)
S.add(arr[i]);
// check each possible sequence from
// the start then update optimal length
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
// if current element is the starting
// element of a sequence
if (!S.has(arr[i] - 1))
{
// Then check for next elements
// in the sequence
let j = arr[i];
while (S.has(j))
j++;
// update optimal length if
// this length is more
ans = Math.max(ans, j - arr[i]);
}
}
return ans;
}
// Driver code
let arr = [1, 9, 3, 10, 4, 20, 2];
let n = arr.length;
document.write("Length of the Longest contiguous subsequence is "
+ findLongestConseqSubseq(arr, n));
// This code is contributed by gfgking.
</script>
# Python program to find longest contiguous subsequence
def findLongestConseqSubseq(arr, n):
s = set()
ans = 0
# Hash all the array elements
for ele in arr:
s.add(ele)
# check each possible sequence from the start
# then update optimal length
for i in range(n):
# if current element is the starting
# element of a sequence
if (arr[i]-1) not in s:
# Then check for next elements in the
# sequence
j = arr[i]
while(j in s):
j += 1
# update optimal length if this length
# is more
ans = max(ans, j-arr[i])
return ans
# Driver code
if __name__ == '__main__':
n = 7
arr = [1, 9, 3, 10, 4, 20, 2]
print("Length of the Longest contiguous subsequence is ",
findLongestConseqSubseq(arr, n))
# Contributed by: Harshit Sidhwa
OutputLength of the Longest contiguous subsequence is 4
Time complexity: O(N), Only one traversal is needed and the time complexity is O(n) under the assumption that hash insert and search takes O(1) time.
Auxiliary space: O(N), To store every element in the hashmap O(n) space is needed
Longest Consecutive Subsequence using Priority Queue:
The Idea is to use Priority Queue. Using priority queue it will sort the elements and eventually it will help to find consecutive elements.
Illustration:
Input: arr[] = {1, 9, 3, 10, 4, 20, 2}
Insert all the elements in the Priority Queue:
Initialise variable prev with first element of priority queue, prev will contain last element has been picked and it will help to check whether the current element is contributing for consecutive sequence or not.
prev = 1, countConsecutive = 1, ans = 1
Run the algorithm till the priority queue becomes empty.
- current element is 2
- prev + 1 == 2, therefore increment countConsecutive by 1
- countConsecutive = countConsecutive + 1 = 1 + 1 = 2
- update prev with current element, prev = 2
- pop the current element
- ans = max(ans, countConsecutive) = (1, 2) = 2
- current element is 3
- prev + 1 == 3, therefore increment countConsecutive by 1
- countConsecutive = countConsecutive + 1 = 2 + 1 = 3
- update prev with current element, prev = 3
- pop the current element
- ans = max(ans, countConsecutive) = (2, 3) = 3
- current element is 4
- prev + 1 == 4, therefore increment countConsecutive by 1
- countConsecutive = countConsecutive + 1 = 3 + 1 = 4
- update prev with current element, prev = 4
- pop the current element
- ans = max(ans, countConsecutive) = (3, 4) = 4
- current element is 9
- prev + 1 != 9, therefore re-initialise countConsecutive by 1
- countConsecutive = 1
- update prev with current element, prev = 9
- pop the current element
- ans = max(ans, countConsecutive) = (4, 1) = 4
- current element is 10
- prev + 1 == 10, therefore increment countConsecutive by 1
- countConsecutive = countConsecutive + 1 = 1 + 1 = 2
- update prev with current element, prev = 10
- pop the current element
- ans = max(ans, countConsecutive) = (4, 2) =4
- current element is 20
- prev + 1 != 20, therefore re-initialise countConsecutive by 1
- countConsecutive = 1
- update prev with current element, prev = 20
- pop the current element
- ans = max(ans, countConsecutive) = (4, 1) = 4
Hence, the longest consecutive subsequence is 4.
Follow the steps below to solve the problem:
- Create a Priority Queue to store the element
- Store the first element in a variable
- Remove it from the Priority Queue
- Check the difference between this removed first element and the new peek element
- If the difference is equal to 1 increase the count by 1 and repeats step 2 and step 3
- If the difference is greater than 1 set counter to 1 and repeat step 2 and step 3
- if the difference is equal to 0 repeat step 2 and 3
- if counter greater than the previous maximum then store counter to maximum
- Continue step 4 to 7 until we reach the end of the Priority Queue
- Return the maximum value
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
// CPP program for the above approach
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int findLongestConseqSubseq(int arr[], int N)
{
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<int> > pq;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
// adding element from
// array to PriorityQueue
pq.push(arr[i]);
}
// Storing the first element
// of the Priority Queue
// This first element is also
// the smallest element
int prev = pq.top();
pq.pop();
// Taking a counter variable with value 1
int c = 1;
// Storing value of max as 1
// as there will always be
// one element
int max = 1;
while (!pq.empty()) {
// check if current peek
// element minus previous
// element is greater than
// 1 This is done because
// if it's greater than 1
// then the sequence
// doesn't start or is broken here
if (pq.top() - prev > 1) {
// Store the value of counter to 1
// As new sequence may begin
c = 1;
// Update the previous position with the
// current peek And remove it
prev = pq.top();
pq.pop();
}
// Check if the previous
// element and peek are same
else if (pq.top() - prev == 0) {
// Update the previous position with the
// current peek And remove it
prev = pq.top();
pq.pop();
}
// If the difference
// between previous element and peek is 1
else {
// Update the counter
// These are consecutive elements
c++;
// Update the previous position
// with the current peek And remove it
prev = pq.top();
pq.pop();
}
// Check if current longest
// subsequence is the greatest
if (max < c) {
// Store the current subsequence count as
// max
max = c;
}
}
return max;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 1, 9, 3, 10, 4, 20, 2 };
int n = 7;
cout << "Length of the Longest consecutive subsequence "
"is "
<< findLongestConseqSubseq(arr, n);
return 0;
}
// this code is contributed by Manu Pathria
// Java Program to find longest consecutive
// subsequence This Program uses Priority Queue
import java.io.*;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
public class Longset_Sub {
// return the length of the longest
// subsequence of consecutive integers
static int findLongestConseqSubseq(int arr[], int N)
{
PriorityQueue<Integer> pq
= new PriorityQueue<Integer>();
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
// adding element from
// array to PriorityQueue
pq.add(arr[i]);
}
// Storing the first element
// of the Priority Queue
// This first element is also
// the smallest element
int prev = pq.poll();
// Taking a counter variable with value 1
int c = 1;
// Storing value of max as 1
// as there will always be
// one element
int max = 1;
for (int i = 1; i < N; i++) {
// check if current peek
// element minus previous
// element is greater than
// 1 This is done because
// if it's greater than 1
// then the sequence
// doesn't start or is broken here
if (pq.peek() - prev > 1) {
// Store the value of counter to 1
// As new sequence may begin
c = 1;
// Update the previous position with the
// current peek And remove it
prev = pq.poll();
}
// Check if the previous
// element and peek are same
else if (pq.peek() - prev == 0) {
// Update the previous position with the
// current peek And remove it
prev = pq.poll();
}
// if the difference
// between previous element and peek is 1
else {
// Update the counter
// These are consecutive elements
c++;
// Update the previous position
// with the current peek And remove it
prev = pq.poll();
}
// Check if current longest
// subsequence is the greatest
if (max < c) {
// Store the current subsequence count as
// max
max = c;
}
}
return max;
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String args[])
throws IOException
{
int arr[] = { 1, 9, 3, 10, 4, 20, 2 };
int n = arr.length;
System.out.println(
"Length of the Longest consecutive subsequence is "
+ findLongestConseqSubseq(arr, n));
}
}
// This code is contributed by Sudipa Sarkar
// C# program to implement
// the above approach
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG {
// return the length of the longest
// subsequence of consecutive integers
static int findLongestConseqSubseq(int[] arr, int N)
{
List<int> pq = new List<int>();
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
// adding element from
// array to PriorityQueue
pq.Add(arr[i]);
pq.Sort();
}
// Storing the first element
// of the Priority Queue
// This first element is also
// the smallest element
int prev = pq[0];
// Taking a counter variable with value 1
int c = 1;
// Storing value of max as 1
// as there will always be
// one element
int max = 1;
for (int i = 1; i < N; i++) {
// check if current peek
// element minus previous
// element is greater than
// 1 This is done because
// if it's greater than 1
// then the sequence
// doesn't start or is broken here
if (pq[0] - prev > 1) {
// Store the value of counter to 1
// As new sequence may begin
c = 1;
// Update the previous position with the
// current peek And remove it
prev = pq[0];
pq.RemoveAt(0);
}
// Check if the previous
// element and peek are same
else if (pq[0] - prev == 0) {
// Update the previous position with the
// current peek And remove it
prev = pq[0];
pq.RemoveAt(0);
}
// if the difference
// between previous element and peek is 1
else {
// Update the counter
// These are consecutive elements
c++;
// Update the previous position
// with the current peek And remove it
prev = pq[0];
pq.RemoveAt(0);
}
// Check if current longest
// subsequence is the greatest
if (max < c) {
// Store the current subsequence count as
// max
max = c;
}
}
return max;
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main()
{
int[] arr = { 1, 9, 3, 10, 4, 20, 2 };
int n = arr.Length;
Console.WriteLine(
"Length of the Longest consecutive subsequence is "
+ findLongestConseqSubseq(arr, n));
}
}
// This code is contributed by code_hunt.
function findLongestConseqSubseq(arr) {
let pq = [];
for (let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
pq.push(arr[i]);
}
pq.sort((a, b) => a - b);
let prev = pq[0];
let c = 1;
let max = 1;
for (let i = 1; i < pq.length; i++) {
if (pq[i] - prev > 1) {
c = 1;
prev = pq[i];
} else if (pq[i] - prev === 0) {
prev = pq[i];
} else {
c++;
prev = pq[i];
}
if (max < c) {
max = c;
}
}
return max;
}
// Driver Code
let arr = [1, 9, 3, 10, 4, 20, 2];
console.log("Length of the Longest consecutive subsequence is " + findLongestConseqSubseq(arr));
# Python program for the above approach
import bisect
def findLongestConseqSubseq(arr, N):
pq = []
for i in range(N):
# adding element from
# array to PriorityQueue
bisect.insort(pq, arr[i])
# Storing the first element
# of the Priority Queue
# This first element is also
# the smallest element
prev = pq[0]
pq.pop(0)
# Taking a counter variable with value 1
c = 1
# Storing value of max as 1
# as there will always be
# one element
max = 1
while(len(pq)):
# check if current peek
# element minus previous
# element is greater than
# 1 This is done because
# if it's greater than 1
# then the sequence
# doesn't start or is broken here
if(pq[0] - prev > 1):
# Store the value of counter to 1
# As new sequence may begin
c = 1
# Update the previous position with the
# current peek And remove it
prev = pq[0]
pq.pop(0)
# Check if the previous
# element and peek are same
elif(pq[0] - prev == 0):
# Update the previous position with the
# current peek And remove it
prev = pq[0]
pq.pop(0)
# If the difference
# between previous element and peek is 1
else:
# Update the counter
# These are consecutive elements
c = c + 1
# Update the previous position
# with the current peek And remove it
prev = pq[0]
pq.pop(0)
# Check if current longest
# subsequence is the greatest
if(max < c):
# Store the current subsequence count as
# max
max = c
return max
# Driver Code
arr = [1, 9, 3, 10, 4, 20, 2]
n = 7
print("Length of the Longest consecutive subsequence is {}".format(
findLongestConseqSubseq(arr, n)))
# This code is contributed by Pushpesh Raj
OutputLength of the Longest consecutive subsequence is 4
Time Complexity: O(N*log(N)), Time required to push and pop N elements is logN for each element.
Auxiliary Space: O(N), Space required by priority queue to store N elements.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...