Given a number N in decimal base, find number of its digits in any base (base b)
Last Updated :
28 Feb, 2023
Given A Number n in a base 10, find the number of digits in its base b representation.
Constraints : 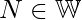 Whole
Whole
Examples :
Input : Number = 48
Base = 4
Output: 3
Explanation : (48)10 = (300)4
Input : Number = 1446
Base = 7
Output: 4
Explanation : (446)10 = (4134)7
A simple approach: convert the decimal number into the given base r and then count number of digits.
An efficient approach : It resides on the relationship between the base of the number and number of digits of that number.
Typically : Let n be a positive integer. The base 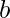 representation of
representation of 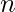 has
has 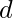 digits if
digits if 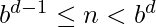 , which is the case if
, which is the case if 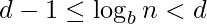 or
or 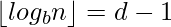 .The number of digits in the base b representation of n is therefore
.The number of digits in the base b representation of n is therefore
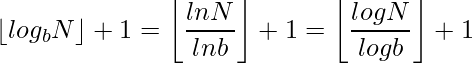
In above equation the base changing logarithmic property has been used. So we calculate the logarithm of the number in that base which we want to calculate the number of digits. And take its floor value and then add 1.
This idea can be further used to find the number of digits of a given number n of base b in base r. All have to be done is to convert the number in base 10 and then apply the above formula of finding digits. It would be easier to calculate log of any base when number is in base 10.
C++
#include <iostream>
#include <math.h>
using namespace std;
void findNumberOfDigits(long n, int base)
{
int dig = (int)(floor( log(n) /
log(base)) + 1);
cout << "The Number of digits of "
<< "Number " << n << " in base "
<< base << " is " << dig;
}
int main()
{
long n = 1446;
int base = 7;
findNumberOfDigits(n, base);
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.io.*;
public class GFG {
static void findNumberOfDigits(long n, int base)
{
int dig = (int)(Math.floor(
Math.log(n) / Math.log(base))
+ 1);
System.out.println("The Number of digits of Number "
+ n + " in base " + base
+ " is " + dig);
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
long n = 1446;
int base = 7;
findNumberOfDigits(n, base);
}
}
|
Python3
import math
def findNumberOfDigits(n, base):
dig = (math.floor(math.log(n) /
math.log(base)) + 1)
print ("The Number of digits of"
" Number {} in base {} is {}"
. format(n, base, dig))
n = 1446
base = 7
findNumberOfDigits(n, base)
|
C#
using System;
class GFG {
static void findNumberOfDigits(long n,
int b)
{
int dig = (int)(Math.Floor(
Math.Log(n) / Math.Log(b)) + 1);
Console.Write("The Number of digits"
+ " of Number " + n + " in base "
+ b + " is " + dig);
}
public static void Main()
{
long n = 1446;
int b = 7;
findNumberOfDigits(n, b);
}
}
|
PHP
<?php
function findNumberOfDigits($n, $b)
{
$dig = (int)(floor(log($n) /
log($b)) + 1);
echo ("The Number of digits".
" of Number ". $n.
" in base ".$b.
" is ".$dig);
}
$n = 1446;
$b = 7;
findNumberOfDigits($n, $b);
?>
|
Javascript
<script>
function findNumberOfDigits(n, base)
{
var dig = parseInt(Math.floor( Math.log(n) /
Math.log(base)) + 1);
document.write("The Number of digits of "
+ "Number " + n + " in base "
+ base + " is " + dig);
}
var n = 1446;
var base = 7;
findNumberOfDigits(n, base);
</script>
|
Output :
The Number of digits of Number 1446 in base 7 is 4
Complexity Analysis:
Time complexity : O(logN)
Space complexity : O(1)
Optimized Approach:
Here are few optimizations that can be made to the given program:
- Avoid using math.h library: The log function provided by the math.h library is a costly operation. Instead of using it, we can use the base changing property of logarithm and use log10 function to calculate the logarithm of n in base b. This will reduce the overhead of including the math.h library.
- Replace floor function with casting: Instead of using the floor function, we can cast the result of the logarithmic operation to an integer type. This is faster and simpler than calling the floor function.
Here’s the optimized version of the program with the above optimizations:
C++
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void findNumberOfDigits(long n, int base)
{
int dig = 0;
while (n > 0) {
n /= base;
dig++;
}
cout << "The Number of digits of "
<< "Number " << n << " in base "
<< base << " is " << dig;
}
int main()
{
long n = 1446;
int base = 7;
findNumberOfDigits(n, base);
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void findNumberOfDigits(long n, int base) {
int dig = 0;
while (n > 0) {
n /= base;
dig++;
}
System.out.println("The Number of digits of Number " + n + " in base " + base + " is " + dig);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
long n = 1446;
int base = 7;
findNumberOfDigits(n, base);
}
}
|
Python3
def findNumberOfDigits(n, base):
dig = 0
while n > 0:
n //= base
dig += 1
print(f"The Number of digits of Number {n} in base {base} is {dig}")
n = 1446
base = 7
findNumberOfDigits(n, base)
|
C#
using System;
public class Program
{
public static void FindNumberOfDigits(long n, int baseVal)
{
int dig = 0;
while (n > 0)
{
n /= baseVal;
dig++;
}
Console.WriteLine("The Number of digits of Number " + n + " in base " + baseVal + " is " + dig);
}
public static void Main()
{
long n = 1446;
int baseVal = 7;
FindNumberOfDigits(n, baseVal);
}
}
|
Javascript
function findNumberOfDigits(n, base) {
let dig = 0;
while (n > 0) {
n = Math.floor(n / base);
dig++;
}
console.log(`The Number of digits of Number ${n} in base ${base} is ${dig}`);
}
let n = 1446;
let base = 7;
findNumberOfDigits(n, base);
|
Output :
The Number of digits of Number 1446 in base 7 is 4
Complexity Analysis:
Time complexity : O(logN)
Auxiliary Space : O(1)
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...