Find the index of the left pointer after possible moves in the array
Last Updated :
08 Sep, 2022
Given an array of size 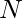 . Move two pointers, one from the left side and one from the right side of the array, a pointer will only move forward if the sum of all the numbers it has already gone through is less than the sum of the numbers the other pointer has gone through. Continue the process while left pointer is less than the right pointer or no move is possible. Print the position of the left pointer in the end.
. Move two pointers, one from the left side and one from the right side of the array, a pointer will only move forward if the sum of all the numbers it has already gone through is less than the sum of the numbers the other pointer has gone through. Continue the process while left pointer is less than the right pointer or no move is possible. Print the position of the left pointer in the end.
Note: 0-based indexing is considered for the array.
Examples:
Input: arr[] = {2, 7, 9, 8, 7}
Output: 2
Initial position : ptrL = 0, ptrR = 4 with sum 2 and 7 respectively
Move 1 : ptrL = 1, ptrR = 4 with sum 9 and 7
Move 2 : ptrL = 1, ptrR = 3 with sum 9 and 15
Move 3 : ptrL = 2, ptrR = 3 with sum 18 and 7
Input: arr[] = {1, 2, 3, 1, 2}
Output: 1
Approach: An efficient approach is to move from the left and from the right at the same time and maintaining the running sum for both the pointers.
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int getIndex(int a[], int n)
{
if(n == 1)
return 0;
int ptrL = 0, ptrR = n-1, sumL = a[0], sumR = a[n-1];
while (ptrR - ptrL > 1) {
if (sumL < sumR) {
ptrL++;
sumL += a[ptrL];
}
else if (sumL > sumR) {
ptrR--;
sumR += a[ptrR];
}
else {
break;
}
}
return ptrL;
}
int main()
{
int a[] = { 2, 7, 9, 8, 7 };
int n = sizeof(a) / sizeof(a[0]);
cout << getIndex(a, n);
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.io.*;
class GFG {
static int getIndex(int a[], int n)
{
if(n == 1)
return 0;
int ptrL = 0, ptrR = n-1, sumL = a[0], sumR = a[n-1];
while (ptrR - ptrL > 1) {
if (sumL < sumR) {
ptrL++;
sumL += a[ptrL];
}
else if (sumL > sumR) {
ptrR--;
sumR += a[ptrR];
}
else {
break;
}
}
return ptrL;
}
public static void main (String[] args) {
int a[] = { 2, 7, 9, 8, 7 };
int n =a.length;
System.out.println ( getIndex(a, n));
}
}
|
Python3
def getIndex(a, n):
if(n == 1):
return 0
ptrL = 0
ptrR = n-1
sumL = a[0]
sumR = a[n-1]
while (ptrR - ptrL > 1) :
if (sumL < sumR) :
ptrL += 1
sumL += a[ptrL]
elif (sumL > sumR) :
ptrR -= 1
sumR += a[ptrR]
else :
break
return ptrL
if __name__ == "__main__":
a = [ 2, 7, 9, 8, 7 ]
n = len(a)
print(getIndex(a, n))
|
C#
using System;
class GFG {
static int getIndex(int []a, int n)
{
if(n == 1)
return 0;
int ptrL = 0, ptrR = n-1, sumL = a[0], sumR = a[n-1];
while (ptrR - ptrL > 1) {
if (sumL < sumR) {
ptrL++;
sumL += a[ptrL];
}
else if (sumL > sumR) {
ptrR--;
sumR += a[ptrR];
}
else {
break;
}
}
return ptrL;
}
public static void Main () {
int []a = { 2, 7, 9, 8, 7 };
int n =a.Length;
Console.WriteLine( getIndex(a, n));
}
}
|
PHP
<?php
function getIndex($a, $n)
{
if($n == 1)
return 0;
$ptrL = 0; $ptrR = $n - 1;
$sumL = $a[0]; $sumR = $a[$n - 1];
while ($ptrR - $ptrL > 1)
{
if ($sumL < $sumR)
{
$ptrL++;
$sumL += $a[$ptrL];
}
else if ($sumL > $sumR)
{
$ptrR--;
$sumR += $a[$ptrR];
}
else
{
break;
}
}
return $ptrL;
}
$a = array( 2, 7, 9, 8, 7 );
$n = count($a);
echo getIndex($a, $n);
?>
|
Javascript
<script>
function getIndex(a, n)
{
if(n == 1)
return 0;
let ptrL = 0, ptrR = n - 1,
sumL = a[0], sumR = a[n - 1];
while (ptrR - ptrL > 1)
{
if (sumL < sumR)
{
ptrL++;
sumL += a[ptrL];
}
else if (sumL > sumR)
{
ptrR--;
sumR += a[ptrR];
}
else
{
break;
}
}
return ptrL;
}
let a = [ 2, 7, 9, 8, 7 ];
let n = a.length;
document.write(getIndex(a, n));
</script>
|
Complexity Analysis:
- Time Complexity: O(n)
- Auxiliary Space: O(1)
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...