How to Upload Multiple Images and Text to MySQL Database in PHP?
Last Updated :
30 Apr, 2024
In web development, many times we need to handle multiple files at once while uploading and storing into the database. So in this article, we will see how to do this by various approaches to achieve this using PHP and MySQL.
Approach 1: Storing Images in the File System
In this approach, the images are uploaded to a server directory, and their paths are stored in the database. This method is good for handling large volumes of images and allows for easily management of files.
Step 1: HTML Form for Uploading Multiple Images
<form action="file1.php" method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data">
<input type="file" name="images[]" multiple>
<input type="text" name="text_data">
<input type="submit" name="submit" value="Upload">
</form>
Step 2: PHP Script to Handle Uploads and Database Insertion
$targetDir = "images/";
foreach ($_FILES['images']['name'] as $key => $value) {
$fileName = basename($_FILES['images']['name'][$key]);
$targetFilePath = $targetDir . $fileName;
move_uploaded_file($_FILES["images"]["tmp_name"][$key], $targetFilePath));
}
$stmt = $conn->prepare("INSERT INTO tbl_images (img_url, img_txt) VALUES (?, ?)");Step 3: Create a Database Table
CREATE TABLE images_table (
id INT AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY,
img_url VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL,
img_txt TEXT NOT NULL
);
- Here we using a HTML forms to upload images along with text data.
- In the PHP script, move the uploaded file to the “images” directory and retrieve its file path.
- Then making an SQL query to insert the file path and text data into the database.
Example:
PHP
<?php
include_once("conn.php");
if (isset($_POST["submit"])) {
$stmt = $conn->prepare("INSERT INTO tbl_images (img_url, img_txt) VALUES (?, ?)");
$stmt->bind_param("ss", $imagePath, $textData);
$uploadedImages = $_FILES['images'];
$textData = $_POST['text_data'];
foreach ($uploadedImages['name'] as $key => $value) {
$targetDir = "images/";
$fileName = basename($uploadedImages['name'][$key]);
$targetFilePath = $targetDir . $fileName;
if (file_exists($targetFilePath)) {
echo "Sorry, file already exists.<br>";
} else {
if (move_uploaded_file($uploadedImages["tmp_name"][$key], $targetFilePath)) {
$imagePath = $targetFilePath;
$stmt->execute();
echo "The file " . $fileName . " has been uploaded successfully.<br>";
} else {
echo "Sorry, there was an error uploading your file.<br>";
}
}
}
$stmt->close();
$conn->close();
}
?>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content=
"width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Image Upload 1</title>
</head>
<body>
<br><br>
<form action="file1.php" method="post"
enctype="multipart/form-data">
Select Image Files:
<input type="file" name="images[]" multiple>
<br><br>
<input type="text" name="text_data">
<br><br>
<input type="submit" name="submit" value="Upload">
</form>
</body>
</html>
<?php
$servername = "localhost";
$username = "root";
$password = "";
$dbname = "gfgdb";
$conn = new mysqli($servername, $username, $password, $dbname);
if ($conn->connect_error) {
die("Connection failed: " . $conn->connect_error);
}
Output:
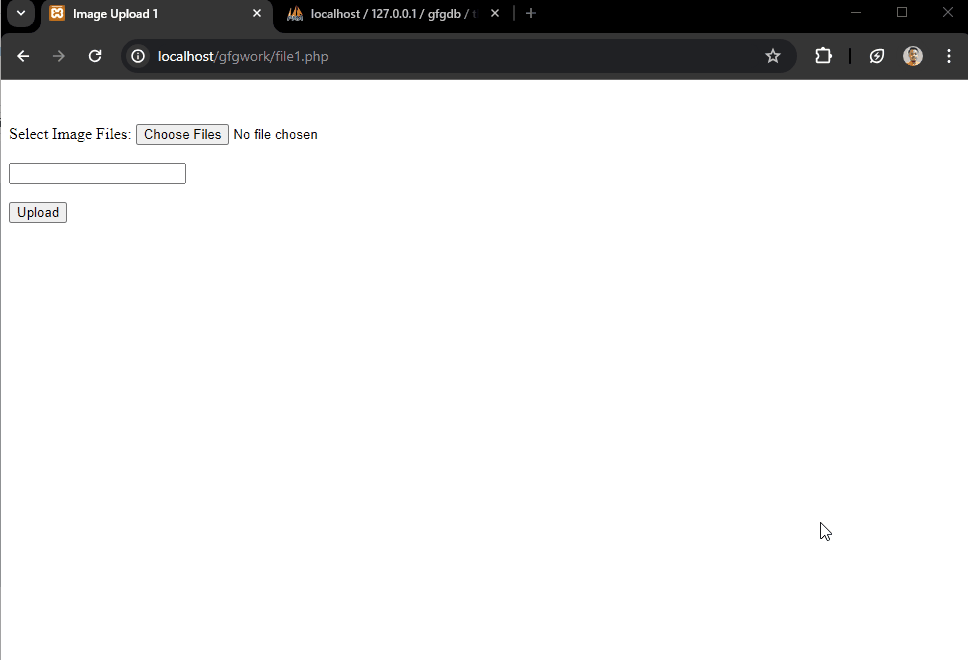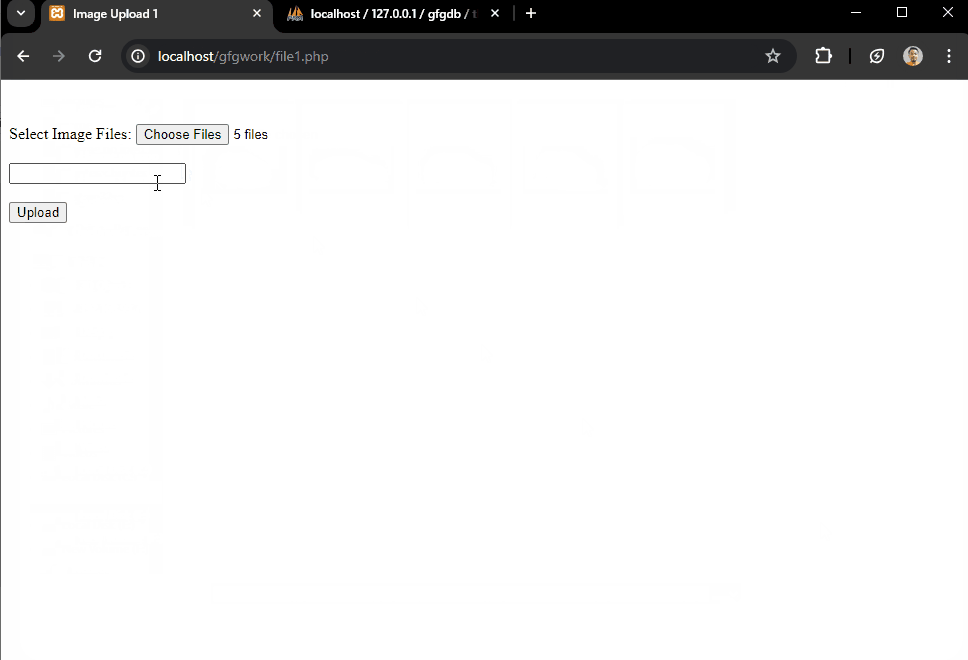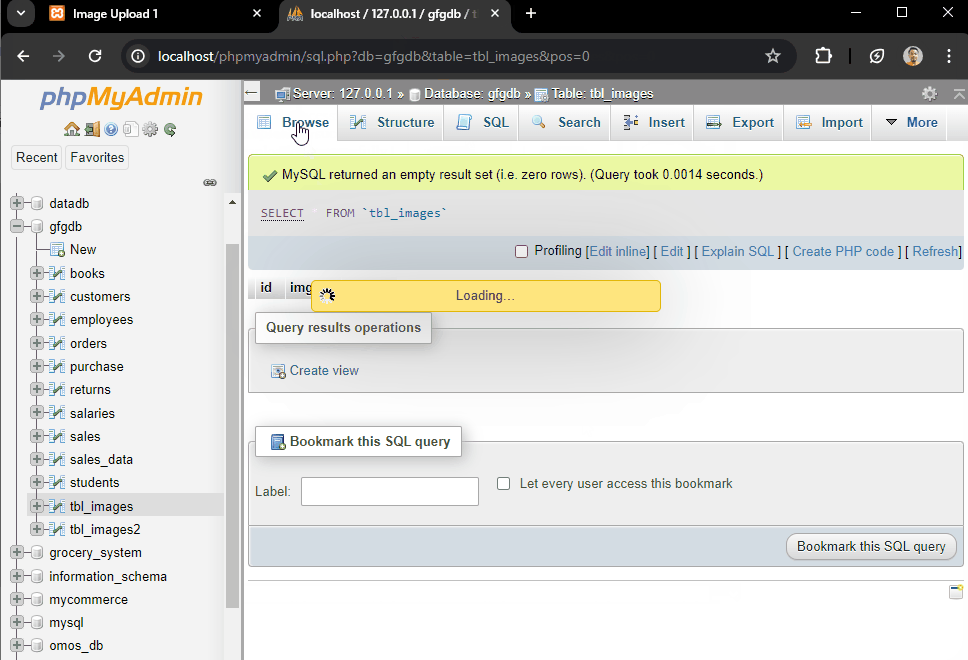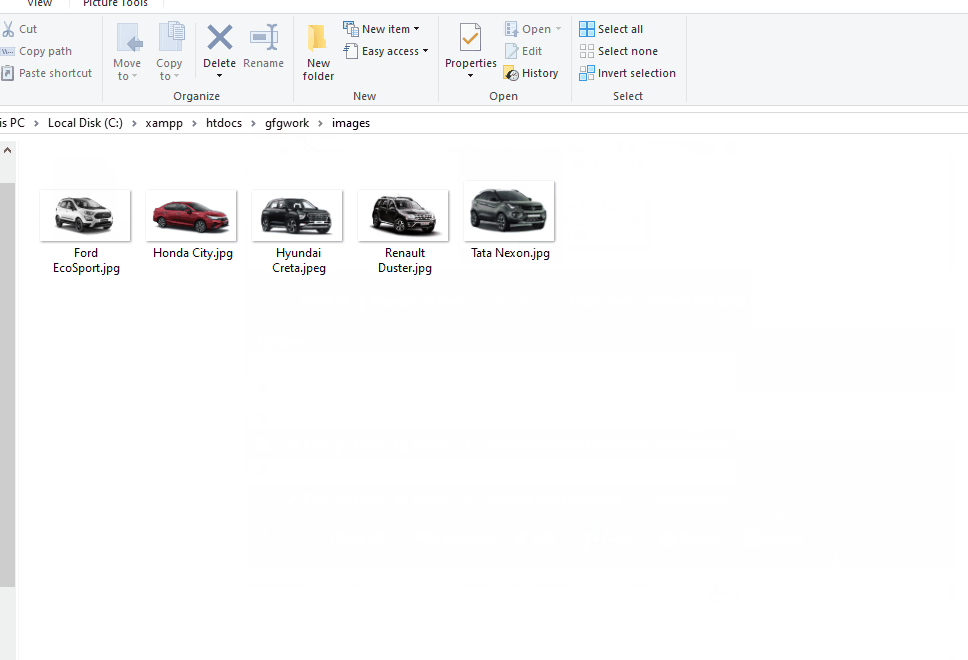
image upload 1
Approach 2: Using Base64 Encoding
Another way is base64 encoding, images are converted to a string format and stored directly in the database. This approach simplifies file management but may increase database size and retrieval time.
Step 1: HTML Form for Uploading Multiple Images
<form action="file1.php" method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data">
<input type="file" name="images[]" multiple>
<input type="text" name="text_data">
<input type="submit" name="submit" value="Upload">
</form>
Step 2: PHP Script to Handle Image upload, incoding and Database Insertion
foreach ($_FILES['images']['tmp_name'] as $key => $tmp_name) {
$imageData = base64_encode(file_get_contents($tmp_name));
$stmt = $conn->prepare("INSERT INTO tbl_images2 (img_data, img_txt) VALUES (?, ?)");
}Step 3: Create a Database Table
CREATE TABLE tbl_images2 (
id INT AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY,
img_data MEDIUMTEXT NOT NULL,
img_txt TEXT NOT NULL
);
- Created a database table with a column to store base64 encoded image data.
- Using HTML forms to upload images.
- In the PHP script, encode the uploaded image to base64 format and store it directly in the database.
Example:
PHP
<?php
include_once("conn.php");
if (isset($_POST["submit"])) {
$stmt = $conn->prepare("INSERT INTO tbl_images2 (img_data, img_txt) VALUES (?, ?)");
$stmt->bind_param("ss", $imageData, $textData);
$uploadedImages = $_FILES['images'];
$textData = $_POST['text_data'];
foreach ($uploadedImages['tmp_name'] as $key => $tmp_name) {
$imageData = base64_encode(file_get_contents($tmp_name));
$stmt->execute();
echo "The file " . $fileName = basename($uploadedImages['name'][$key])
. " has been uploaded successfully.<br>";
}
$stmt->close();
$conn->close();
}
?>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Image Uplaod 2</title>
</head>
<body>
<br><br>
<form action="file2.php" method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data">
Select Image Files:
<input type="file" name="images[]" multiple>
<br><br>
<input type="text" name="text_data">
<br><br>
<input type="submit" name="submit" value="Upload">
</form>
</body>
</html>
<?php
$servername = "localhost";
$username = "root";
$password = "";
$dbname = "gfgdb";
$conn = new mysqli($servername, $username, $password, $dbname);
if ($conn->connect_error) {
die("Connection failed: " . $conn->connect_error);
}
Output:
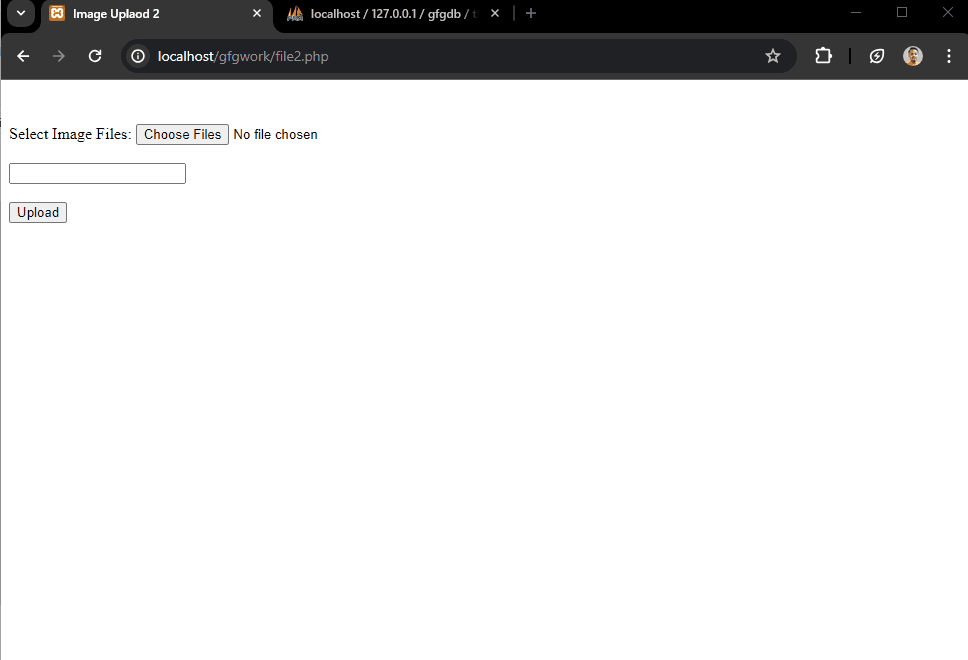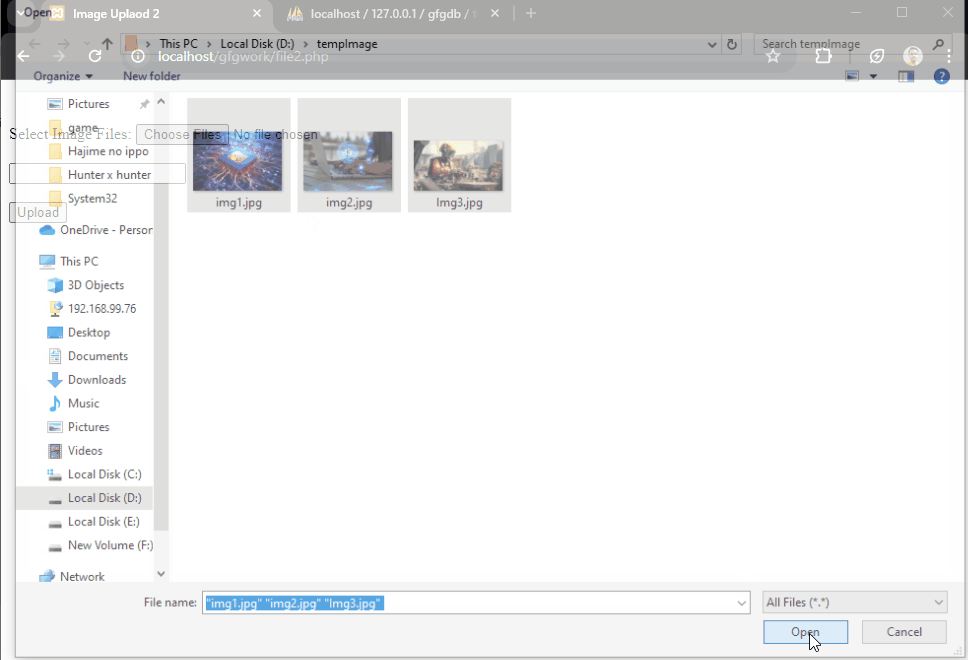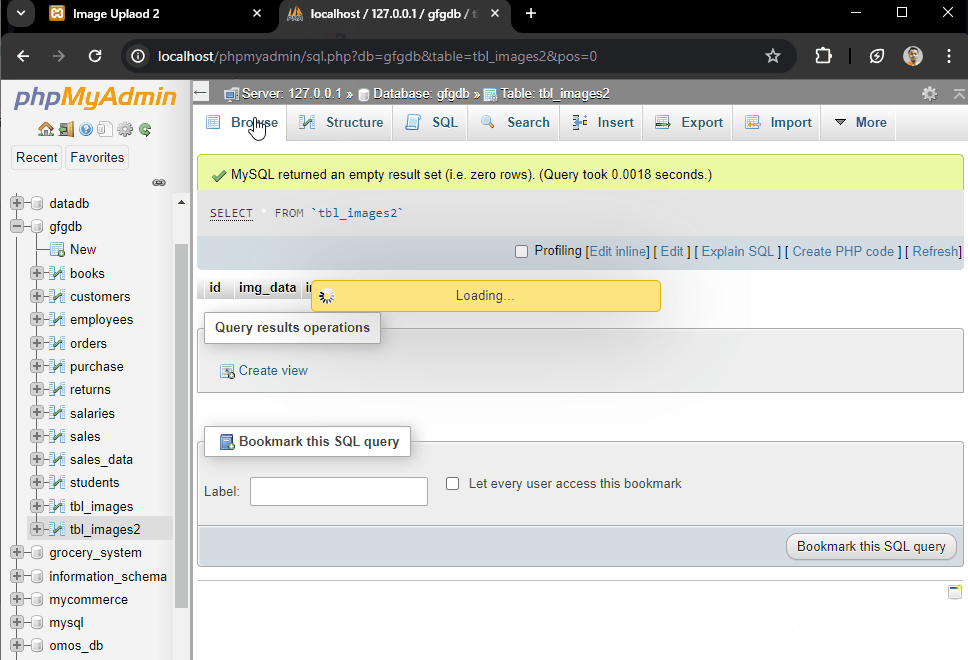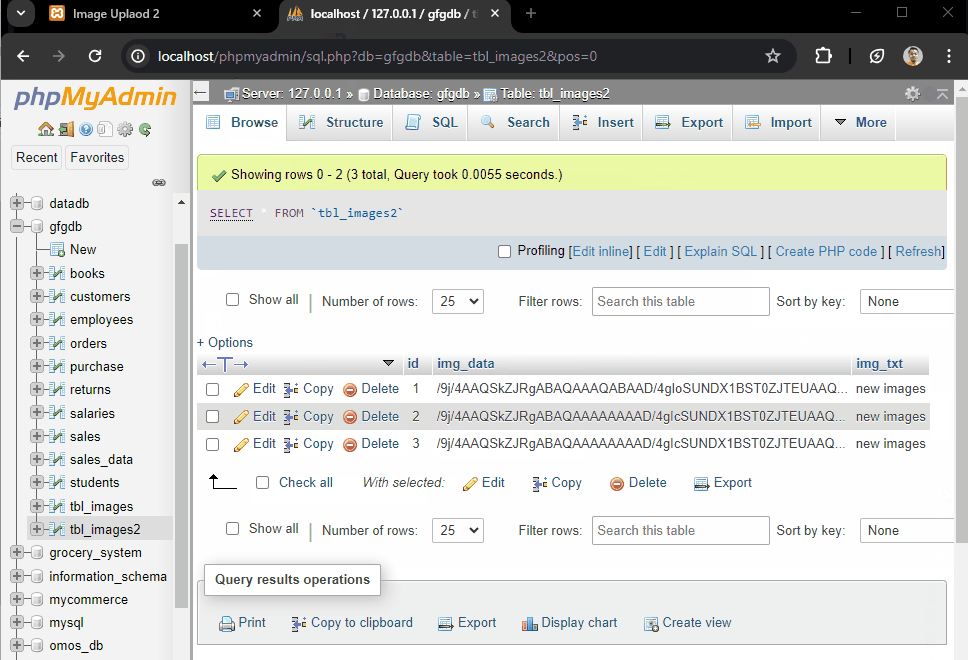
Php image upload 2
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...