How to Select 10 Random Rows from 600K Rows Fast in MySQL?
Last Updated :
12 Apr, 2024
Selecting random rows simultaneously from a database is a common task in SQL especially when handling large datasets. Selecting multiple rows is useful for sampling data or generating random subsets for analysis. In MySQL, this can be achieved using various methods, each has its advantages.
In this article, we explore retrieving 10 random rows from a dataset of 600k rows in MySQL using three methods. We present their syntax, examples, and explanations, providing insights into efficient random row selection.
Retrieving 10 Random Rows from 600K Rows in MySQL
The RAND() function is a type of function in SQL that helps to select multiple rows in the already existing data from the table. Let’s explore some of the common approaches to selecting Multiple Rows. The common approaches are as follows:
- Using the RAND() Function
- Using Primary Key for Random Selection
- Random Sampling with User Variables
Setting up Environment
We can create the Employee table using the following code which defines the table structure with columns such as ‘empId,’ ‘name,’ and ‘dept,’ as Columns.
Query to create EMPLOYEE Table:
CREATE TABLE EMPLOYEE (
empId INTEGER PRIMARY KEY,
name TEXT NOT NULL,
dept TEXT NOT NULL
);
Insert data in the EMPLOYEE table:
INSERT INTO EMPLOYEE VALUES (1, 'Clark', 'Sales');
INSERT INTO EMPLOYEE VALUES (2, 'Dave', 'Accounting');
INSERT INTO EMPLOYEE VALUES (3, 'Ava', 'Marketing');
INSERT INTO EMPLOYEE VALUES (4, 'GFG', 'Development');
INSERT INTO EMPLOYEE VALUES (5, 'Adam', 'Testing');
INSERT INTO EMPLOYEE VALUES (6, 'Evan', 'Operations');
INSERT INTO EMPLOYEE VALUES (7, 'Avanya', 'Accounting');
INSERT INTO EMPLOYEE VALUES (8, 'Ziv', 'Sales');
INSERT INTO EMPLOYEE VALUES (9, 'Gia', 'Development');
INSERT INTO EMPLOYEE VALUES (10, 'Ele', 'Testing');
INSERT INTO EMPLOYEE VALUES (11, 'Jonas', 'Operations');
INSERT INTO EMPLOYEE VALUES (12, 'Hany', 'Accounting');
INSERT INTO EMPLOYEE VALUES (13, 'Sam', 'Sales');
Output:
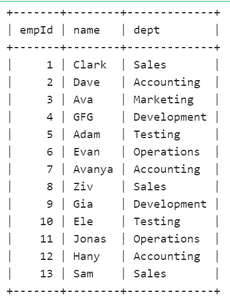
Employee Table
1. Using the RAND() Function
The simplest the easiest way to select random rows is by using the RAND() function. This function generates a random floating-point value between 0 and 1 for each row, allowing us to sort and limit the selection.
Syntax:
SELECT * FROM Table name
ORDER BY RAND()
LIMIT 10;
Example: Select RAND() for Employee Table
Query:
SELECT * FROM Employee
ORDER BY RAND()
LIMIT 10;
This query selects 10 random rows from EMPLOYEE. The ORDER BY RAND() clause randomizes the row order, and the LIMIT 10 clause restricts the output to 10 rows.
Output:

Using RAND() function
Explanation: The SQL query selects 10 random rows from the Employee table and orders them randomly. The output displays those 10 rows in a random order.
2. Using Primary Key for Random Selection
If the table has a numeric primary key with relatively few gaps, you can use it for more efficient random selection.
Syntax:
SELECT * FROM Table Name
WHERE column_name >= (SELECT FLOOR(MAX(column_name) * RAND()) FROM Employee)
ORDER BY column_name
LIMIT 10;
Example: Select Primary key for Employee Table
Query:
SELECT * FROM Employee
WHERE empId >= (SELECT FLOOR(MAX(empId) * RAND()) FROM Employee)
ORDER BY empId
LIMIT 10;
This query randomly selects a starting point based on the primary key and retrieves the next 10 rows.
Output:

Using Primary Key
Explanation: This SQL query selects 10 random rows from the Employee table by setting a minimum empId value equal to a randomly generated value between 0 and the maximum empId in the table. It then orders the selected rows by empId.
3. Random Sampling with User Variables
For more control over randomness, especially in large datasets, we can use user variables to assign a random number to each row and then select based on these numbers.
Syntax:
SET @row_number = 0;
SELECT *
FROM (
SELECT *, (@row_number:=@row_number + 1) AS num
FROM Table Name
ORDER BY RAND()
) AS t
WHERE num % (SELECT ROUND(COUNT(*) / 10) FROM Table Name) = 0
LIMIT 10;
Example: Select Random Sampling for Employee Table
Query:
SET @row_number = 0;
SELECT *
FROM (
SELECT *, (@row_number:=@row_number + 1) AS num
FROM Employee
ORDER BY RAND()
) AS t
WHERE num % (SELECT ROUND(COUNT(*) / 10) FROM Employee) = 0
LIMIT 10;
This query first assigns a row number to each row in a random order, then selects rows based on these numbers.
Output:
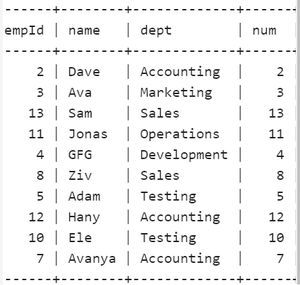
Using Random Sampling
Explanation: This SQL query assigns sequential row numbers to each row in the Employee table, orders them randomly, and then selects every 10th row based on the total row count, resulting in a set of 10 random rows.
Conclusion
Choosing the right method for selecting random rows in MySQL depends on our specific requirements, such as the size of our dataset and the need for reproducibility or performance. This helps us in flexibility to meet our target. Overall, it offers a direct and efficient method of selecting multiple rows in a table at once. Developers can easily edit and manage data ensuring fast operations and accurate record updates.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...