What is Liquidity Management?
Liquidity management is a strategy that an organisation adopts to efficiently manage its cash flow and ensure that it has enough liquid assets to meet its short-term financial obligations. The word liquidity means the ability of a company to convert its assets into cash. Effective liquidity is essential for various reasons including maintaining the financial health and stability of an organization, meeting contingency needs, and maintaining the position of solvency in the organisation. Liquidity management helps companies to optimize cash flow, reduce liquidity risk, and achieve the desired outcome.

Geeky Takeaways:
- Liquidity defines the ability of a company to convert its assets into cash within a year.
- Companies use various tools to streamline the liquidity management process and enhance overall cash flow visibility.
- Companies analyze liquidity risk factors and implement risk management strategies to safeguard liquidity.
- Inventory management helps in optimizing working capital levels and enhances the liquidity of the organisation.
Types of Liquidity
1. Asset Liquidity: Asset liquidity means how fast an asset can be converted into cash without affecting its market price. Highly liquid assets are easy to buy or sell, while assets with low liquidity may take longer to sell. Various assets are considered liquid assets, for instance, bills receivables, short-term investments, cash and cash equivalent, etc.
2. Market Liquidity: It refers to the condition of the market in which a company can easily be bought or sold. High market liquidity indicates that there are enough buyers and sellers in the market to execute the trade easily.
3. Fund Liquidity: Fund liquidity is when a company has enough funds to meet its short-term financial obligation. Businesses should have sufficient fund liquidity to cover operational expenses and other financial commitments. It is essential to have effective cash flow management to maintain fund liquidity.
4. Accounting Liquidity: It refers to the ability of a company to meet its short-term financial obligations using its readily available resources. The accounting liquidity can be measured with the help of the current ratio and quick ratio.
5. Regulatory Liquidity: Regulatory liquidity ensures the stability and ability of financial institutions to stand up against financial shocks. It is the liquidity requirements that are imposed by regulators on financial institutions. These requirements may include maintaining minimum levels of liquid assets or liquidity ratios.
Importance of Liquidity Risk Management
1. Managing Working Capital: Liquidity management helps in optimising the cash flow cycles by which companies can improve their liquidity position and enhance profitability. It plays a crucial role in maintaining the working capital of the company. Working capital represents the operational liquidity of the business and its ability to meet short-term obligations.
2. Financial Stability: Effective liquidity management reduces the risk of liquidity crises and provides financial stability to the business. By maintaining sufficient cash reserves and liquid assets, a business can survive economic fluctuations or disruptions in financial markets. The liquidity position is considered a crucial factor while assessing the creditworthiness of a business.
3. Meeting Short-Term Obligations: A business having adequate cash reserve, and liquid assets can meet its short-term obligations such as paying off short-term debts, payment to employees and any charges. This ensures the faith of the customers and other stakeholders in the organisation.
4. Managing Risk: It is important to maintain appropriate levels of liquidity as it helps in mitigating the risk of financial distress. Maintaining sufficient liquidity can reduce the reliance on bank loans or other credits having interest costs or other financing charges. Self-financing with the help of cash reserve will help reduce the cost and lower the risk.
5. Growth Opportunities: Liquidity management allows businesses to expand by having the necessary funds available to invest in new projects or acquire assets. Adequate liquidity can facilitate strategic decision-making and position a company for long-term success.
How to Assess Liquidity?
Liquidity means the ability of a company to convert its assets into cash. Effectively managing liquidity is crucial for maintaining the financial health and stability of an organization. There are few ratios with the help of which we can assess the liquidity of an organisation. The ratios are as follows,
1. Current Ratio: The current ratio assesses the short-term solvency of the company. Current assets are those assets that can be converted into cash within a year and current liabilities are those liabilities that can be paid off within a year. The ideal current ratio is considered to be 2:1.

2. Quick Ratio: It is also known as Liquid Asset or Acid Test Ratio. It focuses on the company’s ability to cover short-term obligations with its most liquid assets. The ideal quick ratio is considered to be 1:1.
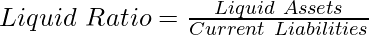
3. Working Capital: Working capital represents the amount of capital available to cover short-term obligations after subtracting short-term liabilities. Positive working capital indicates that the company has more current assets than current liabilities, which is favourable for liquidity.

Factors that Impact Liquidity Risk
1. Market Conditions: Market conditions can impact the liquidity risk of a company. Market conditions may include changes in interest rates, credit availability, and investor sentiment. An increase in the interest rates or tight credit markets may reduce access to funding and increase the liquidity risk. Companies with high debt levels or weak credit profiles suffer more in these critical market situations.
2. Lack of Funding: When an organization fails to obtain finance at competitive rates, it might increase its liquidity risk. The funding structure of a company, lines of credit, or other financing sources, affects liquidity risk.
3. Capital Expenditures: Unplanned capital structure affects the liquidity risk of a company. It can be increased if there is a lack of an asset management system, especially in heavily capital-intensive organizations. These businesses often have a high fixed to variable costs ratio which may increase the liquidity risk.
4. Management Practices: Governance, risk management, and liquidity management policies implemented by companies influence their liquidity risk. Effective liquidity risk management, stress testing, and contingency planning help mitigate liquidity risk and enhance the working.
1. Short-Term Borrowing: Short-term borrowings provide flexible funding options to cover short-term financial obligations. Companies can draw funds as needed and repay them when cash flow improves. It helps to manage their liquidity efficiently.
2. Cash Reserves: Maintaining adequate cash reserves is important for managing liquidity risk. Cash reserve is the amount that companies set aside to cover unexpected expenses, revenue shortfalls, or economic fluctuations.
3. Cash Flow Forecasting: Cash flow forecasting means projecting future cash inflows and outflows to anticipate liquidity needs. Historical data, budgeting, and financial modelling techniques are used by companies to forecast cash flows accurately. It helps in identifying potential cash shortfalls or surpluses of the business.
4. Working Capital Management: This focuses on optimizing the management of current assets and liabilities to improve liquidity. Working capital is the difference between the current assets and current liabilities of an organisation. Techniques such as inventory management help in optimizing working capital levels and enhance the liquidity of the organisation.
5. Hedging Instruments: Hedging instruments can be used to reduce the liquidity risks that arise from interest rate fluctuations or commodity price volatility. These instruments allow the organisation to reduce uncertainty and manage liquidity risks.
6. Central Bank Facilities: Access to central bank facilities, such as discount windows or emergency lending programs, provides emergency liquidity support during periods of financial stress. Companies can borrow from central banks as a last resort to address liquidity shortages and systemic risks.
Conclusion
Liquidity management ensures that a company has sufficient funds or assets to meet its short-term financial needs and can pay off its current liabilities. Effective liquidity is essential for various reasons including maintaining the financial health and stability of an organization, meeting contingency needs, and maintaining the position of solvency in the organisation. By applying liquidity management tools and techniques, companies can optimize cash flow, enhance liquidity, lower liquidity risk, and maintain financial stability.
Liquidity Management – FAQs
Why is liquidity management important?
Liquidity management is important for the financial health and stability of businesses. It enables companies to operate smoothly and maintain confidence among investors, creditors, and stakeholders.
What are the risks associated with liquidity management?
Risks associated with liquidity management include liquidity risk, funding risk, market risk, credit risk, regulatory risk and operational risk.
What are the regulatory requirements related to liquidity management?
Regulatory requirements related to liquidity management may include reporting obligations, stress testing, governance standards, and compliance with regulatory guidelines issued by financial authorities.
How can companies improve liquidity management?
Companies can improve liquidity management by optimizing working capital, maintaining adequate cash reserves, managing costs, implementing risk management strategies and monitoring liquidity metrics regularly.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...