How to Create a Project Roadmap?
Last Updated :
10 Apr, 2024
A project roadmap is a strategic visual aid used in project management that lists the main goals, deadlines, dependencies, and milestones of a project. It’s an interactive document that makes project direction and progress evident to stakeholders.
What is a Project Roadmap?
A project roadmap serves as a strategic planning tool that outlines the journey a project will take from its inception to its completion. Much like a traditional roadmap guides travellers along a route, a project roadmap guides project stakeholders through the various stages and milestones of a project.
Here’s a more detailed breakdown of what a project roadmap typically includes:
- Objectives and Vision: The roadmap begins by clearly defining the project’s objectives and overarching vision. This provides a shared understanding of the purpose and desired outcomes of the project among all stakeholders.
- Main Goals and Deliverables: It outlines the main goals and deliverables that the project aims to achieve. These goals are typically high-level and aligned with the project’s objectives.
- Timeline and Duration: The roadmap includes a timeline indicating the project’s expected duration, including start and end dates. This timeline may be broken down into phases or iterations, each with its own set of milestones and deliverables.
- Key Milestones and Deliverables: Important milestones and deliverables are identified along the timeline. These milestones mark significant achievements or progress points within the project and serve as checkpoints to assess progress.
- Dependencies and Relationships: The roadmap may also highlight dependencies and relationships between different tasks, activities, or milestones within the project. Understanding these dependencies helps stakeholders prioritize and sequence tasks effectively.
Why Do You Need a Project Roadmap?
A project roadmap serves several crucial purposes:
- Strategic Alignment: A roadmap aligns the project with the broader strategic goals of the organization. It outlines how the project contributes to achieving those goals and ensures that resources are allocated effectively.
- Scope Definition: A roadmap helps define the scope of the project by breaking it down into manageable tasks and deliverables. This clarity prevents scope creep and ensures that the project stays focused on its objectives.
- Resource Planning: By outlining the timeline and dependencies of various tasks, a roadmap enables effective resource planning. It helps in allocating human, financial, and other resources efficiently throughout the project lifecycle.
- Risk Management: Identifying potential risks and challenges is crucial for project success. A roadmap allows teams to anticipate and mitigate risks by incorporating contingency plans and alternative approaches into the project plan.
- Communication Tool: A roadmap serves as a communication tool for both internal team members and external stakeholders. It provides a visual representation of the project’s progress, milestones, and timelines, facilitating clear and transparent communication about project status and expectations.
- Decision Making: Having a roadmap in place enables informed decision-making throughout the project lifecycle. It provides stakeholders with the necessary information to make strategic decisions, prioritize tasks, and reallocate resources as needed.
How is a Project Roadmap Different from a Project Plan?
While both documents are essential in project management, they serve different purposes:
Project Roadmap: Provides a high-level overview of the project’s goals, milestones, and timelines. It focuses on strategic planning and communication with stakeholders.
- Think of the project roadmap as a big picture view of the project.
- It’s like a map that shows where you’re going and major landmarks along the way.
- The roadmap focuses on the project’s goals, key milestones, and general timelines.
- It’s mainly for stakeholders like bosses, clients, or team members who want to understand what the project is about and when they can expect major progress.
Project Plan: Offers detailed guidance on how the project will be executed, including tasks, schedules, resources, and budgets. It serves as a tactical tool for project teams to follow during implementation.
- Now, the project plan is like the detailed step-by-step instructions for reaching those landmarks on the map.
- It breaks down tasks, schedules, resources needed, and budgets in detail.
- It’s more for the project team to follow day-to-day during the project execution.
- It helps keep everyone on track and ensures that tasks are completed efficiently and on time.
|
Aspect
|
Project Roadmap
|
Project Plan
|
|
Purpose
|
High-level overview of objectives, goals, and milestones
|
Detailed tasks, resources, timelines
|
|
Scope
|
Broad and strategic
|
Specific and detailed
|
|
Timeframe
|
Entire project duration
|
Shorter, immediate timeframe
|
|
Audience
|
Stakeholders, decision-makers
|
Project team, managers
|
|
Level of Detail
|
Less detailed, high-level
|
Highly detailed
|
|
Flexibility
|
Flexible and adaptable
|
Less flexible, detailed plans
|
|
Visualization
|
Often visual (e.g., timelines)
|
May include visuals, but text-heavy
|
|
Timeline Alignment
|
Aligns with long-term goals
|
Detailed tasks align with roadmap
|
Key Elements in a Project Roadmap:
In order to organise and convey the project’s goals, schedule, and milestones effectively, a project roadmap usually consists of a few essential components. The following are the crucial components:
- Project Goals and Objectives: Clearly defined goals and objectives provide the overarching purpose and direction of the project. These should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART).
- Timeline: The timeline outlines the project’s duration, including start and end dates, as well as key milestones and deliverables along the way. It helps in visualizing the project’s progression over time.
- Milestones: Milestones are significant achievements or events within the project timeline. They mark key points of progress and are used to track the project’s advancement. Milestones should be clearly defined, achievable, and linked to specific deliverables or outcomes.
- Tasks and Activities: Tasks and activities break down the project into actionable steps. They detail the specific actions required to achieve project milestones and deliverables. Tasks are often organized into phases or stages to facilitate project management and coordination.
- Dependencies: Dependencies represent the relationships between tasks and activities. They indicate which tasks must be completed before others can start or proceed. Identifying dependencies helps in sequencing tasks and managing project timelines effectively.
How to Create a Project Roadmap – 9 Steps:
Creating an effective project roadmap involves careful planning and collaboration. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
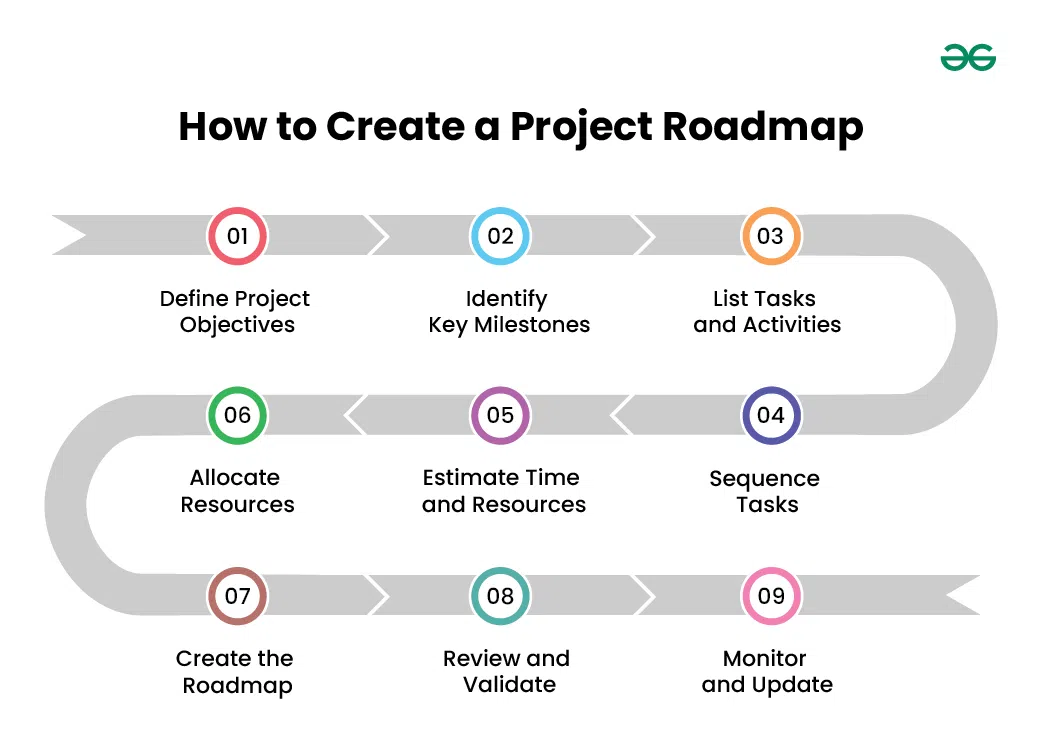
How to Create a Project Roadmap
- Define Project Objectives: Begin by clearly articulating the overarching goals and objectives of the project. These objectives should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). Take the time to ensure that these objectives are aligned with the organization’s strategic priorities and that they represent a clear understanding of what the project aims to accomplish.
- Identify Key Milestones: Break down the project into significant milestones that represent critical points of progress. These milestones should mark key achievements or deliverables throughout the project lifecycle. By identifying milestones, you create a roadmap with clear markers for tracking progress and ensuring that the project stays on schedule.
- List Tasks and Activities: Once you have identified your milestones, break them down into smaller, actionable tasks and activities. These tasks should represent the specific actions required to achieve each milestone. Use techniques like brainstorming, task decomposition, and expert input to ensure that you capture all necessary tasks.
- Sequence Tasks: Determine the order in which tasks need to be completed based on their dependencies and constraints. Some tasks may need to be completed before others can begin, while others can be done concurrently. Use tools like precedence diagrams or dependency charts to visualize task dependencies and identify critical paths.
- Estimate Time and Resources: Estimate the time and resources required to complete each task. This includes considering factors like the effort required, resource availability, and any constraints or dependencies that may impact task duration. Use historical data, expert judgment, or project management software to make realistic estimations.
- Allocate Resources: Once you have estimated the time and resources required for each task, allocate resources accordingly. Ensure that resources are assigned based on availability, skills, and dependencies. Be mindful of resource constraints and prioritize tasks to optimize resource utilization and minimize bottlenecks.
- Create the Roadmap: Use project management software, spreadsheets, or visual tools like Gantt charts to create the roadmap. Lay out the project timeline, milestones, tasks, and dependencies in a clear and organized manner. Consider using color-coding or different formatting to highlight critical tasks or milestones.
- Review and Validate: Review the roadmap with key stakeholders to ensure that it accurately reflects project objectives, constraints, and requirements. Seek input from project sponsors, team members, and subject matter experts to validate the plan. Incorporate feedback and make any necessary revisions or adjustments to ensure alignment and buy-in.
- Monitor and Update: Continuously monitor the progress of the project against the roadmap. Track task completion, milestone achievements, and any deviations from the planned timeline or scope. Regularly update the roadmap to reflect changes in project status, priorities, or requirements. Communicate updates to stakeholders to keep them informed and engaged throughout the project lifecycle.
Related Articles:
Conclusion: Project Roadmap
In conclusion, a project roadmap is a vital tool for guiding projects from start to finish. It outlines goals, timelines, and milestones, helping teams stay focused and stakeholders informed. By following the steps outlined, teams can create effective roadmaps that keep projects on track and ensure everyone is moving in the right direction. With clear objectives, careful planning, and ongoing monitoring, projects can achieve success while keeping everyone aligned and engaged.
FAQs: Project Roadmap
What should a project roadmap include?
A project roadmap should include objectives, milestones, timelines, dependencies, and key deliverables, providing a high-level overview of the project’s direction and progress.
How do I create a roadmap for a project for free?
You can create a project roadmap for free using online tools like Trello, Asana, or Google Sheets. These platforms offer templates and features for organizing tasks, timelines, and milestones.
Is a roadmap a project plan?
No, a roadmap is not a project plan. While a roadmap provides a high-level overview of project goals and milestones, a project plan offers detailed guidance on tasks, schedules, resources, and budgets for project execution.
Is a Gantt chart a roadmap?
A Gantt chart is a type of roadmap that visualizes project timelines, tasks, and dependencies. While it is often used as part of a roadmap, it focuses primarily on scheduling and tracking project activities over time.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...