Introduction of Secondary Memory
Last Updated :
14 Apr, 2023
Primary memory has limited storage capacity and is volatile. Secondary memory overcomes this limitation by providing permanent storage of data and in bulk quantity. Secondary memory is also termed external memory and refers to the various storage media on which a computer can store data and programs. The Secondary storage media can be fixed or removable. Fixed Storage media is an internal storage medium like a hard disk that is fixed inside the computer. A storage medium that is portable and can be taken outside the computer is termed removable storage media.
Secondary memory is a type of computer memory that is used for long-term storage of data and programs. It is also known as auxiliary memory or external memory, and is distinct from primary memory, which is used for short-term storage of data and instructions that are currently being processed by the CPU.
Secondary memory devices are typically larger and slower than primary memory, but offer a much larger storage capacity. This makes them ideal for storing large files such as documents, images, videos, and other multimedia content.
Some examples of secondary memory devices include hard disk drives (HDDs), solid-state drives (SSDs), magnetic tapes, optical discs such as CDs and DVDs, and flash memory such as USB drives and memory cards. Each of these devices uses different technologies to store data, but they all share the common feature of being non-volatile, meaning that they can store data even when the computer is turned off.
Secondary memory devices are accessed by the CPU via input/output (I/O) operations, which involve transferring data between the device and primary memory. The speed of these operations is affected by factors such as the type of device, the size of the file being accessed, and the type of connection between the device and the computer.
Overall, secondary memory is an essential component of modern computing systems and plays a critical role in the storage and retrieval of data and programs.
Difference between Primary Memory and Secondary Memory:
| Primary Memory |
Secondary Memory |
| Primary memory is directly accessed by the Central Processing Unit(CPU). |
Secondary memory is not accessed directly by the Central Processing Unit(CPU). Instead, data accessed from a secondary memory is first loaded into Random Access Memory(RAM) and is then sent to the Processing Unit. |
| RAM provides a much faster-accessing speed to data than secondary memory. By loading software programs and required files into primary memory(RAM), computers can process data much more quickly. |
Secondary Memory is slower in data accessing. Typically primary memory is six times faster than secondary memory. |
| Primary memory, i.e. Random Access Memory(RAM) is volatile and gets completely erased when a computer is shut down. |
Secondary memory provides a feature of being non-volatile, which means it can hold on to its data with or without electrical power supply. |
Uses of Secondary Media:
- Permanent Storage: Primary Memory (RAM) is volatile, i.e. it loses all information when the electricity is turned off, so in order to secure the data permanently in the device, Secondary storage devices are needed.
- Portability: Storage mediums, like CDs, flash drives can be used to transfer the data from one device to another.
Fixed and Removable Storage
Fixed Storage-
Fixed storage is an internal media device that is used by a computer system to store data, and usually, these are referred to as the Fixed disk drives or Hard Drives.
Fixed storage devices are literally not fixed, obviously, these can be removed from the system for repairing work, maintenance purposes, and also for an upgrade, etc. But in general, this can’t be done without a proper toolkit to open up the computer system to provide physical access, and that needs to be done by an engineer.
Technically, almost all of the data i.e. being processed on a computer system is stored on some type of a built-in fixed storage device.
Types of fixed storage:
- Internal flash memory (rare)
- SSD (solid-state disk) units
- Hard disk drives (HDD)
Removable Storage-
Removable storage is an external media device that is used by a computer system to store data, and usually, these are referred to as the Removable Disks drives or the External Drives.
Removable storage is any type of storage device that can be removed/ejected from a computer system while the system is running. Examples of external devices include CDs, DVDs, and Blu-ray disk drives, as well as diskettes and USB drives. Removable storage makes it easier for a user to transfer data from one computer system to another.
In storage factors, the main benefit of removable disks is that they can provide the fast data transfer rates associated with storage area networks (SANs)
Types of Removable Storage:
- Optical discs (CDs, DVDs, Blu-ray discs)
- Memory cards
- Floppy disks
- Magnetic tapes
- Disk packs
- Paper storage (punched tapes, punched cards)
Secondary Storage Media
There are the following main types of storage media:
1. Magnetic storage media:
Magnetic media is coated with a magnetic layer that is magnetized in clockwise or anticlockwise directions. When the disk moves, the head interprets the data stored at a specific location in binary 1s and 0s at reading.
Examples: hard disks, floppy disks, and magnetic tapes.
- Floppy Disk: A floppy disk is a flexible disk with a magnetic coating on it. It is packaged inside a protective plastic envelope. These are one of the oldest types of portable storage devices that could store up to 1.44 MB of data but now they are not used due to very little memory storage.
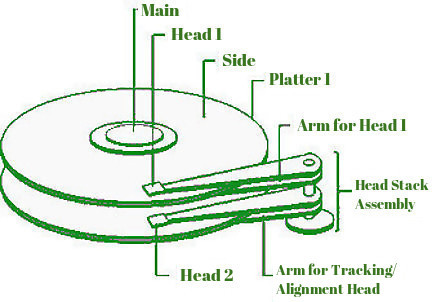
- Hard disk: A hard disk consists of one or more circular disks called platters which are mounted on a common spindle. Each surface of a platter is coated with magnetic material. Both surfaces of each disk are capable of storing data except the top and bottom disks where only the inner surface is used. The information is recorded on the surface of the rotating disk by magnetic read/write heads. These heads are joined to a common arm known as the access arm.
Hard disk drive components:
Most of the basic types of hard drives contain a number of disk platters that are placed around a spindle which is placed inside a sealed chamber. The chamber also includes read/write heads and motors. Data is stored on each of these disks in the arrangement of concentric circles called tracks which are divided further into sectors. Though internal Hard drives are not very portable and are used internally in a computer system, external hard disks can be used as a substitute for portable storage. Hard disks can store data up to several terabytes.
2. Optical storage media
In optical storage, media information is stored and read using a laser beam. The data is stored as a spiral pattern of pits and ridges denoting binary 0 and binary 1.
Examples: CDs and DVDs
- Compact Disk: A Compact Disc drive(CDD) is a device that a computer uses to read data that is encoded digitally on a compact disc(CD). A CD drive can be installed inside a computer’s compartment, provided with an opening for easier disc tray access or it can be used by a peripheral device connected to one of the ports provided in the computer system. A compact disk or CD can store approximately 650 to 700 megabytes of data. A computer should possess a CD Drive to read the CDs. There are three types of CDs:
| CD- ROM |
CD-R |
CD-RW |
| It stands for Compact Disk – Read Only Memory |
It stands for Compact Disk- Recordable. |
It stands for Compact Disk-Rewritable. |
| Data is written on these disks at the time of manufacture. This data cannot be changed, once is it written by the manufacturer, but can only be read. CD- ROMs are used for text, audio and video distribution like games, encyclopedias, and application software. |
Data can be recorded on these disks but only once. Once the data is written in a CD-R, it cannot be erased/modified. |
It can be read or written multiple times but a CD-RW drive needs to be installed on your computer before editing a CD-RW. |
- DVD:
It stands for Digital Versatile Disk or Digital Video Disk. It looks just like a CD and uses similar technology as that of the CDs but allows tracks to be spaced closely enough to store data that is more than six times the CD’s capacity. It is a significant advancement in portable storage technology. A DVD holds 4.7 GB to 17 GB of data.
- Blue Ray Disk:
This is the latest optical storage media to store high-definition audio and video. It is similar to a CD or DVD but can store up to 27 GB of data on a single-layer disc and up to 54 GB of data on a dual-layer disk. While CDs or DVDs use a red laser beam, the blue-ray disk uses a blue laser to read/write data on a disk.
3. Solid State Memories
Solid-state storage devices are based on electronic circuits with no moving parts like the reels of tape, spinning discs, etc. Solid-state storage devices use special memories called flash memory to store data. A solid state drive (or flash memory) is used mainly in digital cameras, pen drives, or USB flash drives.
Pen Drives:
Pen Drives or Thumb drives or Flash drives are the recently emerged portable storage media. It is an EEPROM-based flash memory that can be repeatedly erased and written using electric signals. This memory is accompanied by a USB connector which enables the pen drive to connect to the computer. They have a capacity smaller than a hard disk but greater than a CD. Pendrive has the following advantages:
- Transfer Files:
A pen drive is plugged into a USB port of the system can be used as a device to transfer files, documents, and photos to a PC and also vice versa. Similarly, selected files can be transferred between a pen drive and any type of workstation.
- Portability:
The lightweight nature and smaller size of a pen drive make it possible to carry it from place to place which makes data transportation an easier task.
- Backup Storage:
Most of the pen drives now come with the feature of having password encryption, important information related to family, medical records, and photos can be stored on them as a backup.
- Transport Data:
Professionals/Students can now easily transport large data files and video/audio lectures on a pen drive and gain access to them from anywhere. Independent PC technicians can store work-related utility tools, various programs, and files on a high-speed 64 GB pen drive and move from one site to another.
-
Here are some advantages and disadvantages of secondary memory:
Advantages:
- Large storage capacity: Secondary memory devices typically have a much larger storage capacity than primary memory, allowing users to store large amounts of data and programs.
- Non-volatile storage: Data stored on secondary memory devices is typically non-volatile, meaning it can be retained even when the computer is turned off.
- Portability: Many secondary memory devices are portable, making it easy to transfer data between computers or devices.
- Cost-effective: Secondary memory devices are generally more cost-effective than primary memory.
Disadvantages:
- Slower access times: Accessing data from secondary memory devices typically takes longer than accessing data from primary memory.
- Mechanical failures: Some types of secondary memory devices, such as hard disk drives, are prone to mechanical failures that can result in data loss.
- Limited lifespan: Secondary memory devices have a limited lifespan, and can only withstand a certain number of read and write cycles before they fail.
- Data corruption: Data stored on secondary memory devices can become corrupted due to factors such as electromagnetic interference, viruses, or physical damage.
- Overall, secondary memory is an essential component of modern computing systems, but it also has its limitations and drawbacks. The choice of a particular secondary memory device depends on the user’s specific needs and requirements.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...