Hick’s Law in UX
Last Updated :
05 Mar, 2024
What is Hick’s Law?
Hick’s Law has a multifaceted impact not only on areas such as human-computer interaction, user experience design, and interface design but also on human society as a whole. For this reason, designers who work in such environments commonly engage in processes to decrease the decision time by means of interface simplification, reduction of the choice number, and grouping of options so that users can make decisions easier and faster. The aim is to make interfaces that are user-friendly, and natural, and expect no bombarding of options that will intimidate users in the end for you to have a great user experience.
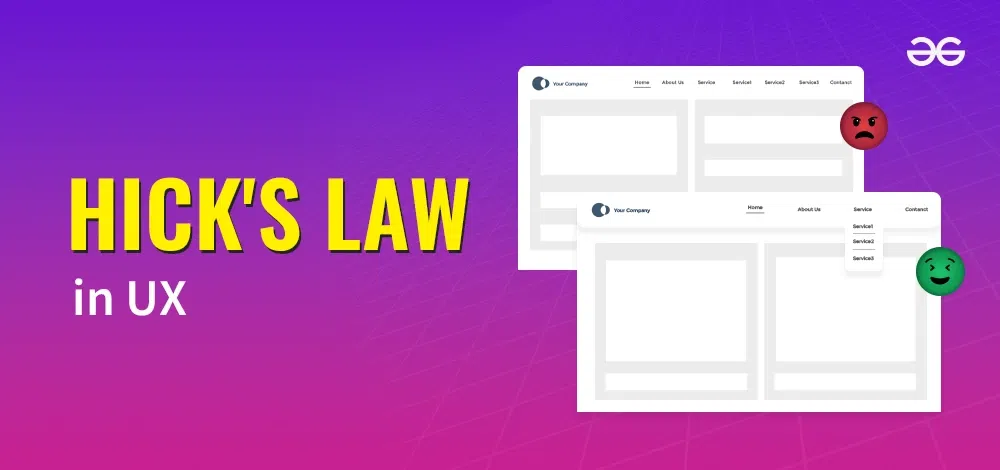
Hick’s Law in UX
Mathematically, Hick’s Law is often expressed as:
[Tex]RT = a +b.log2(N)[/Tex]
where:
- RT is the response time,
- N is the number of stimuli or choices,
- log2 is the base-2 logarithm,
- a and b are constants that depend on the task and specific conditions.
Hick’s law, which takes its name from the discovery of psychologists William Edmund Hick and Ray Hyman, proposes that the time it takes to arrive at a decision is directly proportional to the number of decision-making alternatives. This rule proposes: As time to chose a particular restaurant would increase if the number of restaurants increases logarithmically.
It conversely means that the more option there are, the longer it will take the decision time to be in linear correspondence with the logarithm of the number of choices. The increase in the number of choices is directly proportional to the amount of time to make the decision.
Examples of Hick’s Law
1. Website Navigation:
Having a good designed website with the easy menu with a limit number of entries in each category and has much lighter to find the relevant information.
2. Mobile App Interfaces:
Applications which offer fewer options on each screen, directing users through the process one step at a time, that hasten choice making.
3. E-commerce Platforms:
In this regard, online platforms that have comprehensive and well-organized product menus, making the browsing and purchasing process for the users easier and simple.
4. Restaurant Menus:
The simpler the menu the better; categories that have few choices per section, with the diners not overwhelmed by the selection.
5. Instructional Design:
E-learning modules to break the subject matter into small portions, tracking a logical sequence of learning, and reducing the amount of mental work required .
What is Hick’s Law in User Experience?
Hick’s Law, commonly known as Hick-Hyman Law, is a psychological phenomenon which reveals the amount of time human requires to make a decision by the number of available selections. It is frequently used in the settings of user experience and interface design to explore the bond between the number of choices given to an individual and the decision making time of this individual.
Named after William Edmund Hick and Ray Hyman who first talked about in the early 1952, the law is an explanation of our mental process. In brief, this notion entails that in addition to the number of choices (or better said, stimuli) the decision time will also increase in a logarithmic way! And what is this if not the fact that as more choices are available for the consumer, the amount of time it takes a person to make a decision grows longer?
When it comes to interface design in UX, Hick’s law is usually a thing that designers keep in mind when making some critical decisions such as the quantity of the menu items, navigation options, and choices displayed to users. The main aim of the designers is to discover the golden middle ground by offering a wide variety of options which would enable the users to reach their targets and by that cutting down the overwhelming choices that could be either decision making block or slowing down the task completion.
Minimizing the options or structuring them in a sensible way can have a positive impact on making the decision process shorter and having a higher number of satisfied users. It underlines the significance of simplicity and comprehensibility of design help to make usability by cutting the cognitive load as well as choice paralysis.
How to Implement Hick’s Law?
1. Prioritize Information:
- Find the vital point which will help the users to make the decision.
- By prioritizing and organizing this information with respect to its significance and importance vis-à-vis user’s goals, it will suffice.
2. Simplify Choices:
- Reducing the number of alternatives offered during a single time, will more likely result in a positive shopping event.
- Why not limit numbers of the menu items, links or buttons for making choices easier?
3. Group Related Options:
- Put similar options or actions in one group. That makes it easier and more convenient to search through their options.
- Use categories or sections to group the information in a more logical way.
4. Progressive Disclosure:
- Progressive disclosure involves showing data or options in stages as the user interacts with the interface.
- For fundamental facts, start with them first and add more details as the need arises.
5. Clear Navigation:
- Make a clean, well-organized structure for navigation, as the main goal is to allow users to find whatever they look for easily.
- Reduce nonfunctional steps and create clear roads that lead to the best functions.
6. Visual Hierarchy:
- As for visual hierarchy, focus on the main components it. Indicate vital actions like selecting options with a more prominent style to direct the user’s focus.
7. User Testing:
- Conduct a usability test that allows to see how the actual users act when dealing with it.
- Lay back the feedback mechanism of the decision-making process iterate based on user understanding.
8. Contextual Help:
- Add context importance and details or provide the users tips that will enable them to comprehend the intent and consequences of their choices.
9. Adaptive Interfaces:
- Imagine adaptive interfaces which are capable of offering choice of options that are based on user’s inclination, their past history, and the setting of work.
10. Performance Optimization:
- Ensure that performance of an interface is refined to make response times less delayed. Slow loading of the website can increase the level of end-users’ anger and hesitation.
Conclusion
In nutshell, Hicks law is a fundamental principle that unmasks this cause and effect relation between numbers of alternatives and delays of choice. It is not just User Experience Design, but it is the one which is adding value by making the interface aesthetically pleasing and removing he unnecessary options from it. While implementing Hick’s principle, the designers focus on simple functions, user accessibility, and therefore acceptability of the application by users. Even the digital spaces are under the purview of the law, which covers education, marketing and organizational decision-making as well. Facing Hick’ Law aims at practicality, resourcefulness, and user-friendliness through the identification of users’ needs and the realization of the importance of proper elaboration as a way of presenting users with a comprehensive decision-making environment.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...